Use of additional Metop-C and Fengyun-3 C/D data improves regional weather forecasts
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) Modern weather forecasts rely heavily on data retrieved from numerical weather prediction models. These models continue to improve and have advanced considerably throughout more than half a century. However, forecast reliability depends on the quality and accuracy of initialization data, or a sample of the current global atmosphere when the model run is started. This process of bringing surface observations, radiosonde data, and satellite imagery together to create a picture of the initial atmospheric state is called data assimilation. Satellite upgrades have significantly improved this process, providing more data than ever before. Several recent studies show that passive microwave (PMW) radiance observations from polar orbiting satellites are critical to input into both global and regional weather prediction models.
However, fully utilizing this information comes with challenges. PMW radiance observation coverage varies throughout a given day. Sometimes, data is delayed, making accurate data assimilation difficult. That said, scientists are working toward solutions to use these vital observations more effectively. A paper recently published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences shows how researchers improved daily PMW radiance observation coverage using instruments onboard the Metop-C, Fengyun-3 C/D, and several other operational meteorological satellites.
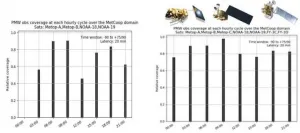
"With these additional observations included in different assimilation cycles, there is a more even distribution of the fraction of the area covered by PMW radiances." said lead author Magnus Lindskog with the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute.
Results show that almost 80% of the model's domain, or coverage area, is accessible by PMW radiance observations for all assimilation cycles. Particularly, for the 0000 UTC model run, a large part of the domain is covered by PMW data alongside additional satellite radiances. However, none of these observations exist in the operational reference version due to the satellite's position at that specific time of day.
Thus, adding more PMW satellite radiances to evenly distribute data points throughout the day has the potential to improve forecast quality by filling existing data gaps in the applied regional weather prediction system. Likewise, enhancing and increasing the use of PMW radiances positively impacts a model's ability to use and process this data, improving its short-range regional weather forecasts.
Lindskog's study also highlights the next research opportunities within the regional weather prediction system. Satellite scientists should consider improving PMW radiances that are influenced by clouds as well as the effect of different surface weather characteristics at initialization. Finally, further research should also focus on developing and applying more refined data assimilation techniques than the current three-dimensional variational technique. A more efficient process should increase the benefits of enhanced PMW radiance observation data.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
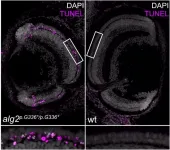
A rare genetic defect that affects the so-called ALG2 gene can cause serious metabolic diseases in humans. It does so through the defective formation of proteins and sugar molecules. Until now, its rareness and complexity made it difficult to study this congenital glycosylation disorder. A research team led by Prof. Dr Joachim Wittbrodt and Dr Thomas Thumberger from the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) of Heidelberg University has finally succeeded in introducing the underlying mutation in the ALG2 gene in a fish model, thus allowing the causes of these complex diseases to be studied at the molecular level.
Human cells are kept alive by the activity of millions of proteins. As they mature, these proteins ...
2021-06-23
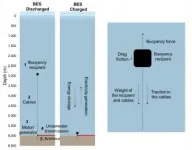
What do pipes and anchors have to do with storing energy? More than you might think! A new IIASA-led study explored the potential of a lesser known, but promising sustainable energy storage system called Buoyancy Energy Storage.
There is general consensus that renewable energy sources will play an important role in ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for the planet and its people, and many countries are indeed already seeing such technologies displacing "dirty" fossil fuels in the power sector in an effort to lower emissions. The biggest problem with renewable energy sources, however, is that power supply is intermittent, meaning that the energy output at any given time does not necessarily meet the demand at that time. ...
2021-06-23
Our homes and offices are only as solid as the ground beneath them. When that solid ground turns to liquid -- as sometimes happens during earthquakes -- it can topple buildings and bridges. This phenomenon is known as liquefaction, and it was a major feature of the 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand, a magnitude 6.3 quake that killed 185 people and destroyed thousands of homes.
An upside of the Christchurch quake was that it was one of the most well-documented in history. Because New Zealand is seismically active, the city was instrumented ...
2021-06-23
Several eye clinics around Sweden are seeing a rise in eye damage related to the racket sport padel. In an article in the Journal of the Swedish Medical Association (Läkartidningen), eye researchers affiliated with the University of Gothenburg state that padel is a potential high-risk sport for eye injuries, and that wearing protective goggles is a good idea.
Ball sports are often associated with an increased risk of eye injuries, and the risk seems to be even greater with padel, a sport that is now highly popular in Sweden (and should not be confused with the North American "paddle tennis").
"The ...
2021-06-23
ITHACA, N.Y. - Coming soon to a lab tabletop near you: a method of magneto-thermal imaging that offers nanoscale and picosecond resolution previously available only in synchrotron facilities.
This innovation in spatial and temporal resolution will give researchers extraordinary views into the magnetic properties of a range of materials, from metals to insulators, all from the comfort of their labs, potentially boosting the development of magnetic storage devices.
"Magnetic X-ray microscopy is a relatively rare bird," said Greg Fuchs, associate professor of applied and engineering physics, who led the project. "The magnetic ...
2021-06-23
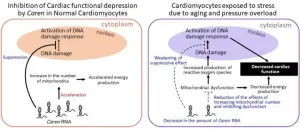
A research collaboration based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has identified a novel lncRNA, Caren, that is abundantly expressed in cardiomyocytes. They showed that it enhances energy production by increasing the number of mitochondria in cardiomyocytes, and inhibits activation of the ATM protein, a key player in the DNA damage response pathway that accelerates heart failure severity. Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes is reduced by aging and high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart failure, and markedly reduced in the hearts of heart failure patients. The researchers believe that ...
2021-06-23
Eating 2.5 grams of pure natural cocoa powder serves to improve visual acuity in healthy young adults and in daylight conditions, according to research by the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) and the ICTAN (Institute of Food and Nutrition Science and Technology) of the CSIC.
The study, published in the Journal of Functional Foods, analyse the effects of two dietary polyphenols: cocoa flavanols and red berry anthocyanins.
"Although this was the baseline hypothesis, we did not see any effect either on adaptation to darkness or on visual acuity measured in low light conditions (mesopic vision), either with cocoa or with berries," indicates María Cinta Puell Marín, researcher at the Optometry and Vision ...
2021-06-23
Children who were exposed to higher levels of trace minerals manganese and selenium during their mothers' pregnancy had a lower risk of high blood pressure in childhood, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers analyzed the levels of toxic metals and trace minerals in blood samples drawn from nearly 1,200 women in the Boston area who gave birth between 2002 and 2013. They found that higher levels of selenium or manganese in the mothers' blood were associated with lower blood pressure readings in their children ...
2021-06-23
A sensitive blood test being developed by a team of researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center shows promise for predicting whether patients with metastatic HPV-positive throat cancer will respond to treatment months earlier than standard imaging scans.
That's according to a study, published in Oncotarget, validating the test in a small group of patients with metastatic human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma -- a type of head and neck cancer that develops in the back of the mouth and in the throat.
If the test can quickly determine that a treatment approach isn't ...
2021-06-23
AMHERST, Mass. - As summer unfolds, more than 500 species of invasive plants will be taking root in fields, lawns, and gardens across the US. As plants continue to move north driven by climate change, the number of invasives will only increase. Unfortunately, inconsistent regulations that vary from state to state means that invasive plants have an edge on our attempts to control them. However, new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published in the Journal of Applied Ecology suggests that we already have an answer in hand - communication.
"We know that invasive plants are causing both ecological and economic harm in the US," says Emily Fusco, one of the paper's lead authors and a postdoctoral research fellow in the department of environmental conservation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Use of additional Metop-C and Fengyun-3 C/D data improves regional weather forecasts