Seeking a treatment for IBS pain in tarantula venom
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) For patients who have inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS), the condition is literally a pain in the gut. Chronic -- or long-term -- abdominal pain is common, and there are currently no effective treatment options for this debilitating symptom. In a new study in ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science, researchers identify a new potential source of relief: a molecule derived from spider venom. In experiments with mice, they found that one dose could stop symptoms associated with IBS pain.
The sensation of pain originates in electrical signals carried from the body to the brain by cells called neurons. Tiny channels in the surfaces of neurons help them transmit these signals by allowing positively charged sodium ions to pass into the cell. There are numerous types of sodium channels, and some pain-killing drugs work by blocking them. However, existing treatments interfere with channels indiscriminately and can only be used briefly -- not for chronic pain. Stuart Brierley, Glenn King and colleagues wanted to find a way to selectively target the channels activated during chronic IBS pain.
The researchers focused on a particular sodium channel they suspected was responsible for chronic IBS pain. Then, to block it, they turned to the richest known source of molecules that alter the activity of sodium channels: spider venom. In the venom of a Peruvian tarantula, they discovered a molecule that they named Tsp1a, which had promising blocking activity. To test its potential as a treatment, the researchers used mice that had an IBS-related condition, and they monitored the mice during the experiment to detect a reflex associated with pain. A single Tsp1a treatment delivered into the mice's colons significantly reduced the occurrence of this reflex, indicating pain relief. What's more, Tsp1a appeared highly selective and did not interfere with other body functions, suggesting it could be used safely in humans. While Tsp1a shows promise as a potential treatment for chronic IBS pain, thorough studies of its activity in the body and the immune system's reaction to it will be critical, the researchers write.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, the Australian Research Council, the U.S. National Institutes of Health and The University of Queensland. Four of the authors are co-inventors on a U.S. patent application that covers the sequence, derivatives and methods of use for Tsp 1a.
The abstract that accompanies this paper is available here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world's scientific knowledge. ACS' main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
Air quality varies greatly within regions and cities around the world, and exposure to air pollution can have severe health impacts. In the U.S., people of color are disproportionately exposed to poor air quality. A cover story in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, highlights how scientists and community activists are using new technologies to gather data that could help address this inequity.
Despite the success of the U.S. Clean Air Act in improving ambient air quality over the past 50 years, discriminatory housing, loan ...
2021-06-23
Over recent years, the retina has established its position as one of the most promising biomarkers for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's. Moving on from the debate as to the retina becoming thinner or thicker, researchers from the Universidad Complutense de Madrid and Hospital Clínico San Carlos are focusing their attention on the roughness of the ten retinal layers.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, "proves innovative" in three aspects according to José Manuel Ramírez, Director of the IIORC (Ramón Castroviejo Institute of Ophthalmologic Research) at the UCM. "This is the first study to propose studying the roughness of the retina and its ten constituent layers. They have devised a mathematical method to measure the degree of wrinkling, through the fractal ...
2021-06-23
Children with obstructive sleep apnea are nearly three times more likely to develop high blood pressure when they become teenagers than children who never experience sleep apnea, according to a new study funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health. However, children whose sleep apnea improves as they grow into adolescence do not show an increased chance of having high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.
The long-term study, one of the largest of its kind in the pediatric population, underscores the seriousness of sleep apnea in children and the importance of early treatment, the researchers said. Their findings appear online in the journal JAMA Cardiology.
Obstructive sleep apnea, ...
2021-06-23
Previous research was falsely reassuring; captured only 2% of cirrhosis patients
Findings underscore lack of access to health care for Black patients
Cirrhosis is leading cause of death and affects more than 600,000 people in U.S.
CHICAGO --- Black patients with cirrhosis - late-stage liver disease - are about 25% more likely to die compared to non-Hispanic white patients and four times less likely to receive a liver transplant, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Estimates of racial disparity in cirrhosis have been limited by a lack of large-scale longitudinal data, which track patients from diagnosis to death and/or transplant.
The paper is one of the first to link all seven large liver centers in Chicago with the death registry and transplant registry to examine ...
2021-06-23
Psycholinguists from the HSE Center for Language and Brain, in collaboration with researchers from the City University of New York and the University of Stuttgart, investigated how reading in Russian varies among different groups of readers. The authors used a novel method in bilingualism research -comparison of the eye-movement sequences (scanpaths) in adult native speakers of Russian, Russian-speaking children, and adult bilinguals with different levels of Russian proficiency. The results of the study were published in Reading Research Quarterly.
A total of 120 readers took part in the study, with 30 participants in each group. Participants included adult ...
2021-06-23
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- The giant plumose anemone is an animal, but it looks a bit like an underwater cauliflower. Its body consists of a stalk-like column that attaches to rocks and other surfaces on one end, and to a crown of tentacles on the other.
The anemones use these feelers to collect and shove food into their mouths, and a new study provides an in-depth look into the rich diversity of prey the anemones are catching. This includes a surprising menu item: ants, specifically the pale-legged field ant, Lasius pallitarsis. And the occasional spider.
The research was published on June 15 in the journal Environmental DNA. The study focused on giant plumose ...
2021-06-23
How long do virus-laden particles persist in an elevator after a person infected with COVID-19 leaves? And is there a way to detect those particles? A group of electrical engineers and computer scientists at KAUST set out to answer these questions using mathematical fluid dynamics equations.
"We found1 that virus-laden particles can still be detected several minutes after a short elevator trip by an infected person," says KAUST electrical engineer Osama Amin.
The team's equations and breath simulations suggest that a biosensor's ability to detect a virus improves when placed on an elevator wall that can reflect particles. Also, to protect future occupants, the amount of particles in the air can be reduced by making the other three walls absorptive.
Amin ...
2021-06-23
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Throughout her 20-year career as a nurse practitioner, Jennifer Hulett noticed survivors of breast cancer would often express gratitude for being alive and mention God or a divine acknowledgement that had improved their health and well-being.
Now an assistant professor at the University of Missouri Sinclair School of Nursing, Hulett is researching the benefits of spirituality on improving immune health and reducing stress, as well as the chances of cancer reoccurrence, among breast cancer survivors.
In a recent study, Hulett collected and froze samples of saliva from 41 breast cancer survivors at MU's Ellis Fischel Cancer Center. ...
2021-06-23
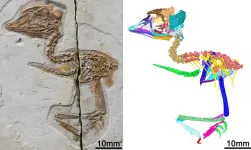
Researchers from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have discovered a 120-million-year-old partial fossil skeleton of a tiny extinct bird that fits in the palm of the hand and preserves a unique skull with a mix of dinosaurian and bird features.
The two-centimeter-long (0.75 inch) skull of the fossil shares many structural and functional features with the gigantic Tyrannosaurus rex, indicating that early birds kept many features of their dinosaurian ancestors and their skulls functioned much like those of dinosaurs rather than living ...
2021-06-23
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (06/23/2021) -- A new report from the University of Minnesota Medical School's Healthy Youth Development - Prevention Research Center (HYD-PRC) highlights that Minnesota youth continue to contract sexually transmitted infections (STIs) at alarmingly high rates, despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
The 2021 Minnesota Adolescent Sexual Health Report says that chlamydia and gonorrhea rates among Minnesota adolescents in 2020 are likely underreported, as both STI testing and case detection were scaled back during the early stages of the pandemic. However, teen pregnancy rates remain virtually unchanged from 2018, and birth rates are at historic lows for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Seeking a treatment for IBS pain in tarantula venom