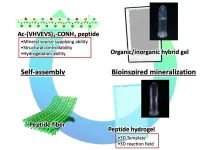
Bioinspired mineralization of calcium carbonate in peptide hydrogel
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers developed a biomimetic mineralization of calcium carbonate using a multifunctional peptide template that can self-supply mineral sources, which in this case is a supply of carbonate ions, the precursor of calcium carbonate, and following the mechanism of biosynthesis of hard tissues by living organisms, called biomineralization, the ability to form hydrogels, which is modeled after the reaction environment of living organisms. Previous studies on mineralization have discussed the formation mechanism of inorganic crystals synthesized on templates with only a single function, such as a system supplying an external mineral source or a hydrogel system.
However, living organisms use their own enzymes to self-supply mineral sources and achieve control of the orientation, crystal phase, and morphology of inorganic crystals by using 3D assemblies with controlled structures as reaction fields. Therefore, elucidating the formation mechanism of inorganic crystals in a mineralization reaction environment that is closer to the biological environment such as the hierarchical hydrogel-like 3D assemblies in addition to the self-supply of mineral sources, is important for clarifying the true relationship for structural control between organic templates and inorganic materials that is achieved in biomineralization. It is important to clarify the true relationship for structural control between organic templates and inorganic materials achieved in biomineralization. The research group led by Assistant Professor Kazuki Murai of Shinshu University's Department of Chemistry and Materials, Faculty of Textile Science and Technology was able to examine the nucleation and crystal growth mechanisms of calcium carbonate under conditions more similar to the biological environment through the self-supply of mineral sources through the expression of enzyme-like activities, and spontaneous formation of hydrogels, which is a model environment for cells. Therefore, the group's findings will facilitate the understanding of the nucleation and crystal growth of inorganic crystals in biomineralization and the role of organic templates for crystal control.
Assistant Professor Kazuki Murai states, "the knowledge gained from this and other mineralization studies is the basis for revealing the amazing processes that organisms have acquired through evolution over a vast amount of time. We take our bones and teeth for granted in our daily life, but even they are not yet fully understood. I believe that the efforts of various researchers, including myself, will lead us to the "solutions" that have been acquired by living organisms over billions of years. I will be happy if my research can be a "stepping stone to unexpected inspiration and discovery."
This study was able to clarify three major points, that a single peptide molecule has the ability to self-supply minerals through enzyme-like activity, the ability to control the crystal phase and morphology of inorganic materials, and the ability to spontaneously form hydrogels. The group was able to investigate the nucleation and crystal growth mechanisms of calcium carbonate using it as a template for mineralization. This research strategy to mimic the reaction environment of living organisms will be a breakthrough for previously unknown or unclarifiable events.
The team of researchers hopes to fully elucidate the formation and growth mechanisms of inorganic crystals, in addition to the structural control factors that occur between organic templates and inorganic materials in biomineralization. However, there are many obstacles in acquiring these findings, including the need for a great deal of research knowledge and far reaching collaboration of researchers belonging to various academic fields.
The group is currently working on developing inorganic materials that are crucial in the engineering and medical fields by using a material synthesis method that is clean and gentle on the environment, as well as elucidating the nanostructure of the constructed materials, the complexation of organic and inorganic materials, and the clarification of the correlation between structure and function of such materials.
INFORMATION:
Acknowledgments:
This research was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number JP16K18250 and 20K15340 and The Foundation for The Promotion of Ion Engineering.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
Current American Heart Association, European Society of Cardiology, and UK National Health Service guidelines recommend a 5-yearly health checks for screening of individuals at high cardiovascular disease risk. These health checks include measurement of major risk factors, such as systolic blood pressure, cholesterol profile, blood glucose, and smoking status.
If lifestyle interventions are unsuccessful in reducing risk factor levels, prevention guidelines recommend initiation of preventive medication therapies such as statins. However, current guidelines advice only using the latest ...
2021-06-23
The results of the study were published in the journal "Neurology" on 19 May 2021 under the leadership of Professor Elena Enax-Krumova, holder of the endowed professorship of the German Social Accident Insurance (DGUV).
Nerve injuries: frequent complication after occupational accidents
Peripheral nerves refer to nerves that lie outside of the brain and spinal cord. They run throughout the entire body. These bundles of nerve fibres can be damaged in the event of blunt or sharp force trauma due to accidents, as well as during surgery. Injuries to the peripheral nerves are a frequent complication, particularly after occupational accidents. Patients often suffer from motor and sensory disorders in the affected area of the body. These can lead to persistent complaints and ...
2021-06-23
Beware of those snack attacks. A new study in Appetite has confirmed the small luxuries, from sweets and chocolate to salty treats, have helped to lift our spirits - and kilojoule intake - during COVID-19 lockdowns.
Researchers in England and Australia have gathered evidence about similar experiences in the UK and Victoria, Australia to warn about the effect of extended pandemic lockdowns on our eating behaviours.
While time at home provides more time for healthy food preparation, intake of high-energy density foods (HED) has risen for some - presenting at-risk adults with the prospect of managing weight gain, the psychology researchers warn.
"The ...
2021-06-23
The response times of footballers is slowed down when part of the kit worn by both teams is of the same colour, a new study shows.
The research from the University of York revealed that when players have any kit colour clash - either shirt or shorts - it takes them twice as long to find a fellow player on the pitch.
Study authors are calling for a change in the laws of the game or for clearer guidance.
Researchers used two experiments to investigate how kit variations affect the visual search for teammates. Their first experiment confirmed that a ...
2021-06-23
Profs. Okujima and Uno at Ehime University, in collaboration with Prof. Kobayashi at Shinshu University, reported the selective synthesis, the molecular structure, optical properties and electronic structure of cyclo[9]pyrrole, a ring-expanded porphyrin consisting of directly connected pyrrole rings.
Porphyrins, which are well-known natural porphyrin molecules, e.g. heme and chlorophyll, are attractive for use in practical materials because of the easy optimization of their optical and physical properties by conjugation expansion and functionalization. In 2002, Sessler reported the first synthesis of cyclo[n]pyrrole (n: ...
2021-06-23
A new analysis of known exoplanets has revealed that Earth-like conditions on potentially habitable planets may be much rarer than previously thought. The work focuses on the conditions required for oxygen-based photosynthesis to develop on a planet, which would enable complex biospheres of the type found on Earth. The study is published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The number of confirmed planets in our own Milky Way galaxy now numbers into the thousands. However planets that are both Earth-like and in the habitable zone - the region around a star where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on the surface - are much less common.
At the moment, only a handful of such rocky and potentially habitable exoplanets ...
2021-06-23
Research Associate Artyom Gusarov studied a vast array of erosion data to make a general takeaway that soil erosion and river sediment load in the aforementioned region has significantly decreased throughout the post-Soviet period.
"The decrease has been especially profound in the forest steppe, a part of which covers the Republic of Tatarstan, because of the combined influence of climate change and land cultivation," explains Gusarov. "To the north of the forest steppe, in the southern part of the boreal zone, the anthropogenic factor was the primary influence on the changes in soil erosion, at least in the east of the East European Plain. ...
2021-06-23
As much as 20% of premature mortality can be attributed to poor urban and transport planning. Nevertheless, quantitative indicators to guide the integration of health components into urban design have been lacking. To address this gap, a team from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has identified 10 principles--and corresponding indicators--to help urban planners incorporate public health into their work.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, was undertaken at the request of the Directorate-General for Environmental Policies and the Natural Environment, which forms ...
2021-06-23
Organic solar elements with the self-assembling molecular-thin layer (SAM) of hole-transporting material, the technology, which was used in producing a record-breaking tandem solar cell, achieved 18.4 power conversion efficiency. The invention of Lithuanian chemists working at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), commercialized by several global companies proved versatile and applicable to different solar technologies.
Organic solar cells are made of common organic elements such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, fluorine, oxygen, and sulphur. Their raw materials are cheap, abundant, and can ...
2021-06-23
The Earth is a sphere, and it comprises spheres: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere -- in short, all of the cycles that interact to influence Earth's weather and climate. Now, to better research how the spheres interact and impact the planet, China is launching EarthLab in Beijing. On June 23, after EarthLab's opening ceremony, researchers will begin trials to demonstrate the facility's ability to integrate simulations and observations to more accurately project outcomes and provide a scientific foundation to predict and mitigate such things as natural weather disasters.
EarthLab's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Bioinspired mineralization of calcium carbonate in peptide hydrogel