China's EarthLab begins trials as country's first facility exploring Earth system interactions
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) The Earth is a sphere, and it comprises spheres: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere -- in short, all of the cycles that interact to influence Earth's weather and climate. Now, to better research how the spheres interact and impact the planet, China is launching EarthLab in Beijing. On June 23, after EarthLab's opening ceremony, researchers will begin trials to demonstrate the facility's ability to integrate simulations and observations to more accurately project outcomes and provide a scientific foundation to predict and mitigate such things as natural weather disasters.
EarthLab's research team published an introduction to the facility on June 23 in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
"Since the earth system is extremely large and complex, traditional theories and observations are too limited to meet the overall requirements of the scientific research community," said paper corresponding author He Zhang, EarthLab researcher affiliated with the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). "EarthLab is the first comprehensive virtual earth laboratory in China for simulation the physical climate system, environmental system, ecological system, solid earth system, and space weather system as a whole with a high-performance scientific computing platform."
In partnership with Tsinghua University, IAP/CAS began construction of EarthLab in 2018. After successful trialing, inspections and approvals, EarthLab is expected to become fully operational -- and open to universities and research institutes across the world -- in 2022.
"Other countries, such as the United States and Japan, as well as some European countries, have built specialized numerical simulations facilities," Zhang said, noting that China's vast and complex topography has been difficult to model accurately with various levels of observational and experimental resources across the country. "Weather, climate and environmental disasters occur frequently and seriously with grave losses of life and property. Consequently, a global earth system simulation system, as well as high-precision regional environmental simulation system, are urgently needed to better predict climate and environment variability, to prevent and mitigate natural disasters more effectively, and to formulate relevant national plans more scientifically."
According to Zhang, EarthLab will also become a science outreach base for children and students to learn more about Earth sciences. During an IAP outreach day in 2017, children voted on EarthLab's Chinese name: Huan. The name means "a place as vast as the earth where people live and upon whose land they depend".
"Our ultimate goal is to predict Earth systems on a vast range of time scale, from seconds to hundreds of years, and of spatial scale, from 10 meters to millions of meters," Zhang said. "Along with other earth simulators around the world, the development and construction of EarthLab will advance not only the understanding of the Earth's spheres and their interactions, and Earth's past, present and future, but also the progress of computational mathematics, high-performance computing and technology, and other broader fields."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
A beetle bores a tree trunk to build a gallery in the wood in order to protect its lay. As it digs the tunnel, it spreads ambrosia fungal spores that will feed the larvae. When these bore another tree, the adult beetles will be the transmission vectors of the fungal spores in another habitat. This mutualism among insects and ambrosia fungi could be more than 100 years old --more than what was thought to date-- according to an article published in the journal Biological Reviews.
The study analyses for the first time the symbiotic associations and the coevolution between ambrosia fungi and beetles from a paleontological perspective using the Cretaceous ...
2021-06-23
Everybody from a child knows that elephants trumpet. Over the past decades research in general and at the University of Vienna has mainly studied the elephants low-frequency rumble. Its fundamental frequency reaches into the infrasonic range below the human hearing threshold. This call is produced by the elephant´s massive vocal folds. Much less was known about how elephants produce their higher pitched sounds, trumpets and squeaks.
The following rule generally applies to sound production in mammals: the larger the vocal fold, the lower the calls fundamental frequency. Conversely the size of the vocal folds sets an upper limit to the fundamental frequencies that can be reached. The high-pitched squeak only Asian but not African elephants ...
2021-06-23
University of Maryland researchers created the first high-resolution image of an expanding bubble of hot plasma and ionized gas where stars are born. Previous low-resolution images did not clearly show the bubble or reveal how it expanded into the surrounding gas.
The researchers used data collected by the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) telescope to analyze one of the brightest, most massive star-forming regions in the Milky Way galaxy. Their analysis showed that a single, expanding bubble of warm gas surrounds the Westerlund 2 star cluster and disproved earlier studies suggesting there may be two bubbles surrounding Westerlund 2. The researchers also identified the source of the bubble ...
2021-06-23
In the United States, more than 12 million children hear a minority language at home from birth. More than two-thirds hear English as well, and they reach school age with varying levels of proficiency in two languages. Parents and teachers often worry that acquiring Spanish will interfere with children's acquisition of English.
A first-of-its kind study in U.S.-born children from Spanish-speaking families led by researchers at Florida Atlantic University finds that minority language exposure does not threaten the acquisition of English by children in the U.S. and that there is no trade-off ...
2021-06-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Nineteenth- and 20th-century archaeologists often made sweeping claims about Native cultures, suggesting that everyone who lived in a particular region at a given time shared the same attitudes and practices. A new study of pipes recovered from Hopewell sites in Illinois and Ohio challenges this assumption, revealing that the manufacture, import, export and use of pipestone pipes for smoking varied significantly between the groups, even though they engaged in trade with one another.
The Hopewell era ran from about 50 B.C. to A.D. 250. The new findings are reported in the journal American Antiquity.
The Havana and Scioto Hopewell people, who lived in what is now Illinois ...
2021-06-23
A Canadian research team has uncovered a new mechanism involved in Bourneville tuberous sclerosis (BTS), a genetic disease of childhood. The team hypothesizes that a mutation in the TSC1 gene causes neurodevelopmental disorders that develop in conjunction with the disease.
Seen in one in 6,000 children, tuberous sclerosis causes benign tumours or lesions that can affect various organs such as the brain, kidneys, eyes, heart and skin. While some patients lead healthy lives, others have significant comorbidities, such as epilepsy, autism and learning disabilities.
Although the role that the TSC1 gene plays in the disease is already known, Montreal scientists have only now identified a critical period in the postnatal development ...
2021-06-23
When a pregnant person declines a recommended treatment such as prenatal testing or an epidural, tension and strife may ensue between the patient and provider, according to a new analysis by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the University of British Columbia.
"People should feel safe, respected, and engaged in their maternity care, but our findings suggest that when providers do not listen to patients, it can foster mistrust and avoidance," said P. Mimi Niles, PhD, MPH, CNM, assistant professor at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the lead author of the study, which is published in the journal PLOS ONE. ...
2021-06-23
Middle school, a time when children's brains are undergoing significant development, is often also a time of new challenges in navigating the social world. Recent research from the Center for BrainHealth at UT Dallas demonstrates the power of combining a virtual platform with live coaching to help students enhance their social skills and confidence in a low-risk environment.
In this study, BrainHealth researchers partnered with low-income public middle schools in Dallas. Teachers recommended 90 students to participate in virtual training sessions via ...
2021-06-23
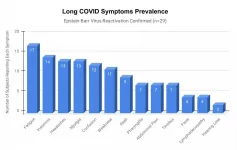
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation resulting from the inflammatory response to coronavirus infection may be the cause of previously unexplained long COVID symptoms -- such as fatigue, brain fog, and rashes -- that occur in approximately 30% of patients after recovery from initial COVID-19 infection. The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long COVID, as well as an analysis of long COVID prevalence, is outlined in a new long COVID study published in the journal Pathogens.
"We ran EBV antibody tests on recovered COVID-19 patients, comparing EBV reactivation rates of those with long COVID symptoms to those without ...
2021-06-23
Niigata, Japan - An estimated 1.13 billion people worldwide have hypertension or high blood pressure, and two-thirds of these individuals are living in low- and middle-income countries. Blood pressure is the force manifested by circulating blood against the walls of the body's arteries, the major blood vessels in the body. Hypertension is when blood pressure is too high.
Blood pressure is written as two numbers. The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats. The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats. Hypertension is diagnosed if, when it is measured on two different days, the systolic blood pressure (SBP) readings on both days is ≥140 mmHg and/or the diastolic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] China's EarthLab begins trials as country's first facility exploring Earth system interactions