Novel lncRNA, Caren, counteracts heart failure progression
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) A research collaboration based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has identified a novel lncRNA, Caren, that is abundantly expressed in cardiomyocytes. They showed that it enhances energy production by increasing the number of mitochondria in cardiomyocytes, and inhibits activation of the ATM protein, a key player in the DNA damage response pathway that accelerates heart failure severity. Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes is reduced by aging and high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart failure, and markedly reduced in the hearts of heart failure patients. The researchers believe that activation of Caren in cardiomyocytes could lead to the development of new heart failure therapies.
Heart failure is when reduced pumping function (contraction and dilatation) of the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to the body. It is still a disease with a poor prognosis and the number of heart failure patients is increasing worldwide. In developed countries, the increase in the number of heart failure patients, especially in the elderly, is a major problem. Therefore, there is a need to develop effective new treatment strategies.
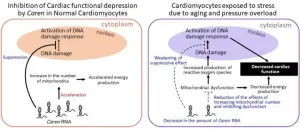
Energy production from mitochondria is essential for maintaining cardiac function. Aging and hypertension, which increase the chances of heart failure development, cause mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes that results in reduced mitochondrial energy production and increased reactive oxygen species production. Reactive oxygen species cause DNA damage, which subsequently activates the DNA damage response resulting in the exacerbation of heart failure. Therefore, mitochondrial dysfunction and the activation of the DNA damage response have both attracted attention as a cause of heart failure.
A research group led by Professor Oike at Kumamoto University has identified a novel lncRNA abundantly expressed in mouse cardiomyocytes and named it Caren (cardiomyocyte-enriched noncoding transcript). They also found that the amount of Caren RNA in mouse cardiomyocytes is reduced by stress, which can lead to heart failure. Further analysis of the function of Caren in the mouse heart revealed that it inhibits the decline of cardiac pump function. The researchers thus suggested that aging and stress reduce the amount of Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes, thereby reducing its effects and promoting mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of the DNA damage response, leading to the development and worsening of heart failure.
The researchers then genetically engineered a non-pathogenic adeno-associated virus to selectively infect cardiomyocytes and express Caren. After infecting heart failure model mice with the virus, they found that the amount of Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes increased, the number of mitochondria increased, and activation of the DNA damage response was suppressed compared to mice that were infected with a control virus, thus inhibiting the progression of heart failure in mice. The researchers also found that Caren RNA is present in human cardiomyocytes, and that its amount is inversely correlated with the expression level of heart failure marker genes in the heart tissue of heart failure patients. (The expression level of heart failure marker genes is high in heart tissues with low Caren RNA levels). Furthermore, they showed that decreasing the amount of human Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes generated from human iPS cells decreased the energy production capacity of mitochondria.
"Our research shows that increasing the amount of Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes can inhibit the onset and progression of heart failure, which we expect can be a strategy for developing new heart failure therapies," said Professor Oike. "In our in vivo mouse experiments, we found that Caren RNA supplement therapy using an adeno-associated virus was effective in counteracting heart failure progression. Now, we are going to verify whether human Caren has the same effect which could lead to the development of a new treatment for heart failure."
This research was posted online in Nature Communications on 5 May 2021.
INFORMATION:
Source:
Sato, M., Kadomatsu, T., Miyata, K., Warren, J. S., Tian, Z., Zhu, S., ... Oike, Y. (2021). The lncRNA Caren antagonizes heart failure by inactivating DNA damage response and activating mitochondrial biogenesis. Nature Communications, 12(1). doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22735-7
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
Eating 2.5 grams of pure natural cocoa powder serves to improve visual acuity in healthy young adults and in daylight conditions, according to research by the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) and the ICTAN (Institute of Food and Nutrition Science and Technology) of the CSIC.
The study, published in the Journal of Functional Foods, analyse the effects of two dietary polyphenols: cocoa flavanols and red berry anthocyanins.
"Although this was the baseline hypothesis, we did not see any effect either on adaptation to darkness or on visual acuity measured in low light conditions (mesopic vision), either with cocoa or with berries," indicates María Cinta Puell Marín, researcher at the Optometry and Vision ...
2021-06-23
Children who were exposed to higher levels of trace minerals manganese and selenium during their mothers' pregnancy had a lower risk of high blood pressure in childhood, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers analyzed the levels of toxic metals and trace minerals in blood samples drawn from nearly 1,200 women in the Boston area who gave birth between 2002 and 2013. They found that higher levels of selenium or manganese in the mothers' blood were associated with lower blood pressure readings in their children ...
2021-06-23
A sensitive blood test being developed by a team of researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center shows promise for predicting whether patients with metastatic HPV-positive throat cancer will respond to treatment months earlier than standard imaging scans.
That's according to a study, published in Oncotarget, validating the test in a small group of patients with metastatic human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma -- a type of head and neck cancer that develops in the back of the mouth and in the throat.
If the test can quickly determine that a treatment approach isn't ...
2021-06-23
AMHERST, Mass. - As summer unfolds, more than 500 species of invasive plants will be taking root in fields, lawns, and gardens across the US. As plants continue to move north driven by climate change, the number of invasives will only increase. Unfortunately, inconsistent regulations that vary from state to state means that invasive plants have an edge on our attempts to control them. However, new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published in the Journal of Applied Ecology suggests that we already have an answer in hand - communication.
"We know that invasive plants are causing both ecological and economic harm in the US," says Emily Fusco, one of the paper's lead authors and a postdoctoral research fellow in the department of environmental conservation ...
2021-06-23
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI)-based brain age prediction model to quantify deviations from a healthy brain-aging trajectory in patients with mild cognitive impairment, according to a study published in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. The model has the potential to aid in early detection of cognitive impairment at an individual level.
Amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) is a transition phase from normal aging to Alzheimer's disease (AD). People with aMCI have memory deficits that are more ...
2021-06-23
A year-long Australian population study has found that full time workers employed by organisations that fail to prioritise their employees' mental health have a threefold increased risk of being diagnosed with depression.
And while working long hours is a risk factor for dying from cardiovascular disease or having a stroke, poor management practices pose a greater risk for depression, the researchers found.
The University of South Australia study, published in the British Medical Journal today, is led by UniSA's Psychosocial Safety Climate Observatory, the world's first research platform exploring workplace psychological health and safety.
Psychosocial safety climate (PSC) is the term used to describe management practices ...
2021-06-23
In our future electrified world, the demand for battery storage is projected to be enormous, reaching to upwards of 2 to 10 terawatt-hours (TWh) of annual battery production by 2030, from less than 0.5 TWh today. However, concerns are growing as to whether key raw materials will be adequate to meet this future demand. The lithium-ion battery - the dominant technology for the foreseeable future - has a component made of cobalt and nickel, and those two metals face severe supply constraints on the global market.
Now, after several years of research led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), scientists have made significant progress in developing battery cathodes using ...
2021-06-23
Tokyo, Japan - Stem cell therapy is at the cutting edge of regenerative medicine, but until now researchers and clinicians have had to painstakingly evaluate stem cell quality by looking at each cell individually under a microscope. Now, researchers from Japan have found a way to speed up this process, using the power of artificial intelligence (AI).
In a study published in February in Stem Cells, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) reported that their AI system, called DeepACT, can identify healthy, productive skin stem cells with the same accuracy that a human can.
Stem cells are able to develop into several different kinds of mature ...
2021-06-23
A team of researchers developed a biomimetic mineralization of calcium carbonate using a multifunctional peptide template that can self-supply mineral sources, which in this case is a supply of carbonate ions, the precursor of calcium carbonate, and following the mechanism of biosynthesis of hard tissues by living organisms, called biomineralization, the ability to form hydrogels, which is modeled after the reaction environment of living organisms. Previous studies on mineralization have discussed the formation mechanism of inorganic crystals synthesized on ...
2021-06-23
Current American Heart Association, European Society of Cardiology, and UK National Health Service guidelines recommend a 5-yearly health checks for screening of individuals at high cardiovascular disease risk. These health checks include measurement of major risk factors, such as systolic blood pressure, cholesterol profile, blood glucose, and smoking status.
If lifestyle interventions are unsuccessful in reducing risk factor levels, prevention guidelines recommend initiation of preventive medication therapies such as statins. However, current guidelines advice only using the latest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel lncRNA, Caren, counteracts heart failure progression