(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, June 22, 2021 -- About 2.2 billion people globally lack reliable access to clean drinking water, according to the United Nations, and the growing impacts of climate change are likely to worsen this reality.
Solar steam generation (SSG) has emerged as a promising renewable energy technology for water harvesting, desalination, and purification that could benefit people who need it most in remote communities, disaster-relief areas, and developing nations. In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, Virginia Tech researchers developed a synthetic tree to enhance SSG.
SSG turns solar energy into heat. Water from a storage tank continuously wicks up small, floating porous columns. Once water reaches the layer of photothermal material, it evaporates, and the steam is condensed into drinking water.
One major challenge in scaling up SSG technology is the limit in the capillary force beyond a certain column height, when the water cannot wick fast enough to keep up with the evaporation process. The capillary force, based on the surface tension that causes water to "climb" a porous paper towel, drives the water toward the evaporator.
Inspired by mangrove trees thriving along coastlines, the researchers bypassed this hurdle by creating a synthetic tree to replace the capillary action with transpiration, the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from leaves, stems, and flowers. Transpiration can pump water up insulating tubes of any desired height.
In real trees, transpiration begins at the roots, which suck up water through hollow vessels made from xylem tissue. As the water warms, it releases as vapor through pores on the underside of leaves.
The synthetic tree consists of a 19-tube array, covered by a nanoporous ceramic disk, which serves as the leaf. Each plastic tube, imitating the xylem conduits, is 6 centimeters high, just under 2.5 inches, with an inner diameter of 3.175 millimeters, about a tenth of an inch.
The setup enables the evaporating interface to thermally separate from the bulk water in the tank, so the evaporator does not dry out. Water evaporating from the disk is replenished by suction, which continuously pumps more water from a bottom tank up the tube array.
"We expect our tree-based solar steam generator will be of interest for applications in underground water extraction and purification," author Jonathan Boreyko said. "The ultimate goal is to achieve a suction pressure strong enough to pull ocean water through a salt-excluding filter without requiring a mechanical pump, analogous to how mangrove trees are able to grow in ocean water."
Future research could focus on fabricating taller trees, adding more leaves to increase the area over which evaporation occurs, and incorporating desalination membranes at the tube inlets to prevent salt buildup.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Synthetic trees for enhanced solar evaporation and water harvesting," is authored by Ndidi Eyegheleme, Weiwei Shi, Lance H. De Koninck, Julia L. O'Brien, and Jonathan B. Boreyko. The article will appear in Applied Physics Letters on June 22, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0049904). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0049904.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Letters features rapid reports on significant discoveries in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/apl.
A team of scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has now discovered that the odorant receptor OR5K1 is specialized to recognize pyrazines in both humans and domesticated animals. These are volatile substances that contribute to the typical odor of many vegetables or are formed when food is heated. In addition, pyrazines also play a role as signaling substances in intra- or interspecific communication. The new research results contribute to a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the odor perception ...
A single measurement result is not a proof - this has been shown again and again in science. We can only really rely on a research result when it has been measured several times, preferably by different research teams, in slightly different ways. In this way, errors can usually be detected sooner or later.
However, a new study by Prof. Andrej Pustogow from the Institute of Solid State Physics at TU Wien together with other international research teams shows that this can sometimes take quite a long time. The investigation of strontium ruthenate, a material that plays an important role in unconventional superconductivity, has now disproved an experiment that gained fame in the 1990s: it was believed that a novel form of superconductivity ...
The spinal cord is an important component of our central nervous system: it connects the brain with the rest of the body and plays a crucial part in coordinating our sensations with our actions. Falls, violence, disease - various forms of trauma can cause irreversible damage to the spinal cord, leading to paralysis, sometimes even death.
Although many vertebrates, including humans, are unable to recover from a spinal cord injury, some animals stand out. For instance, the axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum), a salamander from Mexico, has the remarkable ability to regenerate its spinal cord after an injury. When an axolotl's tail is amputated, neural stem cells residing in the spinal cord are recruited to the injury ...
Researchers have identified a combination of biological markers in patients with dengue that could predict whether they go on to develop moderate to severe disease, according to a study published today in eLife.
Biomarkers are used to identify the state or risk of a disease in patients. Examples of biomarkers can include naturally occurring molecules or genes in the vascular, inflammatory or other biological pathways. The new findings could aid the development of biomarker panels for clinical use and help improve triage and risk prediction in patients with dengue.
Dengue is the most common mosquito-borne viral disease to affect humans globally. In 2019, the World Health Organization identified dengue as one of the top 10 threats to global health, with transmission occurring ...
The ancient Maya city of Tikal was a bustling metropolis and home to tens of thousands of people.
The city comprised roads, paved plazas, towering pyramids, temples and palaces and thousands of homes for its residents, all supported by agriculture.
Now researchers at the University of Cincinnati say Tikal's reservoirs -- critical sources of city drinking water -- were lined with trees and wild vegetation that would have provided scenic natural beauty in the heart of the busy city.
UC researchers developed a novel system to analyze ancient plant DNA in the sediment of Tikal's temple and palace reservoirs to identify more than 30 species ...
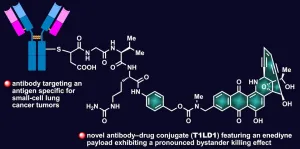
HOUSTON - (June 22, 2021) - How do you kill tumor cells that can't be targeted? Get their more susceptible neighbors to help.
The Rice University lab of synthetic chemist K.C. Nicolaou, in collaboration with AbbVie Inc., has created unique antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) that link a synthetic uncialamycin analogue to antibodies that target cancer cells.
Once they enter the targeted tumor cells, these ADCs exhibit a "significant bystander effect," according to the study. In other words, cancerous neighbor cells that aren't directly attacked by the drugs are also affected.
The study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences presents "an intriguing opportunity ...
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine have developed a blueprint for a protein that plays an important role in the development and regulation of reproductive organs.
The knowledge advances our understanding of the protein anti-Müllerian hormone hormone (AMH), which helps form male reproductive organs and in females regulates follicle development and ovulation in the ovaries, explains Thomas Thompson, PhD, professor in the UC Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry and Microbiology.
Scientists have been looking to regulate AMH because it might play a role in developing a novel contraceptive, aid in treatments for infertility ...
An enzyme found in fat tissue in the centre of our bones helps control the production of new bone and fat cells, shows a study in mice published today in eLife.
The findings may help scientists better understand how the body maintains fat stores and bone production in response to changing conditions, such as during aging. They may also suggest new approaches to treating conditions that cause bone loss in older adults.
Fat cells, including those found in the bone marrow, are increasingly recognised as an important part of the body that helps regulate body weight, insulin sensitivity and bone mass. Fat tissue ...
DETROIT - Jessica Damoiseaux, Ph.D., an associate professor with the Institute of Gerontology at Wayne State University, recently published the results of a three-year study of cognitive changes in older adults. The team followed 69 primarily African American females, ages 50 to 85, who complained that their cognitive ability was worsening though clinical assessments showed no impairments. Three magnetic resonance imaging scans (MRIs) at 18-month intervals showed significant changes in functional connectivity in two areas of the brain.
"An older adult's perceived cognitive decline could be an important precursor to dementia," Damoiseaux said. "Brain alterations that underlie the experience of decline could reflect ...
(Boston)--Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80-85 percent cases of lung cancer and when diagnosed early, has a five-year survival rate of 50-80 percent. Black patients have lower overall incidence of NSCLC than white patients, but are more likely to be diagnosed at later stages. They also are less likely to receive surgery for early-stage cancer.
Now a new study from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) highlights the impact that structural racism and residential segregation has on NSCLC outcomes.
The researchers analyzed patient data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program--a database of Black and white patients diagnosed with NSCLC from 2004-2016 in the 100 ...