East Antarctic summer cooling trends caused by tropical rainfall clusters
A new study identifies key linkages between rainfall occurring in the tropics and climate trends in Antarctica
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) Our planet is warming due to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions; but the warming differs from region to region, and it can also vary seasonally. Over the last four decades scientists have observed a persistent austral summer cooling on the eastern side of Antarctica. This puzzling feature has received world-wide attention, because it is not far away from one of the well-known global warming hotspots - the Antarctic Peninsula.
A new study published in the journal Science Advances by a team of scientists from the IBS Center for Climate Physics at Pusan National University in South Korea, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Ewha Womans University, and National Taiwan University, uncovers a new mechanism that can explain the regional warming/cooling patchwork over Antarctica. At the heart of the mechanism are clusters of rainfall events in the western tropical Pacific, which release massive amounts of heat into the atmosphere by condensation of water vapor. Warm air rises over the organized rainfall clusters and sinks farther away. This pressure difference creates winds which are further influenced by the effect of earth's rotation. The interplay of these factors generates a large-scale atmospheric pressure wave which travels from west to east along the equator with a speed of about several hundred kilometers per day and which drags along with it the initial rainfall clusters. This propagating atmospheric wave is known as the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), named after Roland Madden and Paul Julian, who discovered this phenomenon in 1971. The characteristic atmospheric pressure, convection and wind anomalies, which fluctuate on timescales of 20-70 days, can extend into the extratropics, reaching even Antarctica.
The international research team arrived at their conclusions by analyzing observational datasets and specially designed supercomputer climate model simulations. "Our analysis provides clear evidence that tropical weather systems associated with the Madden-Julian Oscillation can directly impact surface temperatures over East Antarctica." says Prof. Pang-Chi Hsu from Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, who co-led the study.
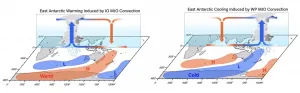
More specifically, as the MJO rainfall clusters move into the western Pacific towards the location of the Solomon Islands, the corresponding global atmospheric wave tends to cool East Antarctica three to eleven days later (Image, right panel). In contrast, when the MJO-related rainfall occurs in the Indian Ocean, East Antarctic shows a pronounced warming (Image, left panel).
"During recent decades, MJO rainfall and pressure changes preferably occurred over the western tropical Pacific but decreased over the Indian Ocean. This situation has favored cooling of East Antarctica during austral summer.", says Prof. June-Yi Lee from the IBS Center for Climate Physics and Pusan National University, and co-leader of the study.
The research team estimated that up to 20% to 40% of the observed summer cooling trend in East Antarctica from 1979 to 2014 can be attributed to the long-term changes in the character and longitudinal core location of the MJO. Other contributing factors include the ozone hole and the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation - a slowly varying weaker companion of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. The new Science Advances study highlights that climate change even in remote regions such as Antarctica, can be linked to processes that happen nearly 10,000 km away.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
A new study from archaeologists at University of Sydney and Simon Fraser University in Vancouver, has provided important new evidence to answer the question "Who exactly were the Anglo-Saxons?"
New findings based on studying skeletal remains clearly indicates the Anglo-Saxons were a melting pot of people from both migrant and local cultural groups and not one homogenous group from Western Europe.
Professor Keith Dobney at the University of Sydney said the team's results indicate that "the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of early Medieval Britain were strikingly similar to contemporary Britain - full of people of different ancestries sharing a common language and culture".
The Anglo-Saxon (or early medieval) period in England runs from the 5th-11th centuries AD. Early Anglo-Saxon dates from ...
2021-06-23
Newspapers regularly carry stories of terrifying shark attacks, but in a paper published today, Oxford-led researchers reveal their discovery of a 3,000-year-old victim - attacked by a shark in the Seto Inland Sea of the Japanese archipelago.
The research in Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, shows that this body is the earliest direct evidence for a shark attack on a human and an international research team has carefully recreated what happened - using a combination of archaeological science and forensic techniques.
The grim discovery of the victim was made by Oxford researchers, J. Alyssa White and Professor Rick Schulting, while investigating evidence for violent trauma on the skeletal remains of prehistoric hunter-gatherers at ...
2021-06-23
SAN ANTONIO, June 23, 2021 - A typical Western high-fat diet can increase the risk of painful disorders common in people with conditions such as diabetes or obesity, according to a groundbreaking paper authored by a team led by The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, also referred to as UT Health San Antonio.
Moreover, changes in diet may significantly reduce or even reverse pain from conditions causing either inflammatory pain - such as arthritis, trauma or surgery - or neuropathic pain, such as diabetes. The novel finding could help treat chronic-pain patients by simply altering diet or developing drugs that block ...
2021-06-23
By José Tadeu Arantes | Agência FAPESP – Mathematical models that describe the physical behavior of magnetic materials can also be used to describe the spread of the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
This is the conclusion of a study conducted in Brazil by researchers affiliated with São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Rio Claro and Ilha Solteira and reported in an article published in Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications.
The study was part of a project led by Mariano de Souza, a professor at UNESP’s Rio Claro Physics Department, and of the PhD research of Isys Mello, whose thesis advisor is Souza, last author of the article. Another co-author is Antonio Seridonio, a professor at UNESP’s Ilha Solteira Physics ...
2021-06-23
Only 1 in 10 older adults in a large national survey who were found to have cognitive impairment consistent with dementia reported a formal medical diagnosis of the condition.
Using data from the Health and Retirement Study to develop a nationally representative sample of roughly 6 million Americans age 65 or older, researchers at the University of Michigan, North Dakota State University and Ohio University found that 91% of people with cognitive impairment consistent with dementia told questioners they had a formal medical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease or dementia.
"(The discrepancy) was higher than I was expecting," ...
2021-06-23
Flavoring can change how the brain responds to e-cigarette aerosols that contain nicotine, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. Andrea Hobkirk and her team used functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to understand how the brain's reward areas react to e-cigarette aerosol with and without flavor.
"There are nearly 12 million e-cigarette users in the United States," Hobkirk, an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral health at Penn State College of Medicine, said. "The vast majority use e-cigarettes with menthol, mint, fruity and dessert-type flavors. Although regulations that limit the sale of flavored e-cigarettes may help curb use among youth, they might also stop adults from using e-cigarettes as a smoking ...
2021-06-23
Researchers from Bentley University have been exploring how readers at partisan news sites respond to news events that challenge their worldview.
In a forthcoming paper in the journal ACM Transactions on Social Computing, they report results of a study that examines reader comments on stories surrounding the 2017 Roy Moore Alabama senate race at two partisan news sites: a left-leaning news site (Daily Kos) and a right-leaning news site (Breitbart). They consider the alleged sexual misconduct of Mr. Moore as a challenging news event for the right-leaning readers; and the subsequent nomination of Mr. Moore as the Republican candidate as a challenging news event for the left-leaning readers.
Their analysis identifies the obstacles that readers face as they try to make sense ...
2021-06-23
NEW YORK CITY, June 23, 2021 -- From amoebas to zebras, all living things evolve. They change over time as pressures from the environment cause individuals with certain traits to become more common in a population while those with other traits become less common.
Cancer is no different. Within a growing tumor, cancer cells with the best ability to compete for resources and withstand environmental stressors will come to dominate in frequency. It's "survival of the fittest" on a microscopic scale.
But fitness -- how well suited any particular individual is to its environment -- isn't set in stone; it can change when the environment changes. The cancer cells that might do best in an environment saturated ...
2021-06-23
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--June 23, 2021--A healthy heart is a pliable, ever-moving organ. But under stress--from injury, cardiovascular disease, or aging--the heart thickens and stiffens in a process known as fibrosis, which involves diffuse scar-like tissue. Slowing or stopping fibrosis to treat and prevent heart failure has long been a goal of cardiologists.
Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes have discovered a master switch for fibrosis in the heart. When the heart is under stress, they found, the gene MEOX1 is turned on in cells called fibroblasts, spurring fibrosis. Their new study, published in the journal Nature, suggests that blocking ...
2021-06-23
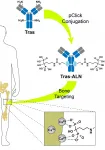
HOUSTON - (June 23, 2021) - Bone cancer is hard to treat and prone to metastasis. Research teams at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine have a new strategy to attack it.
Chemist Han Xiao at Rice and biologist Xiang Zhang at Baylor and their labs have developed an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.
Their open-access study, which appears in Science Advances, shows how Xiao's pClick technology can be used to link bone-targeting antibodies and therapeutic molecules.
In experiments, they used pClick to couple a molecule used to treat osteoporosis, alendronate, with the HER2-targeting antibody trastuzumab used to treat breast cancer and found it significantly enhanced the concentration ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] East Antarctic summer cooling trends caused by tropical rainfall clusters
A new study identifies key linkages between rainfall occurring in the tropics and climate trends in Antarctica