New method developed to detect and adjust population structure in genetic summary data
Summix was developed by CU Denver researchers to increase equity in DNA databases, making them more useful for ancestries such as African-American and Latinx
2021-06-21
(Press-News.org) In a new study published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics, researchers announced the development of a new method to increase the utility and equity of large genetic databases. The research was conducted by Audrey Hendricks, an associate professor of statistics at the University of Colorado Denver (CU Denver).
Summix, the new method developed by Hendricks and her team of CU Denver undergraduate and graduate students, estimates the genetic ancestry in databases and adjusts the information to match the ancestry of a person or sample of people. This method leads large genetic databases to become more useful for people of various ancestries such as African American or Latinx, as they are underrepresented in genetic databases and studies. Hendricks compares this method to translating a book from English to another language.
"Think of DNA as the words of our body," says Hendricks. "All of the words of our body make the instruction book that makes each of us up. Right now, it's like the DNA books are only written in English so the information in the library is not as useful for people who don't speak English. We're working to create books in the library that are more universal."
According to Hendricks, individuals and samples from understudied populations, such as African American and Latnix, are the most likely to lack large public resources with precisely matched ancestry data. As a result, researchers working with those populations often resort to the closest, but still poorly matched ancestral group. This leads to biased results in the very populations where high-quality research is needed the most.
The team showed the effectiveness of Summix in over 5,000 simulation scenarios and in the widely used Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD), a publicly available genetic resource. They found Summix's estimates of ancestry proportions to be highly accurate (within 0.001%) and the ancestry-adjusted genetic information to be less biased. The Summix method is available in open access software increasing the utility of the method and its applications.
"Most people are a combination of multiple continental (e.g. African and European) or finer scale (e.g. Italian and German) ancestries," said Hendricks. "As healthcare moves forward with precision medicine, matching the unique ancestral make-up of each person will become increasingly important. The ability of Summix to update a genetic resource to match the ancestry of an individual is an important step in this direction and helps to increase the utility and equity of genetic summary data."
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute through the Genome Sequencing Program and the 2020 Genomic Innovator Award.
About University of Colorado Denver
CU Denver is Denver's partner in progress and ally in innovation. Our connection to our vibrant city inspires leading research, creative work, and civic engagement. Our collaboration with Denver's businesses and local government helps set us apart from other universities. With a history that began in 1912, CU Denver has operated independently since 1973. Our location in downtown Denver serves more than 15,000 students. In Colorado and around the world, our talented graduates form a diverse and growing Lynx family. We work to create welcoming and respectful learning environments where a culture of inclusion can flourish. At CU Denver, we honor our diversity of experiences and perspectives in the committed belief that they enrich the educational experience for all. For more information, visit https://www.ucdenver.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-21
Every day, our bodies face a bombardment of UV rays, ozone, cigarette smoke, industrial chemicals and other hazards.
This exposure can lead to free-radical production in our bodies, which damages our DNA and tissues. A new study from West Virginia University researcher Eric E. Kelley--in collaboration with the University of Minnesota--suggests that unrepaired DNA damage can increase the speed of aging.
The study appears in the journal Nature.
Kelley and his team created genetically-modified mice with a crucial DNA-repair protein missing from their hematopoietic stem cells, immature immune cells that develop into white blood cells. Without this ...
2021-06-21
Broadband sounds embedded with short pauses can maintain temporal sound processing in a mouse model of hearing loss, according to new research published in eNeuro.
Hearing loss treatments supplement auditory system function but don't repair it. However a new intervention -- playing broadband sounds during the onset of hearing loss -- may be able to prevent the damage from ever occurring. Augmented auditory environments have been able to preserve auditory processing of a wide range of sound frequencies in mice models. In a new study, Dziorny et al. modified the traditional paradigm and preserved the processing of time-related, or temporal, sound features which are vital for understanding speech.
The research team exposed mice with congenital hearing loss to ...
2021-06-21
DURHAM, N.C. - In the fight against viruses, antibodies have the potential to either block infection or enable infection and make the disease worse, leading to concern about their use as a therapy for COVID-19.
In a study published in the journal END ...
2021-06-21
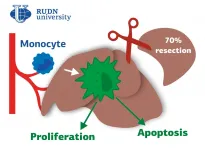
RUDN University doctors found out what role macrophages play in the recovery of the liver after the removal of its significant part. The results are published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
The liver in mammals is the most regenerative internal organ. It can restore the original size from as little as 25% of the preserved tissue. An important role in this process is played by macrophages. These are the cells that can engulf and digest particles. It is known, for example, that if the liver is affected by foreign substances, including drugs, macrophages migrate to the liver, absorb harmful microorganisms and dead cells, cause inflammation and thus contribute to the restoration of the organ. However, it is still unknown unambiguously how macrophages affect the ...
2021-06-21
Nearly a third of Americans who arranged for paid care for an older person or someone with dementia employed workers who were not hired through a regulated agency, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Individuals who hired gray market caregivers were less likely to be employed and more likely to also use unpaid care for their family members. In addition, people who lived in rural areas had an almost five-times higher odds of arranging dementia care through gray markets as compared to those who lived in urban areas.
The study is the first national survey to probe the use of gray market care for older adults and people with dementia. The findings ...
2021-06-21
HOUSTON - (June 21, 2021) - Rice University engineers have created microscopic seeds for growing remarkably uniform 2D perovskite crystals that are both stable and highly efficient at harvesting electricity from sunlight.
Halide perovskites are organic materials made from abundant, inexpensive ingredients, and Rice's seeded growth method addresses both performance and production issues that have held back halide perovskite photovoltaic technology.
In a study published online in Advanced Materials, chemical engineers from Rice's Brown School of Engineering describe how to make the seeds and use them to grow homogenous thin films, highly sought ...
2021-06-21
A team of scientists from NUST MISIS and MIPT have developed and tested a new platform for realization of the ultra-strong photon-to-magnon coupling. The proposed system is on-chip and is based on thin-film hetero-structures with superconducting, ferromagnetic and insulating layers. This discovery solves a problem that has been on the agenda of research teams from different countries for the last 10 years, and opens new opportunities in implementing quantum technologies. The study was published in the highly ranked journal Science Advances.
The last decade has seen significant progress ...
2021-06-21
AMHERST, Mass. - Millions of Americans will visit New England's beaches this summer to cool off, play in the waves and soak up the sun. Until now, the factors governing which beaches slope gradually to the sea and which ones end abruptly in a steep drop-off have been largely unknown. However, new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst reveals, with unprecedented detail, how the grain size of beach sand relates to the slope of the beach itself. These new findings are critical to understanding how New England's beaches will respond to both rising sea levels and increased storm activity.
Many of New England's beaches are made up of a mixture of sand and small stones. Or, to be more precise, the grain sizes on these beaches are "bi-modal" ...
2021-06-21
WASHINGTON -- Although quantum technology has proven valuable for highly precise timekeeping, making these technologies practical for use in a variety of environments is still a key challenge. In an important step toward portable quantum devices, researchers have developed a new high-flux and compact cold-atom source with low power consumption that can be a key component of many quantum technologies.
"The use of quantum technologies based on laser-cooled atoms has already led to the development of atomic clocks that are used for timekeeping on a national level," said research team ...
2021-06-21
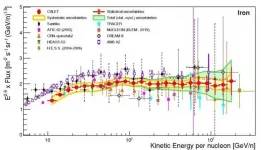
New findings published this week in Physical Review Letters, Measurement of the Iron Spectrum in Cosmic Rays from 10??GeV/n to 2.0??TeV/n with the Calorimetric Electron Telescope on the International Space Station, suggest that cosmic ray nuclei of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen travel through the galaxy toward Earth in a similar way, but, surprisingly, that iron arrives at Earth differently.
A series of recent publications based on results from the CALorimetric Electron Telescope, or CALET, instrument on the International Space Station, or ISS, have cast new light on the abundance of high-energy cosmic ray nuclei -- atoms stripped of their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New method developed to detect and adjust population structure in genetic summary data
Summix was developed by CU Denver researchers to increase equity in DNA databases, making them more useful for ancestries such as African-American and Latinx