Stopping the onset and progression of intractable immune diseases
2021-06-25
(Press-News.org) The development of therapeutic drugs for inflammatory bowel disease, an intractable immune disease, and multiple sclerosis - an autoimmune disorder - is gaining traction. A research team from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH and a joint research team at ImmunoBiome Inc. have uncovered that a yeast-derived polysaccharide mixture inhibits the onset and progression of immune disorders.
The number of cases of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis - both inflammatory bowel diseases - in Korea was about 18,000 and 37,000 respectively as of 2019, increasing about 2.3 times over the past decade. Multiple sclerosis is a rare and incurable disease that affects about 2,500 patients in Korea. Both diseases are intractable inflammatory diseases caused by abnormalities in the human immune system. The exact cause of the inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis is still unknown but it is presumed that environmental and genetic factors play a role.
Various immune cells such as monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells are involved in the onset and development of these diseases, but T cells in particular play a pivotal role. Currently, agents that suppress the overall inflammatory response are used in clinical practice, but this method has major side effects including vulnerability to infections and there are no clear effective treatments as of now.
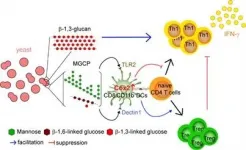
To this, the POSTECH researchers and the joint research team from ImmunoBiome Inc. focused on the microbiome and the active substances derived from them, which have a big impact on the development and regulation of the immune system. The joint research team isolated specific polysaccharides from yeast - one of the symbiotic microorganisms in the human body - and first observed their anti-inflammatory effects. Then, using high-performance liquid chromatography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques, the researchers identified the constituents and chemical structures of the polysaccharides and named it MGCP (Mannan/β-1,6-Glucan-containing polysaccharides).
Using a mouse model for inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis, MGCP-administered mice suppressed the generation of inflammatory cells, which are T helper type 1 cells (Th1 cells). On the other hand, it selectively inhibited the progression of inflammatory diseases by inducing the generation of regulatory T cells (Regulatory T cells, hereinafter Treg cells) with anti-inflammatory function. The researchers additionally confirmed that the mechanism of action of the immunosuppressive response by MGCP is mediated by TLR2 and Dectin1, which are the two different innate immune receptors expressed in dendritic cells.
This study also presents a clear solution to an unsolved immunological question about beta-glucan (β-glucan), which is known to suppress hypersensitivity while inducing immune enhancement at the same time. The research team has uncovered that the immune response enhancing effect of β-glucan identified so far is due to β-1,3-glucan, and found that β-1,6-glucan that makes up the MGCP has a hypersensitivity immunosuppressive effect. These findings show that β-glucan of a specific structure is applicable as an immune enhancing or anti-inflammatory response inducer. These active substances show promise to be developed into the next-generation microbiome treatment.
This study revealed that the immunological efficacy is determined by the chemical structure of the obscure polysaccharide, which was largely unknown. It is significant that a novel polysaccharide MGCP that effectively inhibits inflammatory diseases has been discovered. "We have successfully demonstrated that MGCP can selectively suppress inflammatory T-cells," explained Professor Sin-Hyeog Im. "This will help to provide a great turning point for a new anti-inflammatory treatment with no side effects that can selectively suppress the inflammatory response."
The findings from this research were published online in the June 14 issue of Nature Communications.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-25
With a goal of breeding resilient crops that are better able to withstand drought and disease, University of California San Diego scientists have developed the first CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive in plants.
While gene drive technology has been developed in insects to help stop the spread of vector-borne diseases such as malaria, researchers in Professor Yunde Zhao's lab, along with colleagues at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, demonstrated the successful design of a CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive that cuts and copies genetic elements in Arabidopsis plants.
Breaking ...
2021-06-25
Tsukuba, Japan - The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the way people eat, work, shop and go to school. Now, researchers from Japan have found surprising differences in the way people use healthcare services--including house calls from doctors.
In a study published this month in BMC Emergency Medicine, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that patterns in illness type and severity did change during the pandemic--with unexpected trends that may tell us about how people use health care services when personal contact carries inherent risk.
In Tokyo, private after-hours house call services (AHHC) provide in-home medical service outside of regular ...
2021-06-25
Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles only a few nanometers across that, thanks to their small size, exhibit peculiar optical and electronic properties due to quantum mechanics. With existing and foreseen applications in screens, lighting, lasers, and energy harvesting, research in quantum dots has been steadily progressing. In particular, colloidal QDs (CQDs) have been in the nanotechnology spotlight for over a decade.
CQDs are semiconductor nanocrystals that can be produced easily from solution-based processes, which make them suitable for mass production. However, for CQD-based devices to operate at their best, the quantum dots should be monodisperse--that is, ...
2021-06-25
The contemporary materials industry raises the problem of creating a microscopic theory that allows to describe the observed physicochemical properties of a wide class of substances which are in demand in modern industry, medicine, and agriculture. A general and consistent theory will help to obtain reliable information from experimental data on the structure of matter, existing interactions and dynamic processes occurring in it, which can help in the synthesis and quality control of prospective materials.
The study of the molecular structure of a substance and its intermolecular interactions is one of the most important and interesting tasks facing modern science. Of particular ...
2021-06-25
Medical materials that can be inserted into the human body have been used for decades in the field of regenerative medicine - for example, stents that can help dilate clogged blood vessels and implants that can replace teeth or bones. The prolonged use of these materials can result in serious adverse effects and loss of various functions - for example, inflammatory responses, generation of fibrous tissues around the material, and generation of blood clots that block blood vessels.
Recently, a Korean research team has drawn attention for developing a technology to reduce ...
2021-06-25
Curtin University research has found tiny amounts of gold can be trapped inside pyrite, commonly known as 'fool's gold', which would make it much more valuable than its name suggests.
This study, published in the journal Geology in collaboration with the University of Western Australia and the China University of Geoscience, provides an in-depth analysis to better understand the mineralogical location of the trapped gold in pyrite, which may lead to more environmentally friendly gold extraction methods.
Lead researcher Dr Denis Fougerouse from Curtin's School of Earth and Planetary Sciences ...
2021-06-25
Effective diagnostics, therapies and treatments for diseases and infections could increasingly involve re-engineering the body's internal biomechanisms at their most basic chemical and molecular foundations.
Growing knowledge about the body's biological processes is increasing the possibilities for restoring human health, says Xiao Wang, an associate professor of biomedical engineering in Arizona State University's Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering. He and a team of researchers are exploring ways to trigger and control cell differentiation and transition to unlock properties that may change bioengineers' approach to diagnostics, ...
2021-06-25
PITTSBURGH, June 25, 2021 - It is widely assumed that Americans' sexual activity took a nosedive during the early chaotic months of the coronavirus pandemic. But a new study from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine challenges this popular narrative.
In a research letter published in the Journal of Internal Medicine, scientists from Pitt and UPMC found that some people were having more sex during the pandemic than ever before. That group? Older men with erectile dysfunction.
"People's sexual lives contribute to the psychosocial fabric of society," said senior author Benjamin Davies, M.D., director of the Urologic Oncology Program at ...
2021-06-25
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Wavsens LLC have developed a method for using radio signals to create real-time images and videos of hidden and moving objects, which could help firefighters find escape routes or victims inside buildings filled with fire and smoke. The technique could also help track hypersonic objects such as missiles and space debris.
The new method, described in Nature Communications, could provide critical information to help reduce deaths and injuries. Locating and tracking first responders indoors is a prime goal for the public safety ...
2021-06-25
A new University of Liverpool study could help scientists mitigate the future spread of zoonotic and livestock diseases caused by existing viruses.
Researchers have used a form or artificial intelligence (AI) called machine-learning to predict more than 20,000 unknown associations between known viruses and susceptible mammalian species. The findings, which are published in Nature Communications, could be used to help target disease surveillance programmes.
Thousands of viruses are known to affect mammals, with recent estimates indicating that less than 1% of mammalian viral diversity has been discovered to date. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Stopping the onset and progression of intractable immune diseases