Throwing an 'axion bomb' into a black hole challenges fundamental law of physics
2021-06-25
(Press-News.org) Singularities such as those at the centre of black holes, where density becomes infinite, are often said to be places where physics 'breaks down'. However, this doesn't mean that 'anything' could happen, and physicists are interested in which laws could break down, and how.
Now, a research team from Imperial College London and the Cockcroft Institute and Lancaster University have proposed a way that singularities could violate the law of conservation of charge. Their theory is published in Annalen der Physik.
Co-author Professor Martin McCall, from the Department of Physics at Imperial, said: "'Physics breaks down at a singularity' is one of the most famous statements in pop-physics. But by showing how this might actually happen, we take aim at one of the most cherished laws of physics: the conservation of charge."
The conservation of charge says that the total electric charge of any isolated system - including the Universe as a whole - never changes. This means that if negatively or positively charged particles move into one area, the same amount of respectively charged particles must move out.
This has been shown at the very smallest scales: when different particles are created or eliminated in experiments such as the Large Hadron Collider, the same amount of negatively and positively charged particles are always produced or destroyed, respectively.
Now, by modifying classic physics equations to include axions, a candidate for dark matter, the team have been able to show that temporary singularities - such as black holes that appear and then later evaporate - could destroy charge when they come to the end of their life.
Axions are hypothetical particles that may explain dark matter - the 'missing' 85 percent of the matter of the Universe. Their predicted properties could form a field that would interact with the kind of fields physicists have known about for centuries - electromagnetic fields, which are described by a set of equations called Maxwell's equations.
Using a branch of mathematics called differential geometry, the team found out how to create or destroy charge, violating the charge conservation of the Universe.
Co-author Jonathan Gratus said: "You can imagine creating an 'axion bomb' that holds charge by combining coupled axion and magnetic fields; and then dropping it into an evaporating black hole. As the construction shrinks and disappears into the singularity, it takes electrical charge with it. It is the combination of a temporary singularity and a newly proposed type of axion field that is crucial to its success."
Co-author Dr Paul Kinsler, from the Department of Physics at Imperial, said: "There are also philosophical implications. Although people often like to say that physics 'breaks down', here we show that although exotic phenomena might occur, what actually happens is nevertheless constrained by the still-working laws of physics around the singularity."
The team say the axion phenomenon would only occur under extreme conditions that currently cannot be created in a lab, but that future advances in intense laser fields might allow the theory to be tested in a terrestrial environment.
INFORMATION:
'Temporary Singularities and Axions: An Analytic Solution that Challenges Charge Conservation' by Jonathan Gratus, Paul Kinsler and Martin W. McCall is published in Annalen der Physik.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-25
To make computer chips, technologists around the world rely on atomic layer deposition (ALD), which can create films as fine as one atom thick. Businesses commonly use ALD to make semiconductor devices, but it also has applications in solar cells, lithium batteries and other energy-related fields.
Today, manufacturers increasingly rely on ALD to make new types of films, but figuring out how to tweak the process for each new material takes time.
Part of the problem is that researchers primarily use trial and error to identify optimal growth conditions. But a recently published study -- one of the first in this scientific field -- suggests that using artificial intelligence (AI) can be more efficient.
In the ACS Applied ...
2021-06-25
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Like two superheroes finally joining forces, Sandia National Laboratories' Z machine -- generator of the world's most powerful electrical pulses -- and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's National Ignition Facility -- the planet's most energetic laser source -- in a series of 10 experiments have detailed the responses of gold and platinum at pressures so extreme that their atomic structures momentarily distorted like images in a fun-house mirror.
Similar high-pressure changes induced in other settings have produced oddities like hydrogen appearing as a metallic fluid, helium in the form of rain and sodium a transparent metal. But until now there has been no way to accurately calibrate these pressures and responses, the first step to ...
2021-06-25
Tsukuba, Japan - Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) are widely used in display technology and are also being investigated for lighting applications. A comprehensive understanding of these devices is therefore important if their properties are to be harnessed to their full potential. Researchers from the University of Tsukuba have directly observed the photoexcited electron dynamics in an organic film using time-resolved photoelectron emission microscopy. Their findings are published in Advanced Optical Materials .
OLED displays are popular because they are bright, lightweight, and do not consume a lot of power. Their output is generated when an exciton--a combination of an electron and an electron hole--releases its energy. However, this ...
2021-06-25
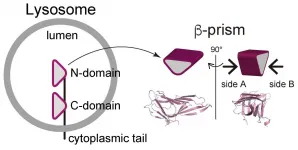
Tokyo, Japan - A cell is composed of numerous organelles, each with a unique role that helps contribute to its overall functionality. The lysosome is an organelle that contains digestive enzymes and functions as a molecular garbage disposal and recycling center. Since the role of lysosome is crucial to maintain the cellular homeostasis, the lysosomal dysfunction causes neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases, cancer, as well as lysosomal storage disorders.
In a new article published in Autophagy, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) performed a novel type of structural analysis to demonstrate how a certain molecular interaction is crucial for one lysosomal membrane protein to perform effectively.
LAMP1 (lysosomal-associated ...
2021-06-25
LA JOLLA, CA--Chemists at Scripps Research have solved a long-standing problem in their field by developing a method for making a highly useful and previously very challenging type of modification to organic molecules. The breakthrough eases the process of modifying a variety of existing molecules for valuable applications such as improving the potency and duration of drugs.
The flexible new method, for "directed C--H hydroxylation with molecular oxygen," does what only natural enzymes have been able to do until now. It's described in a paper this week in Science.
"We ...
2021-06-25
James Cook University scientists in Australia believe they have made a breakthrough in the science of keeping premature babies alive.
As part of her PhD work, JCU engineering lecturer Stephanie Baker led a pilot study that used a hybrid neural network to accurately predict how much risk individual premature babies face.
She said complications resulting from premature birth are the leading cause of death in children under five and over 50 per cent of neonatal deaths occur in preterm infants.
"Preterm birth rates are increasing almost everywhere. In neonatal intensive care units, assessment of mortality risk assists in making difficult decisions regarding which treatments should be used and if and when treatments are working effectively," said Ms Baker. ...
2021-06-25
RICHLAND, Wash.--Earth bears many signs of human influence, from warming that exceeds pre-industrial temperatures to a rising sea. Add to that list, now, the human influence on the timing of Earth's water cycle, revealed by a new study led by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
The research, published this week in the journal Nature Climate Change, peels back layers of climatological noise to uncover a clear signal: from 1979 to 2019, increases in greenhouse gases and reductions in human-generated aerosols triggered an approximate four-day delay in seasonal rainfall over tropical land and the Sahel. The lag could mean delayed crop production, ...
2021-06-25
We can generally recognize an object, even if it is presented for a very brief time. However, if another object appears immediately following the first object, the perception on the first object is impaired such that we do not notice its existence. This perceptual phenomenon, called "visual backward masking," is used in vision science to study how visual perception is processed in the brain. Interestingly, this phenomenon occurs even if the second object does not spatially overlap the first object, such as a contour or four dots surrounding the object.
The occurrence of this phenomenon is assumed to be due to a disruption of "feedback processing." When we see something, visual ...
2021-06-25
In 2021 Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is celebrating its 10th anniversary. The journal was founded with the goal of creating a global high-level forum centred around drug discovery and pharmaceutical research/application. APSB was included by Chemical Abstracts in 2011, accepted by PubMed Central in 2015, indexed by Science Citation Index in 2017 and has evolved to become one of the most important international journals in the field of pharmaceutical sciences.
Volume 11, issue 6 is a special issue marking the beginning of a series of celebratory events ...
2021-06-25
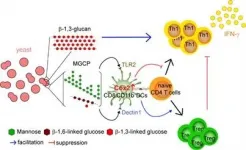
The development of therapeutic drugs for inflammatory bowel disease, an intractable immune disease, and multiple sclerosis - an autoimmune disorder - is gaining traction. A research team from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH and a joint research team at ImmunoBiome Inc. have uncovered that a yeast-derived polysaccharide mixture inhibits the onset and progression of immune disorders.
The number of cases of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis - both inflammatory bowel diseases - in Korea was about 18,000 and 37,000 respectively as of 2019, increasing about 2.3 times ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Throwing an 'axion bomb' into a black hole challenges fundamental law of physics