(Press-News.org) Men - more often than women - need passion to succeed at things. At the same time, boys are diagnosed as being on the autism spectrum four times as often as girls.
Both statistics may be related to dopamine, one of our body's neurotransmitters.
"This is interesting. Research shows a more active dopamine system in most men" than in women, says Hermundur Sigmundsson, a professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU)Department of Psychology.
He is behind a new study that addresses gender differences in key motivating factors for what it takes to become good at something. The study uses men's and women's differing activity in the dopamine system as an explanatory model.
"We looked at gender differences around passion, self-discipline and positive attitude," Sigmundsson says.
The study refers to these qualities as passion, grit and mindset. The researchers also applied theories to possible links with dopamine levels.
Dopamine is linked to learning, attention and our ability to focus.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is released in the brain. It can contribute to a feeling of satisfaction.
Men normally secrete more dopamine, which is often called the "happy hormone," but it plays a far more complex role than that. The effects of dopamine are linked to learning, attention and our ability to focus.
Previous studies on Icelandic students have shown that men are more dependent on passion in order to succeed at something. This study confirms the earlier findings. Men require more passion. In six out of eight test questions, men score higher on passion than women.
However, the association with dopamine levels has not been established previously.
"The fact that we've developed a test to measure passion for goal achievement means that we can now relate dopamine levels to passion and goal achievement," says Sigmundsson.
Women, on the other hand, may have greater self-discipline - or grit - and be more conscientious, according to other studies. Their level of passion may not be as pronounced in general, but they still are able to do what it takes to be good.
The results for the women, however, are somewhat more ambiguous than men's strong need to burn for something, and this study found no such gender difference.
Nor did the researchers find any difference between the sexes in terms of growth mindset.
In the past, the dopamine system has been associated with many different conditions, such as ADHD, psychoses, manias and Parkinson's disease. But it may also be related to a certain form of autistic behaviour.
Some individuals with autism may become very interested in certain topics, which can be a bit unusual, or even strange, for most people. People on the autism spectrum can focus intensely on these topics or pursuits, at least for a while. Dopamine may play a role.
"Other research in neuroscience has shown hyperactivity in the dopamine system in individuals with autism, and boys make up four out of five children on the autism spectrum. This, and dopamine's relationship to passion, might be a mechanism that helps to explain this behaviour," says Sigmundsson.
The research group tested 917 people aged 14 to 77, consisting of 502 women and 415 men. This is considered a major study in this context.
Sigmundsson collaborated with Stéfan Guðnason from the University of Akureyri and Sigurrós Jóhannsdóttir from the Icelandic State Diagnostic and Counselling Centre (SDCC).
INFORMATION:
Reference: Hermundur Sigmundsson, StéfanGuðnason, Sigurrós Jóhannsdóttir. Passion, grit and mindset: Exploring gender differences. Science Direct. Available online 3 June 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newideapsych.2021.100878
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues have shown that adaptation to similar environments hardly involves similar genomic positions when species are distantly related. The team investigated recurrent adaptations of wildlife birds' mitochondria to high altitude, migration, diving, wintering, and flight. Repeatable substitutions are rather a coincidence than adaptation, which confirms the scientific opinion that distant species "choose" different ways of similar trait evolution. The paper was published in the journal Genome Biology and Evolution.
If an organism wants to survive in unusual conditions, such as oxygen starvation typical for high altitudes or elevation of metabolism rate due to extreme temperatures, it has to adapt. If different species meet similar environment ...
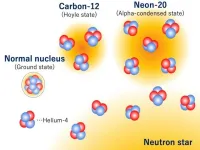
Osaka, Japan - Scientists from the Department of Physics and the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) at Osaka University, in collaboration with Kyoto University, used alpha particle inelastic scattering to show that the theorized "5α condensed state" does exist in neon-20. This work may help us obtain a better understanding the low-density nucleon many-body systems.
All elements besides hydrogen and helium must have been fused inside the nuclear furnace of a star. The yield during these reactions of carbon-12, which has six protons and six neutrons, is increased by an ...
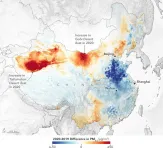
Early in the pandemic, it was expected that satellite imagery around the world would show cleaner air as a result of COVID-19 lockdowns. But not all pollutants were taken out of circulation. For tiny airborne-particle pollution, known as PM 2.5, researchers using NASA data found that variability from meteorology obscured the lockdown signals when observed from space.
"Intuitively you would think if there is a major lockdown situation, that we would see dramatic changes, but we didn't," said Melanie Hammer, a visiting research associate at Washington University in St. Louis who led the study. "It was kind of a surprise ...
Tooth loss is often accepted as a natural part of aging, but what if there was a way to better identify those most susceptible without the need for a dental exam?
New research led by investigators at Harvard School of Dental Medicine suggests that machine learning tools can help identify those at greatest risk for tooth loss and refer them for further dental assessment in an effort to ensure early interventions to avert or delay the condition.
The study, published June 18 in PLOS ONE, compared five algorithms using a different combination of variables to screen for risk. The results showed those that factored medical characteristics and socioeconomic variables, such as race, education, arthritis, and diabetes, outperformed algorithms that relied on dental clinical indicators alone.
"Our ...
A new resource developed at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and The Kinghorn Cancer Centre for oncologists could help make targeted cancer therapies more accessible for Australian patients.
The TOPOGRAPH (Therapy-Oriented Precision Oncology Guidelines for Recommending Anti-cancer Pharmaceuticals) database is an online tool that catalogues oncology research to streamline the process of recommending therapeutic treatments in precision cancer medicine.
Garvan Senior Research Officer Dr Frank Lin led the development of the platform reported this week in the journal npj Precision Oncology.
"TOPOGRAPH is uniquely useful in the Australian context because it combines ...
Wastewater treatment facilities clean the water that goes down our sinks and flushes our toilets, but they do not remove everything. A recent study by Portland State researchers detected low levels of pharmaceuticals and personal care product chemicals in oysters the team deployed at various distances from wastewater effluent pipes along the Oregon and Washington coast. Elise Granek, professor of environmental science and management at Portland State University, and Amy Ehrhart, a recent graduate of PSU's Earth, Environment, and Society doctoral program, conducted the study.
To explore how aquatic pollution varies based on proximity to wastewater facilities, Ehrhart and Granek placed one-week-old ...
Researchers at Harvard University and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have created a first detailed atlas of a critical region of the developing mouse brain, applying multiple advanced genomic technologies to the part of the cerebral cortex that is responsible for processing sensation from the body. By measuring how gene activity and regulation change over time, researchers now have a better understanding of how the cerebral cortex is built, as well as a brand new set of tools to explore how the cortex is affected in neurodevelopmental disease. The study is published in the journal Nature.
"We have had a long-standing interest in understanding the development of the mammalian cerebral cortex, as it is ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Using an unusually well-preserved subfossil jawbone, a team of researchers -- led by Penn State and with a multi-national team of collaborators including scientists from the Université d'Antananarivo in Madagascar -- has sequenced for the first time the nuclear genome of the koala lemur (Megaladapis edwardsi), one of the largest of the 17 or so giant lemur species that went extinct on the island of Madagascar between about 500 and 2,000 years ago. The findings reveal new information about this animal's position on the primate family tree and how it interacted with its environment, which could help in understanding the impacts of past lemur extinctions on Madagascar's ecosystems.
"More than 100 species of lemurs live on Madagascar today, ...
To better understand the role of bacteria in health and disease, National Institutes of Health researchers fed fruit flies antibiotics and monitored the lifetime activity of hundreds of genes that scientists have traditionally thought control aging. To their surprise, the antibiotics not only extended the lives of the flies but also dramatically changed the activity of many of these genes. Their results suggested that only about 30% of the genes traditionally associated with aging set an animal's internal clock while the rest reflect the body's response to bacteria.
"For ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - When the summer sun blazes on a hot city street, our first reaction is to flee to a shady spot protected by a building or tree.
A new study is the first to calculate exactly how much these shaded areas help lower the temperature and reduce the "urban heat island" effect.
Researchers created an intricate 3D digital model of a section of Columbus and determined what effect the shade of the buildings and trees in the area had on land surface temperatures over the course of one hour on one summer day.
"We can use the information from our model to formulate guidelines for community greening and tree planting efforts, and even where to locate buildings to maximize shading on other buildings and roadways," said Jean-Michel Guldmann, co-author of the study and ...