Improve photosynthesis performance via photosystem II-based biomimetic assembly
2021-06-24
(Press-News.org) In the recent decade, scientists have paid more attention to studying light harvest for producing novel bionic materials or integrating naturally biological components into synthetic systems. Inspiration is the imitation of natural photosynthesis in green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria to convert light energy into chemical energy. Photosystem II (PSII) is a light-intervened protein complex responsible for the light harvest and water splitting to release O2, protons, and electrons. The development of PSII-based biomimetic assembly in vitro is favorable for the investigation of photocatalysis, biological solar cells, and bionic photosynthesis, further help us reveal more secret of photosynthesis.
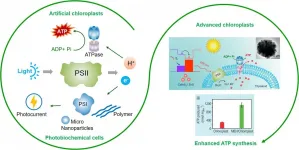
The combination of PSII and artificially synthetic structures is successful for making biohybrid assemblies to harvest light. The evolution of material science advances the development of PSII-based assemblies, PSII-mimicking hybrid systems, and utilization of PSII-related products for energy conversion. Relative applications and explorations occur through coupling PSII within lipid membranes, multilayer polymeric structures, and nanoparticles to maximize the efficient range of light absorbance and offer a high PSII payload yield.
The desired light-harvest performance enables a dramatic energy conversion from sunlight to electric power or biochemical energy. Apart from integrating with synthetic materials, naturally active components, photosystem I (PSI), bacteriorhodopsin (BR), or ATP synthase (ATPase), attain in vitro reassembly with PSII to form artificial chloroplasts and achieve partial natural photosynthesis process, including electron generation and transfer as well as ATP synthesis. Subsequent studies found that manipulation of light absorption range is critical to improving the photosynthetic activity of PSII. Synthetic luminescent materials (e.g., fluorescent polymers, quantum dots) are applied to help PSII or chloroplast convert UV light into visible light, resulting in productivity improvement of ATP synthesis.
At present, although reassembly of PSII-based hybrid systems is successful, this system suffers from typical drawbacks shares by common protein species in terms of stability, durability, biological activity, and environmental restrictions for applying PSII-based systems in the near future. Therefore, efforts and explorations still focus on investigating PSII-based biomimetic assembly to challenge these above weaknesses.
This Reviews Article published in National Science Review by Prof. Junbai Li's group at Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Lab of Colloid, Interface and Chemical Thermodynamics, Institute of Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences, summarizes recent studies on how PSII protein complex combines with artificial structures via molecular assembly, and highlights PSII-based semi-natural biosystems. Moreover, they discuss this biomimetic systems regarding the remaining problem, challenges, and outlooks.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
Mingjun Xuan and Junbai Li
Photosystem II-based biomimetic assembly for enhanced photosynthesis
Natl Sci Rev (June 2021) doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab051
https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab051
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-24
Ishikawa, Japan - Nanostructured metal surface has novel physical and chemical properties, which have sparked scientific interest for heterogeneous catalysis, biosensors, and electrocatalysis. The fabrication process can influence the shapes and sizes of metal nanostructures. Among various fabrication processes, the electrochemical deposition technique is widely used for clean metal nanostructures. Applying the technique, a team of researchers led by Dr. Yuki Nagao, Associate Professor at Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) and Md. Mahmudul Hasan, a PhD student at JAIST, succeeded to construct Pd-based catalysts having unique morphology.
In this study, the team has successfully synthesized Christmas-tree-shaped palladium nanostructures on the GCE ...
2021-06-24
Toxoplasma gondii, the parasite responsible for toxoplasmosis, is capable of infecting almost all cell types. It is estimated that up to 30% of the world's population is chronically infected, the vast majority asymptomatically. However, infection during pregnancy can result in severe developmental pathology in the unborn child. Like the other members of the large phylum of Apicomplexa, Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite which, to survive, must absolutely penetrate its host's cells and hijack their functions to its own advantage. Understanding how the parasite manages to enter host cells offers new opportunities to develop more effective prevention and control strategies than those currently available. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration ...
2021-06-24
An international study led by Helmholtz Zentrum München has revealed the structure of a membrane-remodeling protein that builds and maintains photosynthetic membranes. These fundamental insights lay the groundwork for bioengineering efforts to strengthen plants against environmental stress, helping to sustaining human food supply and fight against climate change.
Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis, using the energy of sunlight to produce the oxygen and biochemical energy that power most life on Earth. They also adsorb carbon dioxide (CO?) from the atmosphere, counteracting the accumulation of this greenhouse gas. However, climate change ...
2021-06-24
Men - more often than women - need passion to succeed at things. At the same time, boys are diagnosed as being on the autism spectrum four times as often as girls.
Both statistics may be related to dopamine, one of our body's neurotransmitters.
"This is interesting. Research shows a more active dopamine system in most men" than in women, says Hermundur Sigmundsson, a professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU)Department of Psychology.
He is behind a new study that addresses gender differences in key motivating factors for what it takes to become good at something. The study uses men's and women's differing activity in the dopamine system as an explanatory model.
"We looked at gender differences around passion, self-discipline ...
2021-06-24
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues have shown that adaptation to similar environments hardly involves similar genomic positions when species are distantly related. The team investigated recurrent adaptations of wildlife birds' mitochondria to high altitude, migration, diving, wintering, and flight. Repeatable substitutions are rather a coincidence than adaptation, which confirms the scientific opinion that distant species "choose" different ways of similar trait evolution. The paper was published in the journal Genome Biology and Evolution.
If an organism wants to survive in unusual conditions, such as oxygen starvation typical for high altitudes or elevation of metabolism rate due to extreme temperatures, it has to adapt. If different species meet similar environment ...
2021-06-24
Osaka, Japan - Scientists from the Department of Physics and the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) at Osaka University, in collaboration with Kyoto University, used alpha particle inelastic scattering to show that the theorized "5α condensed state" does exist in neon-20. This work may help us obtain a better understanding the low-density nucleon many-body systems.
All elements besides hydrogen and helium must have been fused inside the nuclear furnace of a star. The yield during these reactions of carbon-12, which has six protons and six neutrons, is increased by an ...
2021-06-24
Early in the pandemic, it was expected that satellite imagery around the world would show cleaner air as a result of COVID-19 lockdowns. But not all pollutants were taken out of circulation. For tiny airborne-particle pollution, known as PM 2.5, researchers using NASA data found that variability from meteorology obscured the lockdown signals when observed from space.
"Intuitively you would think if there is a major lockdown situation, that we would see dramatic changes, but we didn't," said Melanie Hammer, a visiting research associate at Washington University in St. Louis who led the study. "It was kind of a surprise ...
2021-06-24
Tooth loss is often accepted as a natural part of aging, but what if there was a way to better identify those most susceptible without the need for a dental exam?
New research led by investigators at Harvard School of Dental Medicine suggests that machine learning tools can help identify those at greatest risk for tooth loss and refer them for further dental assessment in an effort to ensure early interventions to avert or delay the condition.
The study, published June 18 in PLOS ONE, compared five algorithms using a different combination of variables to screen for risk. The results showed those that factored medical characteristics and socioeconomic variables, such as race, education, arthritis, and diabetes, outperformed algorithms that relied on dental clinical indicators alone.
"Our ...
2021-06-24
A new resource developed at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and The Kinghorn Cancer Centre for oncologists could help make targeted cancer therapies more accessible for Australian patients.
The TOPOGRAPH (Therapy-Oriented Precision Oncology Guidelines for Recommending Anti-cancer Pharmaceuticals) database is an online tool that catalogues oncology research to streamline the process of recommending therapeutic treatments in precision cancer medicine.
Garvan Senior Research Officer Dr Frank Lin led the development of the platform reported this week in the journal npj Precision Oncology.
"TOPOGRAPH is uniquely useful in the Australian context because it combines ...
2021-06-24
Wastewater treatment facilities clean the water that goes down our sinks and flushes our toilets, but they do not remove everything. A recent study by Portland State researchers detected low levels of pharmaceuticals and personal care product chemicals in oysters the team deployed at various distances from wastewater effluent pipes along the Oregon and Washington coast. Elise Granek, professor of environmental science and management at Portland State University, and Amy Ehrhart, a recent graduate of PSU's Earth, Environment, and Society doctoral program, conducted the study.
To explore how aquatic pollution varies based on proximity to wastewater facilities, Ehrhart and Granek placed one-week-old ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Improve photosynthesis performance via photosystem II-based biomimetic assembly