Cosmic hand hitting a wall
2021-06-24
(Press-News.org) Motions of a remarkable cosmic structure have been measured for the first time, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The blast wave and debris from an exploded star are seen moving away from the explosion site and colliding with a wall of surrounding gas.
Astronomers estimate that light from the supernova explosion reached Earth about 1,700 years ago, or when the Mayan empire was flourishing and the Jin dynasty ruled China. However, by cosmic standards the supernova remnant formed by the explosion, called MSH 15-52, is one of the youngest in the Milky Way galaxy. The explosion also created an ultra-dense, magnetized star called a pulsar, which then blew a bubble of energetic particles, an X-ray-emitting nebula.
Since the explosion the supernova remnant - made of debris from the shattered star, plus the explosion's blast wave - and the X-ray nebula have been changing as they expand outward into space. Notably, the supernova remnant and X-ray nebula now resemble the shape of fingers and a palm.
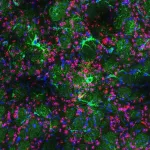
Previously, astronomers had released a full Chandra view of the "hand," as shown in the main graphic. A new study is now reporting how quickly the supernova remnant associated with the hand is moving, as it strikes a cloud of gas called RCW 89. The inner edge of this cloud forms a gas wall located about 35 light-years from the center of the explosion.
To track the motion the team used Chandra data from 2004, 2008, and then a combined image from observations taken in late 2017 and early 2018. These three epochs are shown in the inset of the main graphic.
The rectangle (fixed in space) highlights the motion of the explosion's blast wave, which is located near one of the fingertips. This feature is moving at almost 9 million miles per hour. The fixed squares enclose clumps of magnesium and neon that likely formed in the star before it exploded and shot into space once the star blew up. Some of this explosion debris is moving at even faster speeds of more than 11 million miles per hour. A color version of the 2018 image shows the fingers in blue and green and the clumps of magnesium and neon in red and yellow.
While these are startling high speeds, they actually represent a slowing down of the remnant. Researchers estimate that to reach the farthest edge of RCW 89, material would have to travel on average at almost 30 million miles per hour. This estimate is based on the age of the supernova remnant and the distance between the center of the explosion and RCW 89. This difference in speed implies that the material has passed through a low-density cavity of gas and then been significantly decelerated by running into RCW 89.
The exploded star likely lost part or all of its outer layer of hydrogen gas in a wind, forming such a cavity, before exploding, as did the star that exploded to form the well-known supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A), which is much younger at an age of about 350 years. About 30% of massive stars that collapse to form supernovas are of this type. The clumps of debris seen in the 1,700-year-old supernova remnant could be older versions of those seen in Cas A at optical wavelengths in terms of their initial speeds and densities. This means that these two objects may have the same underlying source for their explosions, which is likely related to how stars with stripped hydrogen layers explode. However, astronomers do not understand the details of this yet and will continue to study this possibility.
A paper describing these results appeared in the June 1, 2020, issue of The Astrophysical Journal Letters, and a preprint is available online. The authors of the study are Kazimierz Borkowski, Stephen Reynolds, and William Miltich, all of North Carolina State University in Raleigh.
INFORMATION:
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science from Cambridge Massachusetts and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-24
INDIANAPOLIS -- A new study demonstrates that many younger adult dental patients are taking medications and highlights the importance of dental providers reviewing medication histories regardless of age.
The study from Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University School of Dentistry looked at dental records from 11,220 dental patients over the age of 18. The results showed:
53 percent of all patients reported taking at least one medication
12 percent of those age 18-24 were taking at least one medication
20 percent of those age 25-34 were taking at least one ...
2021-06-24
In a study in Nature Plants, Yiping Qi, associate professor of Plant Science at the University of Maryland (UMD), introduces a new and improved CRISPR 3.0 system in plants, focusing on gene activation instead of traditional gene editing. This third generation CRISPR system focuses on multiplexed gene activation, meaning that it can boost the function of multiple genes simultaneously. According to the researchers, this system boasts four to six times the activation capacity of current state-of-the-art CRISPR technology, demonstrating high accuracy and efficiency in up to seven genes at once. While CRISPR is more often known for its gene editing capabilities that can knock out genes that are undesirable, activating genes to gain functionality is essential to creating better plants ...
2021-06-24
LA JOLLA--(June 24, 2021) When looking at a complex landscape, the eye needs to focus in on important details without losing the big picture--a charging lion in a jungle, for example. Now, a new study by Salk scientists shows how inhibitory neurons play a critical role in this process.
The study, published May 25, 2021, in the journal Cell Reports, shows that inhibitory neurons do more than just inhibit neuron activity like an off-switch; paradoxically, they actually increase the amount of information transmitted through the nervous system when it needs to be flexible. To make this possible, inhibitory neurons need to be integrated into the circuit in a specific way. These observations could help scientists better understand and treat disorders involving our ability to focus and modulate ...
2021-06-24
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- It can be difficult to get young kids to eat enough vegetables, but a new Penn State study found that simply adding more veggies to their plates resulted in children consuming more vegetables at the meal.
The researchers found that when they doubled the amount of corn and broccoli served at a meal -- from 60 to 120 grams -- the children ate 68% more of the veggies, or an additional 21 grams. Seasoning the vegetables with butter and salt, however, did not affect consumption.
The daily recommended amount of vegetables for kids is ...
2021-06-24
Rude behavior at work has come to be expected, like donuts in the breakroom. Two decades of research on employee relationships shows that 98 percent of employees experience rude behavior at work, but now a new study suggests a large majority of workplace relationships are not characterized by rudeness. Isolated incidents of rude behavior at work, although somewhat common, do not point to widespread incivility between employees and their colleagues, according to a new UCF study.
"Because prior research suggests workplace mistreatment is harmful and widespread, it is often called an epidemic, but our findings show that rude behavior is less like the flu and more like cholera," says Shannon Taylor, an associate professor of management and co-author of the ...
2021-06-24
Berlin and Bath, 24th June 2021 - Precision-fermentation company Formo and the University of Bath co-published the first large-scale study of consumer acceptance for animal-free dairy products.
Researchers surveyed 5,054 individuals from Brazil, Germany, India, the UK, and the USA to understand what consumers think of animal-free dairy products.
Precision fermentation is a process that allows specific proteins to be produced via microorganisms. By inserting a copied stretch of cow DNA, microorganisms produce milk proteins. The process is more efficient than using animals to make proteins and avoids the negative side effects of industrial animal agriculture, which is responsible for 18% of all greenhouse gas emissions.
The findings of the study, published in ...
2021-06-24
Leukemia is a group of blood cancers that affects thousands of people worldwide. However, with advances in medicine, several different types of leukemia can be effectively treated with donor stem cells through allogenic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT). One such type of leukemia is B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), which is caused by uncontrolled proliferation and prolonged existence of cancerous B-cells. While allo-SCT can 'cure' B-ALL in several cases, there are also cases of failure, characterized by deterioration in health after a period ...
2021-06-24
The brain is not a passive recipient of injury or disease. Research has shown that when neurons die and disrupt the natural flow of information they maintain with other neurons, the brain compensates by redirecting communications through other neuronal networks. This adjustment or rewiring continues until the damage goes beyond compensation.
This process of adjustment, a result of the brain's plasticity, or its ability to change or reorganize neural networks, occurs in neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease (HD). As the conditions progress, many genes change the way they are normally expressed, turning some genes up and others down. The challenge for researchers like Dr. Juan Botas ...
2021-06-24
The central goal of cloud computing is to provide fast, easy-to-use computing and data storage services at a low cost. However, the cloud environment comes with data confidentiality risks attached.
Cryptography is the primary tool used to enhance the security of cloud computing. This mathematical technique protects the stored or transmitted data by encrypting it, so that it can only be understood by intended recipients. While there are many different encryption techniques, none are completely secure, and the search continues for new technologies that can counter the rising threats to data privacy and security.
In a recent study published in KeAi's International Journal of Intelligent Networks, a team of researchers from India and Yemen describe a novel, two-step cryptography ...
2021-06-24
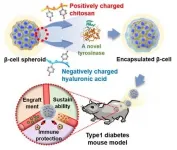
A research team, led by Prof. Nathaniel S. Hwang and Prof. Byung-gee Kim, from Seoul National University (SNU) and Prof. Dong Yun Lee, from Hanyang University, has used enzymatic crosslinking to create nanofilms on cell surfaces. SNU has announced that it has developed a "cell caging" technology for the applications in cell-based therapies. The "cell caging" technique can prevent immune rejection during heterologous islet cell transplantation, facilitate smooth cell insulin secretion, and treat type 1 diabetic patients without immunosuppressants.
The research team succeeded in producing a nanofilm by using the electrostatic force to stack chitosan, which is a biological polymer, and hyaluronic acid in that order. To overcome the shortcomings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cosmic hand hitting a wall