Profiling gene expression in plant embryos one nucleus at a time
2021-06-21
(Press-News.org) Following fertilization, early plant embryos arise through a rapid initial diversification of their component cell types. As a result, this series of coordinated cell divisions rapidly sculpts the embryo's body plan. The developmental phenomenon in question is orchestrated by a transcriptional activation of the plant genome. However, the underlying cellular differentiation programs have long remained obscured as the plant embryos were hard to isolate. In fact, previous attempts at creating datasets of the plant embryonic differentiation programs were incapable of overcoming two main obstacles: either the information gathered lacked cell specificity, or the datasets were contaminated with material from surrounding non-embryonic tissues. Now, a team of PhD students from GMI Group Leader Michael Nodine's lab developed a method to profile gene expression at the single cell level in Arabidopsis embryos.
The authors led by Ping Kao in collaboration with Michael Schon from the Nodine group use an approach that consists of coupling fluorescence-activated nuclei sorting together with single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq). Hence, they sort the individual cells in an early plant embryo and sequence the messenger RNA within the individual nuclei. This provides insights into the various transcription profiles, or transcriptomes, within each cell in the plant embryo. With this approach, the team was capable of surmounting the obstacles that undermined previous attempts at creating gene expression atlases in plant embryos.
To explain their team's unique approach, Michael Schon from Nodine's group readily finds a striking parallel: "If you put a hamburger in a blender, it still has all the same components in all the same ratios, but you lose critical information about the burger's spatial organization. Elements essential to 'burger-ness' exist in the organization of the burger's parts, and these elements are lost in a 'burger smoothie'." Schon elaborates: "Earlier methods consisted of grinding entire plant embryos into an 'plant embryo smoothie'; these were still useful in telling us the molecular components of the plant embryo and their ratios, but important information about the organism's organization was lost. Our transcriptome atlas is an effort to restore the information that most likely got 'averaged-out' in previous attempts."
Using this approach, the Nodine group was able to show gene expression patterns that could clearly distinguish the early Arabidopsis embryonic cell types. Consequently, the current work opens the door for uncovering the molecular basis of pattern formation in plant embryos. "This is the beginning of an exciting era of developmental biology and approaches like ours promise to help reveal how emerging cell types are defined at the beginning of plant life", concludes Michael Nodine with a confident smile of satisfaction.
INFORMATION:
This work was done in collaboration with the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Facility of the Vienna Biocenter Core Facilities (VBCF).
Original publication:
Kao P. et al., "Gene Expression Variation in Arabidopsis Embryos at Single-Nucleus Resolution". Development, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.199589
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-21
A commonly studied perovskite can superfluoresce at temperatures that are practical to achieve and at timescales long enough to make it potentially useful in quantum computing applications. The finding from North Carolina State University researchers also indicates that superfluorescence may be a common characteristic for this entire class of materials.
Superfluorescence is an example of quantum phase transition - when individual atoms within a material all move through the same phases in tandem, becoming a synchronized unit.
For example, when atoms in an optical material such as a perovskite are excited they can individually radiate light, create energy, and fluoresce. Each atom will start moving through these phases randomly, but given the right conditions, they can synchronize in ...
2021-06-21
All plant cells obtain their energy mainly from two organelles they contain - chloroplasts (responsible for photosynthesis) and mitochondria (responsible for the biochemical cycle of respiration that converts sugars into energy). However, a large number of a plant cell's genes in its mitochondria and chloroplasts can develop defects, jeopardising their function. Nevertheless, plant cells evolved an amazing tool called the RNA editosome (a large protein complex) to repair these kinds of errors. It can modify defective messenger RNA that result from defective DNA by transforming (deamination) of certain mRNA nucleotides.
Automatic error correction in plant cells
Automatic error correction in plants was discovered about 30 years ago by a team headed by plant physiologist Axel Brennicke ...
2021-06-21
While the LGBTQ+ community has seen significant advancements in legal rights, political representation and social acceptance over recent years, mental and physical health disparities still exist for queer Americans - and are even worse among younger generations, says a new study from Michigan State University.
In the first-ever population-based national study comparing mental and physical health of lesbian, gay and bisexual (LGB) Americans to their straight counterparts, MSU sociologist Hui Liu and research partner Rin Reczek, professor of sociology from Ohio State University, found that when compared to their straight counterparts, LGB Millennials have worse health disadvantages than their older peers, though disparities persist throughout older generations as ...
2021-06-21
All coronaviruses produce four primary structural proteins and multiple nonstructural proteins. However, the majority of antibody-based SARS-CoV-2 research has focused on the spike and nucleocapsid proteins. A study published in PLOS Biology by Anna Heffron, Irene Ong and colleagues at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, suggests that immune responses may develop against other proteins produced by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The efficacy of spike protein-based vaccines is variable and not everyone infected with SARS-CoV-2 produces detectable antibodies against the spike or ...
2021-06-21
In a new study published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics, researchers announced the development of a new method to increase the utility and equity of large genetic databases. The research was conducted by Audrey Hendricks, an associate professor of statistics at the University of Colorado Denver (CU Denver).
Summix, the new method developed by Hendricks and her team of CU Denver undergraduate and graduate students, estimates the genetic ancestry in databases and adjusts the information to match the ancestry of a person or sample of people. This method leads large genetic databases to become more useful for people of various ancestries such as African American or Latinx, as they are underrepresented in genetic ...
2021-06-21
Every day, our bodies face a bombardment of UV rays, ozone, cigarette smoke, industrial chemicals and other hazards.
This exposure can lead to free-radical production in our bodies, which damages our DNA and tissues. A new study from West Virginia University researcher Eric E. Kelley--in collaboration with the University of Minnesota--suggests that unrepaired DNA damage can increase the speed of aging.
The study appears in the journal Nature.
Kelley and his team created genetically-modified mice with a crucial DNA-repair protein missing from their hematopoietic stem cells, immature immune cells that develop into white blood cells. Without this ...
2021-06-21
Broadband sounds embedded with short pauses can maintain temporal sound processing in a mouse model of hearing loss, according to new research published in eNeuro.
Hearing loss treatments supplement auditory system function but don't repair it. However a new intervention -- playing broadband sounds during the onset of hearing loss -- may be able to prevent the damage from ever occurring. Augmented auditory environments have been able to preserve auditory processing of a wide range of sound frequencies in mice models. In a new study, Dziorny et al. modified the traditional paradigm and preserved the processing of time-related, or temporal, sound features which are vital for understanding speech.
The research team exposed mice with congenital hearing loss to ...
2021-06-21
DURHAM, N.C. - In the fight against viruses, antibodies have the potential to either block infection or enable infection and make the disease worse, leading to concern about their use as a therapy for COVID-19.
In a study published in the journal END ...
2021-06-21
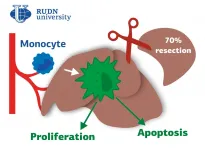
RUDN University doctors found out what role macrophages play in the recovery of the liver after the removal of its significant part. The results are published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
The liver in mammals is the most regenerative internal organ. It can restore the original size from as little as 25% of the preserved tissue. An important role in this process is played by macrophages. These are the cells that can engulf and digest particles. It is known, for example, that if the liver is affected by foreign substances, including drugs, macrophages migrate to the liver, absorb harmful microorganisms and dead cells, cause inflammation and thus contribute to the restoration of the organ. However, it is still unknown unambiguously how macrophages affect the ...
2021-06-21
Nearly a third of Americans who arranged for paid care for an older person or someone with dementia employed workers who were not hired through a regulated agency, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Individuals who hired gray market caregivers were less likely to be employed and more likely to also use unpaid care for their family members. In addition, people who lived in rural areas had an almost five-times higher odds of arranging dementia care through gray markets as compared to those who lived in urban areas.
The study is the first national survey to probe the use of gray market care for older adults and people with dementia. The findings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Profiling gene expression in plant embryos one nucleus at a time