Influence of land use on soil erosion in European Russia for the last 30 years
A comprehensive study of this large region of Russia saw light in Water
2021-06-23
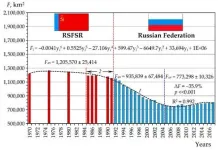
(Press-News.org) Research Associate Artyom Gusarov studied a vast array of erosion data to make a general takeaway that soil erosion and river sediment load in the aforementioned region has significantly decreased throughout the post-Soviet period.
"The decrease has been especially profound in the forest steppe, a part of which covers the Republic of Tatarstan, because of the combined influence of climate change and land cultivation," explains Gusarov. "To the north of the forest steppe, in the southern part of the boreal zone, the anthropogenic factor was the primary influence on the changes in soil erosion, at least in the east of the East European Plain. Here, the reduction of cultivated land was the biggest in the post-Soviet time. In the steppes, the primary role can be attributed to climate change, especially the warming of the near-soil air, which led to decreased frosting of soils during winters, and, therefore, decreased erosion-inducing sediment from tillage."
The research shows that there is a complex intertwining between seemingly negative socio-economic developments and environmental conditions.
"The recession of agriculture in contemporary Russia, including decreases in tillage areas, numbers of agricultural machines, livestock population, etc., led to decreased soil and ravine erosion in the region, decreased river sediment load and concomitant pollution," says Gusarov.
The results are very important for the comprehensive planning of soil preservation, hydrogeological construction, and artificial water bodies. Artyom Gusarov aims to continue this research, now moving to the northern part of the East European Plain and the rivers running into the Arctic Ocean.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
As much as 20% of premature mortality can be attributed to poor urban and transport planning. Nevertheless, quantitative indicators to guide the integration of health components into urban design have been lacking. To address this gap, a team from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has identified 10 principles--and corresponding indicators--to help urban planners incorporate public health into their work.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, was undertaken at the request of the Directorate-General for Environmental Policies and the Natural Environment, which forms ...
2021-06-23
Organic solar elements with the self-assembling molecular-thin layer (SAM) of hole-transporting material, the technology, which was used in producing a record-breaking tandem solar cell, achieved 18.4 power conversion efficiency. The invention of Lithuanian chemists working at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), commercialized by several global companies proved versatile and applicable to different solar technologies.
Organic solar cells are made of common organic elements such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, fluorine, oxygen, and sulphur. Their raw materials are cheap, abundant, and can ...
2021-06-23
The Earth is a sphere, and it comprises spheres: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere -- in short, all of the cycles that interact to influence Earth's weather and climate. Now, to better research how the spheres interact and impact the planet, China is launching EarthLab in Beijing. On June 23, after EarthLab's opening ceremony, researchers will begin trials to demonstrate the facility's ability to integrate simulations and observations to more accurately project outcomes and provide a scientific foundation to predict and mitigate such things as natural weather disasters.
EarthLab's ...
2021-06-23
A beetle bores a tree trunk to build a gallery in the wood in order to protect its lay. As it digs the tunnel, it spreads ambrosia fungal spores that will feed the larvae. When these bore another tree, the adult beetles will be the transmission vectors of the fungal spores in another habitat. This mutualism among insects and ambrosia fungi could be more than 100 years old --more than what was thought to date-- according to an article published in the journal Biological Reviews.
The study analyses for the first time the symbiotic associations and the coevolution between ambrosia fungi and beetles from a paleontological perspective using the Cretaceous ...
2021-06-23
Everybody from a child knows that elephants trumpet. Over the past decades research in general and at the University of Vienna has mainly studied the elephants low-frequency rumble. Its fundamental frequency reaches into the infrasonic range below the human hearing threshold. This call is produced by the elephant´s massive vocal folds. Much less was known about how elephants produce their higher pitched sounds, trumpets and squeaks.
The following rule generally applies to sound production in mammals: the larger the vocal fold, the lower the calls fundamental frequency. Conversely the size of the vocal folds sets an upper limit to the fundamental frequencies that can be reached. The high-pitched squeak only Asian but not African elephants ...
2021-06-23
University of Maryland researchers created the first high-resolution image of an expanding bubble of hot plasma and ionized gas where stars are born. Previous low-resolution images did not clearly show the bubble or reveal how it expanded into the surrounding gas.
The researchers used data collected by the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) telescope to analyze one of the brightest, most massive star-forming regions in the Milky Way galaxy. Their analysis showed that a single, expanding bubble of warm gas surrounds the Westerlund 2 star cluster and disproved earlier studies suggesting there may be two bubbles surrounding Westerlund 2. The researchers also identified the source of the bubble ...
2021-06-23
In the United States, more than 12 million children hear a minority language at home from birth. More than two-thirds hear English as well, and they reach school age with varying levels of proficiency in two languages. Parents and teachers often worry that acquiring Spanish will interfere with children's acquisition of English.
A first-of-its kind study in U.S.-born children from Spanish-speaking families led by researchers at Florida Atlantic University finds that minority language exposure does not threaten the acquisition of English by children in the U.S. and that there is no trade-off ...
2021-06-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Nineteenth- and 20th-century archaeologists often made sweeping claims about Native cultures, suggesting that everyone who lived in a particular region at a given time shared the same attitudes and practices. A new study of pipes recovered from Hopewell sites in Illinois and Ohio challenges this assumption, revealing that the manufacture, import, export and use of pipestone pipes for smoking varied significantly between the groups, even though they engaged in trade with one another.
The Hopewell era ran from about 50 B.C. to A.D. 250. The new findings are reported in the journal American Antiquity.
The Havana and Scioto Hopewell people, who lived in what is now Illinois ...
2021-06-23
A Canadian research team has uncovered a new mechanism involved in Bourneville tuberous sclerosis (BTS), a genetic disease of childhood. The team hypothesizes that a mutation in the TSC1 gene causes neurodevelopmental disorders that develop in conjunction with the disease.
Seen in one in 6,000 children, tuberous sclerosis causes benign tumours or lesions that can affect various organs such as the brain, kidneys, eyes, heart and skin. While some patients lead healthy lives, others have significant comorbidities, such as epilepsy, autism and learning disabilities.
Although the role that the TSC1 gene plays in the disease is already known, Montreal scientists have only now identified a critical period in the postnatal development ...
2021-06-23
When a pregnant person declines a recommended treatment such as prenatal testing or an epidural, tension and strife may ensue between the patient and provider, according to a new analysis by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the University of British Columbia.
"People should feel safe, respected, and engaged in their maternity care, but our findings suggest that when providers do not listen to patients, it can foster mistrust and avoidance," said P. Mimi Niles, PhD, MPH, CNM, assistant professor at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the lead author of the study, which is published in the journal PLOS ONE. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Influence of land use on soil erosion in European Russia for the last 30 years
A comprehensive study of this large region of Russia saw light in Water








