(Press-News.org) The ability to precisely control the various properties of laser light is critical to much of the technology that we use today, from commercial virtual reality (VR) headsets to microscopic imaging for biomedical research. Many of today's laser systems rely on separate, rotating components to control the wavelength, shape and power of a laser beam, making these devices bulky and difficult to maintain.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have developed a single metasurface that can effectively tune the different properties of laser light, including wavelength, without the need of additional optical components. The metasurface can split light into multiple beams and control their shape and intensity in an independent, precise and power-efficient way.
The research opens the door for lightweight and efficient optical systems for a range of applications, from quantum sensing to VR/AR headsets.
"Our approach paves the way to new methods to engineer the emission of optical sources and control multiple functions, such as focusing, holograms, polarization, and beam shaping, in parallel in a single metasurface," said Federico Capasso, the Robert L. Wallace Professor of Applied Physics and Vinton Hayes Senior Research Fellow in Electrical Engineering at SEAS and senior author of the paper.
The research was published recently in Nature Communications.
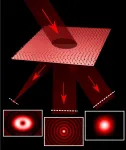
The tunable laser has just two components -- a laser diode and a reflective metasurface. Unlike previous metasurfaces, which relied on a network of individual pillars to control light, this surface uses so-called supercells, groups of pillars which work together to control different aspects of light.
When light from the diode hits the supercells on the metasurface, part of the light is reflected back, creating a laser cavity between the diode and the metasurface. The other part of the light is reflected into a second beam that is independent from the first.
"When light hits the metasurface, different colors are deflected in different directions," said Christina Spägele, a graduate student at SEAS and first author of the paper. "We managed to harness this effect and design it so that only the wavelength that we selected has the correct direction to enter back in the diode, enabling the laser to operate only at that specific wavelength."
To change the wavelength, the researchers simply move the metasurface with respect to the laser diode.
"The design is more compact and simpler than existing wavelength-tunable lasers, since it does not require any rotating component," said Michele Tamagnone, former postdoctoral fellow at SEAS and co-author of the paper.
The researchers also showed that the shape of the laser beam can be fully controlled to project a complex hologram -- in this case the complex, century-old Harvard shield. The team also demonstrated the ability to split the incident light into three independent beams, each with different properties -- a conventional beam, an optical vortex and a beam known as a Bessel beam, which looks like a bullseye and is used in many applications including optical tweezing.
"In addition to controlling any type of laser, this ability to generate multiple beams in parallel and directed at arbitrary angles, each implementing a different function, will enable many applications from scientific instrumentation to augmented or virtual reality and holography," said Capasso.
INFORMATION:
The research was co-authored by Dmitry Kazakov, Marcus Ossiander and Marco Piccardo. It was supported in part by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research grant FA95550-19-1-0135 and the Office of Naval Research MURI grant no. N00014-20-1-2450.
In the context of recent debate over the FDA's approval of aducanumab, it's refreshing to learn about a model of Alzheimer's neurodegeneration that doesn't start with the pathogenic proteins amyloid or Tau.
A new paper in Alzheimer's & Dementia from Emory neuroscientist Shan Ping Yu and colleagues focuses on an unusual member of the family of NMDA receptors, signaling molecules that are critical for learning and memory. Their findings contain leads for additional research on Alzheimer's, including drugs that are already FDA-approved that could be used preventively, and genes ...
Deployable structures -- objects that transition from a compact state to an expanded one -- are used everywhere from backyards to Mars. But as anyone who has ever struggled to open an uncooperative folding chair knows, transforming two-dimensional forms into three-dimensional structures is sometimes a challenge.
Now, researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and the Harvard Graduate School of Design have developed a deployable system that is light, compact, inexpensive, easy to manufacture, and, most importantly, easy to deploy. By harnessing the mechanical instabilities in curved beams, the system can transform objects into elaborate and customizable 3D configurations on a range of scales, from large-scale furniture to small medical ...
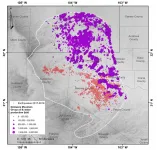
Boulder, Colo., USA: Subsurface carbon sequestration--storing carbon in
rocks deep underground--offers a partial solution for removing carbon from
the atmosphere. Used alongside emissions reductions, geologic carbon
sequestration could help mitigate anthropogenic climate change. But like
other underground operations, it comes with risks--including earthquakes.
Geophysicists are still working to understand what can trigger
human-induced earthquakes, which have been documented since the 1960s. A
new study, published in Geology on Thursday, explores why part of
a heavily produced oilfield in the U.S. has ...
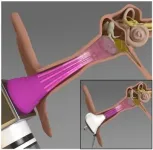
Middle ear infections, also known as otitis media, affect more than 80% of the children in the U.S. In a new study, researchers have designed a miniaturized 3D-printed device to inactivate Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a common bacterium that causes the infection.
The device--a microplasma jet array--generates plasma, which is composed of charged particles and reactive molecules that have been previously shown to inactivate various pathogens. "This is the first time anyone has tried treating middle ear infections using plasma technology," said Jungeun Won, a graduate student in the Boppart lab. "Usually, the treatment involves using ...
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. - According to researchers at Marshall University, a maternal diet rich in Omega-3 fatty acids protects from breast cancer development in offspring. In a new study recently published by Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, researchers noted a significant difference in mice from mothers that were fed a diet rich in canola oil, compared with mothers fed a diet rich in corn oil. A maternal Omega 3-rich diet affected genome-wide epigenetic landscape changes in offspring and potentially modulated gene expression patterns.
Dr. Ata Abbas, a former postdoctoral research fellow in Marshall's Department of Biological Sciences, headed a research team under the leadership ...
New Brunswick, N.J. (June 28, 2021) - A Rutgers-led study sheds new light on the evolution of photosynthesis in plants and algae, which could help to improve crop production.
The paper appears in the journal New Phytologist.
The scientists reviewed research on the photosynthetic amoeba Paulinella, which is a model to explore a fundamental question about eukaryote evolution: why was there a single origin of algae and plants? That is, why did photosynthesis by primary plastid endosymbiosis not originate multiple times in the tree of life?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to synthesize ...
A first-of-its-kind longitudinal study of infant curiosity found that months-old babies most captivated by magic tricks became the most curious toddlers, suggesting a pre-verbal baby's level of interest in surprising aspects of the world remains constant over time and could predict their future cognitive ability.
"Something about a baby's curiosity about magic tricks is predicting how curious they become as preschoolers," said Lisa Feigenson, co-director of the Johns Hopkins University Laboratory for Child Development. "What the data suggest is that some three-year-olds have a leg up or seem particularly well positioned to learn a lot about the world."
The findings appear today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Until this study, little was known about curiosity ...
New Brunswick, N.J. (June 28, 2021) - COVID-19's socio-economic effects will likely cause another severe production crisis in the coffee industry, according to a Rutgers University-led study.
The study, which appears in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, included researchers from the University of Arizona, University of Hawaii at Hilo, CIRAD, Santa Clara University, Purdue University West Lafayette and University of Exeter.
"Any major impacts in the global coffee industry will have serious implications for millions of people across the globe, including the coffee retail ...
An Australian mammal thought to have been wiped out over 150 years ago can now be crossed off our list of extinct animals, following a new study.
Researchers compared DNA samples fromeight extinct Australian rodents, as well as 42 of their living relatives, to look at the decline of native species since the arrival of Europeans in Australia.
The study showed the extinctGould's mouse was indistinguishable from the Shark Bay mouse, still found on several small islands off the coast of Western Australia.
According to lead author Dr Emily Roycroft ...
Scientists have made a breakthrough in understanding the process that leads to a blood clot forming in the lungs - a condition that kills more than two thousand people in the UK each year.
The clot forms a pulmonary embolism or blockage, cutting off blood flow to major blood vessels in the lungs.
In many cases, the blockage is caused by fragments that have broken away from a blood clot elsewhere in the body, such as a deep vein thrombosis in one of the legs. The fragments are transported to the lungs via the blood stream.
In a paper published today (28 June) in the scientific ...