Lighting the LAMP to reveal mystery of lysosomes
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use expanded genetic code technologies to uncover the structural aspect of how one protein functions in lysosomes for intracellular clearance
2021-06-25
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - A cell is composed of numerous organelles, each with a unique role that helps contribute to its overall functionality. The lysosome is an organelle that contains digestive enzymes and functions as a molecular garbage disposal and recycling center. Since the role of lysosome is crucial to maintain the cellular homeostasis, the lysosomal dysfunction causes neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases, cancer, as well as lysosomal storage disorders.
In a new article published in Autophagy, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) performed a novel type of structural analysis to demonstrate how a certain molecular interaction is crucial for one lysosomal membrane protein to perform effectively.
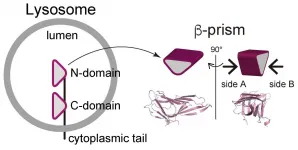
LAMP1 (lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1) and LAMP2 the most abundant protein components of lysosome membranes. Both LAMP1 and LAMP2 are composed of a large lumenal domain, a transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal cytoplasmic tail (Fig. 1). The lumenal domains of LAMPs are composed of two domains (N-domain and C-domain, which are membrane-distal and -proximal, respectively). Each domain has the unique ?-prims fold structure (a triangular prism). On the other hand, genetic experiments have shown that mice embryos without both LAMP-1 and 2 die a little more than two weeks after fertilization. Mice without LAMP-1 are born and can thrive, while those without LAMP-2 often die a few weeks after birth, suggesting that LAMP-2 is more important for lysosome activity. The research of the TMDU group further investigates this protein's biological role.
"Mice lacking LAMP-2 also display issues with autophagy progression," says one of the lead authors of the study Kazue Terasawa. "Expanding our knowledge of how LAMP-2 interacts and operates at the molecular level will ultimately help us understand autophagy better."
The researchers demonstrated LAMP2 molecules assemble by facing each other with one side the ?-prism (defined as side A, as shown in Fig. 1) of the C-domain (Fig. 2). The N-domain truncation permitted the nonspecific involvement of both sides of the ?-prims (side A and side B). In combination with some biochemical studies, "we believe that the homophilic interaction we demonstrated is crucial for function of LAMP-2, via ensuring a proper arrangement of the cytoplasmic tails, which is crucial for the function of LAMP2, on the lysosome membrane," says Miki Hara-Yokoyama, senior author.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Direct homophilic interaction of LAMP-2A with the two-domain architecture revealed by site-directed photo-crosslinks and steric hindrances in mammalian cells," was published in Autophagy at DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1911017
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-25
LA JOLLA, CA--Chemists at Scripps Research have solved a long-standing problem in their field by developing a method for making a highly useful and previously very challenging type of modification to organic molecules. The breakthrough eases the process of modifying a variety of existing molecules for valuable applications such as improving the potency and duration of drugs.
The flexible new method, for "directed C--H hydroxylation with molecular oxygen," does what only natural enzymes have been able to do until now. It's described in a paper this week in Science.
"We ...
2021-06-25
James Cook University scientists in Australia believe they have made a breakthrough in the science of keeping premature babies alive.
As part of her PhD work, JCU engineering lecturer Stephanie Baker led a pilot study that used a hybrid neural network to accurately predict how much risk individual premature babies face.
She said complications resulting from premature birth are the leading cause of death in children under five and over 50 per cent of neonatal deaths occur in preterm infants.
"Preterm birth rates are increasing almost everywhere. In neonatal intensive care units, assessment of mortality risk assists in making difficult decisions regarding which treatments should be used and if and when treatments are working effectively," said Ms Baker. ...
2021-06-25
RICHLAND, Wash.--Earth bears many signs of human influence, from warming that exceeds pre-industrial temperatures to a rising sea. Add to that list, now, the human influence on the timing of Earth's water cycle, revealed by a new study led by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
The research, published this week in the journal Nature Climate Change, peels back layers of climatological noise to uncover a clear signal: from 1979 to 2019, increases in greenhouse gases and reductions in human-generated aerosols triggered an approximate four-day delay in seasonal rainfall over tropical land and the Sahel. The lag could mean delayed crop production, ...
2021-06-25
We can generally recognize an object, even if it is presented for a very brief time. However, if another object appears immediately following the first object, the perception on the first object is impaired such that we do not notice its existence. This perceptual phenomenon, called "visual backward masking," is used in vision science to study how visual perception is processed in the brain. Interestingly, this phenomenon occurs even if the second object does not spatially overlap the first object, such as a contour or four dots surrounding the object.
The occurrence of this phenomenon is assumed to be due to a disruption of "feedback processing." When we see something, visual ...
2021-06-25
In 2021 Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is celebrating its 10th anniversary. The journal was founded with the goal of creating a global high-level forum centred around drug discovery and pharmaceutical research/application. APSB was included by Chemical Abstracts in 2011, accepted by PubMed Central in 2015, indexed by Science Citation Index in 2017 and has evolved to become one of the most important international journals in the field of pharmaceutical sciences.
Volume 11, issue 6 is a special issue marking the beginning of a series of celebratory events ...
2021-06-25
The development of therapeutic drugs for inflammatory bowel disease, an intractable immune disease, and multiple sclerosis - an autoimmune disorder - is gaining traction. A research team from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH and a joint research team at ImmunoBiome Inc. have uncovered that a yeast-derived polysaccharide mixture inhibits the onset and progression of immune disorders.
The number of cases of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis - both inflammatory bowel diseases - in Korea was about 18,000 and 37,000 respectively as of 2019, increasing about 2.3 times ...
2021-06-25
With a goal of breeding resilient crops that are better able to withstand drought and disease, University of California San Diego scientists have developed the first CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive in plants.
While gene drive technology has been developed in insects to help stop the spread of vector-borne diseases such as malaria, researchers in Professor Yunde Zhao's lab, along with colleagues at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, demonstrated the successful design of a CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive that cuts and copies genetic elements in Arabidopsis plants.
Breaking ...
2021-06-25
Tsukuba, Japan - The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the way people eat, work, shop and go to school. Now, researchers from Japan have found surprising differences in the way people use healthcare services--including house calls from doctors.
In a study published this month in BMC Emergency Medicine, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that patterns in illness type and severity did change during the pandemic--with unexpected trends that may tell us about how people use health care services when personal contact carries inherent risk.
In Tokyo, private after-hours house call services (AHHC) provide in-home medical service outside of regular ...
2021-06-25
Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles only a few nanometers across that, thanks to their small size, exhibit peculiar optical and electronic properties due to quantum mechanics. With existing and foreseen applications in screens, lighting, lasers, and energy harvesting, research in quantum dots has been steadily progressing. In particular, colloidal QDs (CQDs) have been in the nanotechnology spotlight for over a decade.
CQDs are semiconductor nanocrystals that can be produced easily from solution-based processes, which make them suitable for mass production. However, for CQD-based devices to operate at their best, the quantum dots should be monodisperse--that is, ...
2021-06-25
The contemporary materials industry raises the problem of creating a microscopic theory that allows to describe the observed physicochemical properties of a wide class of substances which are in demand in modern industry, medicine, and agriculture. A general and consistent theory will help to obtain reliable information from experimental data on the structure of matter, existing interactions and dynamic processes occurring in it, which can help in the synthesis and quality control of prospective materials.
The study of the molecular structure of a substance and its intermolecular interactions is one of the most important and interesting tasks facing modern science. Of particular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lighting the LAMP to reveal mystery of lysosomes
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use expanded genetic code technologies to uncover the structural aspect of how one protein functions in lysosomes for intracellular clearance