(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (June 28, 2021) - Rice University computer scientists are sending RAMBO to rescue genomic researchers who sometimes wait days or weeks for search results from enormous DNA databases.
DNA sequencing is so popular, genomic datasets are doubling in size every two years, and the tools to search the data haven't kept pace. Researchers who compare DNA across genomes or study the evolution of organisms like the virus that causes COVID-19 often wait weeks for software to index large, "metagenomic" databases, which get bigger every month and are now measured in petabytes.
RAMBO, which is short for "repeated and merged bloom filter," is a new method that can cut indexing times for such databases from weeks to hours and search times from hours to seconds. Rice University computer scientists presented RAMBO last week at the Association for Computing Machinery data science conference SIGMOD 2021.
"Querying millions of DNA sequences against a large database with traditional approaches can take several hours on a large compute cluster and can take several weeks on a single server," said RAMBO co-creator Todd Treangen, a Rice computer scientist whose lab specializes in metagenomics. "Reducing database indexing times, in addition to query times, is crucially important as the size of genomic databases are continuing to grow at an incredible pace."
To solve the problem, Treangen teamed with Rice computer scientist Anshumali Shrivastava, who specializes in creating algorithms that make big data and machine learning faster and more scalable, and graduate students Gaurav Gupta and Minghao Yan, co-lead authors of the peer-reviewed conference paper on RAMBO.
RAMBO uses a data structure that has a significantly faster query time than state-of-the-art genome indexing methods as well as other advantages like ease of parallelization, a zero false-negative rate and a low false-positive rate.
"The search time of RAMBO is up to 35 times faster than existing methods," said Gupta, a doctoral student in electrical and computer engineering. In experiments using a 170-terabyte dataset of microbial genomes, Gupta said RAMBO reduced indexing times from "six weeks on a sophisticated, dedicated cluster to nine hours on a shared commodity cluster."
Yan, a Ph.D student in computer science, said, "On this huge archive, RAMBO can search for a gene sequence in a couple of milliseconds, even sub-milliseconds using a standard server of 100 machines."
RAMBO improves on the performance of Bloom filters, a half-century-old search technique that has been applied to genomic sequence search in a number of previous studies. RAMBO improves on earlier Bloom filter methods for genomic search by employing a probabilistic data structure known as a count-min sketch that "leads to a better query time and memory trade-off" than earlier methods, and "beats the current baselines by achieving a very robust, low-memory and ultrafast indexing data structure," the authors wrote in the study.
Gupta and Yan said RAMBO has the potential to democratize genomic search by making it possible for almost any lab to quickly and inexpensively search huge genomic archives with off-the-shelf computers.
"RAMBO could decrease the wait time for tons of investigations in bioinformatics, such as searching for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater metagenomes across the globe," Yan said. "RAMBO could become instrumental in the study of cancer genomics and bacterial genome evolution, for example."
INFORMATION:
Shrivastava is an associate professor of computer science and Treangen is an assistant professor of computer science.
Additional study co-authors include Benjamin Coleman, Bryce Kille, Leo Elworth and Tharun Medini.
The research was funded by that National Science Foundation, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Office of Naval Research.
DOI: 10.1145/3448016.3457333
Read the paper at: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3448016.3457333
High-resolution IMAGES are available for download at:
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/06/0628_SIGMOD-gg-lg.jpg
CAPTION: Gaurav Gupta (Photo courtesy G. Gupta/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/06/0628_SIGMOD-my-lg.jpg
CAPTION: Minghao Yan (Photo by Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
This release can be found online at news.rice.edu.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
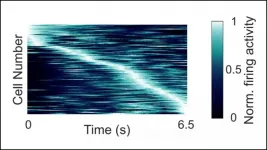
Neurons in the hippocampus fire during specific moments in time, according to research recently published in JNeurosci. The cells may contribute to memory by encoding information about the time and order of events.
Episodic memories involve remembering the "what, where, and when" of past experiences. The "where" may be encoded by place cells in the hippocampus, which fire in response to specific locations. Rodents have hippocampal neurons that fire in response to specific moments in time -- the "when" -- but until recently it was not known if the human brain contained them too.
Reddy et al. recorded the electrical activity of neurons in the hippocampus of epilepsy patients undergoing diagnostic invasive monitoring ...
In cancer therapy, the effectiveness of an approach is determined by its ability to preserve the non-cancerous cells. Simply put, the higher the collateral damage, the greater are the side-effects of a therapy. An ideal situation is where only the cancer cells can be targeted and destroyed. In this regard, photothermal therapy--an approach in which cancer cells infused with gold nanoparticles can be heated up and destroyed using near-infrared (NIR) light that is strongly absorbed by the gold nanoparticles--has emerged as a promising strategy due to its minimally invasive nature.
"Because NIR light is able to penetrate biological tissues, it can illuminate ...
The Structural Bioinformatics and Network Biology laboratory, led by ICREA Researcher Dr. Patrick Aloy, has completed the bioactivity information for a million molecules using deep machine-learning computational models. It has also disclosed a tool to predict the biological activity of any molecule, even when no experimental data are available.
This new methodology is based on the Chemical Checker, the largest database of bioactivity profiles for pseudo pharmaceuticals to date, developed by the same laboratory and published in 2020. The Chemical Checker collects information from 25 spaces of bioactivity for each molecule. These spaces are linked to the chemical structure of the molecule, the targets with which it interacts or the changes ...
For the first time, scientists from the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK) partner site in Essen/Düsseldorf have discovered stem cells of the hematopoietic system in glioblastomas, the most aggressive form of brain tumor. These hematopoietic stem cells promote division of the cancer cells and at the same time suppress the immune response against the tumor. This surprising discovery might open up new possibilities for developing more effective immunotherapies against these malignant brain tumors.
The DKTK is a consortium centered around the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Heidelberg, which has long-term collaborative partnerships with specialist oncological centers at universities across Germany.
Glioblastomas ...
Metabolic activators were found to reduce recovery time by as many as 3.5 days in patients with mild-to-moderate Covid-19, according to a Swedish-British study published today in Advanced Science.
The researchers also found that treatment with the metabolic activators improved liver health and decreased the levels of inflammation, as shown by inflammatory markers.
Conducted by researchers at Science for Life Laboratory at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, in collaboration with the Sahlgrenska Academy in Gothenburg and King's College, London, the ...
Want to have a happy relationship? Make sure both partners feel they can decide on issues that are important to them. Objective power measured by income, for example, doesn't seem to play a big role, according to a new study in the "Journal of Social and Personal relationships" by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Bamberg. Instead, how lovers perceive power dynamics in their relationship is most important for relationship satisfaction.
Power is about being able to influence people and successfully resist the attempts of others to influence you. "It sounds like a dog-eat-dog world or the world of business. ...
The examined tissue does not need to be marked for this. The analysis only takes around half an hour. "This is a major step that shows that infrared imaging can be a promising methodology in future diagnostic testing and treatment prediction," says Professor Klaus Gerwert, director of PRODI. The study is published in the American Journal of Pathology on 1 July 2021.
Treatment decision by means of a genetic mutation analysis
Lung tumours are divided into various types, such as small cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Many rare tumour types and sub-types also exist. This diversity hampers reliable rapid diagnostic methods in everyday clinical ...
There are spiders that eat snakes. Observations of snake-eating spiders have been reported around the world. Two researchers from Basel and the US consolidated and analyzed over 300 reports of this unusual predation strategy.
Spiders are primarily insectivores, but they occasionally expand their menu by catching and eating small snakes. Dr. Martin Nyffeler, arachnologist at the University of Basel, and American herpetologist Professor Whitfield Gibbons of the University of Georgia, USA, got to the bottom of this phenomenon in a meta-analysis. Their findings from ...
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this article the authors Chunxiong Zheng, Mingqiang Li and Jianxun Ding from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China and Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Changchun, China discuss the challenges and opportunities of nanomedicines in clinical translation.
Researchers are rapidly gaining a much deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities of nanomedicines allowing for improvements in disease treatment and improved patient survival.
Deep exploration of the connections between preclinical and clinical ...
In March 2020, daily life in the United States changed in an instant as the country locked down to deal with the initial wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. New research reveals how residents in one community returned to their routines as the restrictions lifted, according to a team of Penn State scientists.
"We used sound signals captured by underground fiber-optic sensors to understand how COVID measures impacted human activities," said Junzhu Shen, a graduate student in geosciences at Penn State. "These sensors provide very accurate, high-resolution data that can help us understand what's happening in our communities."
The scientists analyzed sound data recorded from March through June 2020 in and around the Penn State University Park campus and State College, ...