(Press-News.org) Many drivers use tollways to get from point A to point B because they are a faster and more convenient option. The fees associated with these roadways are higher during peak traffic hours of the day, such as during the commute to and from work. With this structure, drivers who are not adding to the heavy flow of traffic do not have to pay higher toll prices. However, those who utilize the toll road during more congested hours pay a premium to use the faster, more convenient highways.
Similarly, not everyone uses the same amount of electricity throughout the day. There are peak load hours that put more strain on the grid, and there are users within those times who use more electricity while there are those who conserve.
Dr. Le Xie, professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and assistant director-energy digitization of the Energy Institute at Texas A&M University, together with two co-authors, is proposing a user-impact tailored rate plan for utility companies to employ that is similar to toll roads. His rate plan will benefit individuals who use less power or utilize solar power to offset some of the strain on the distribution power grid, while those who use an excess of power from the electrical grid during peak times will cover more of the delivery cost.
In a typical monthly utility bill, users can see how much energy is used over that month and the kilowatt-hour rate, which is then multiplied together to determine the payment due. Through this project, Xie aims to provide new options for modernizing the power delivery rate structure for the utility industry through a data-driven approach.
This research was published in the June issue of the journal Utilities Policy.
Xie explained that the costs associated with delivering power are not necessarily the same for every customer, and further, not every customer is the same in terms of their impact and contribution to the grid. He proposes the use of electric smart meters, which can record with a granularity of 15 minutes how much energy a consumer has used during a given period. This would provide the utility company a more refined, closer to real-time understanding of a customer who contributes to the peak consumption of the grid and a customer who relieves the stress of the grid through the use of solar panels or lower consumption.
"If a particular customer is actually sending some of their solar panel energy back to the grid during the peak hours, they should be viewed as a positive asset to the grid, and that individual should be somehow compensated," Xie said. "And if someone is using their air conditioner an excessive amount when the grid is extremely stressed, then that individual is contributing to the strain on the grid and might need to pay a higher portion of the delivery cost."
Power distribution grids across the world are undergoing profound changes due to advances in grid edge technologies, such as solar panels and electric vehicles (EVs). The rate model Xie envisions would include a shift from charging end users based on their kilowatt-hour volumetric consumption and instead charging them a grid access fee that approximates the impact of end-users' time-varying demand on their local distribution network.
The dataset used in the case study is a system of 200 residential demand profiles, with 50 EV homes, 50 solar photovoltaic (PV) homes, and 100 non-DER homes -- those without distributed energy resources (DERs), such as an electric vehicle, solar panel or battery storage device.
Typically, customers charge their EVs during the night (off-peak hours, low grid impact). So, it follows that over 90% of EV customers see reduced bills under the proposed rate model. For solar PV customers, the results are more varied. For PV customers to minimize grid impact, combining solar PV with battery storage under a smart scheduling algorithm for charging and discharging would achieve the highest cost savings on bills. As for non-DER customers, over 80% experienced a small reduction in their bills under the proposed rate.
"The most exciting part is how we can translate technology innovations into a real-world impact," Xie said. "That impact is going to pave the way for a more sustainable operation of the grid -- leading to a more sustainable future."
INFORMATION:
This work is supported in part by the Power Systems Engineering Research Center and in part by National Science Foundation.
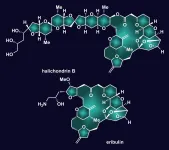
HOUSTON - (June 29, 2021) - The story of halichondrin B, an inspirational molecule obtained from a marine creature, goes back to the molecule's discovery in an ocean sponge in 1986.
Though it has been replicated in the laboratory several times before, new work by Rice University chemists could make halichondrin B and its naturally occurring or designed variations easier to synthesize.
Synthetic chemist K.C. Nicolaou and his lab reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society their success in simplifying several processes used to make halichondrin B and its variations.
Halichondrin's molecular structure and potent antitumor ...
Dark Energy is widely believed to be the driving force behind the universe's accelerating expansion, and several theories have now been proposed to explain its elusive nature. However, these theories predict that its influence on quantum scales must be vanishingly small, and experiments so far have not been accurate enough to either verify or discredit them. In new research published in EPJ ST, a team led by Hartmut Abele at TU Wien in Austria demonstrate a robust experimental technique for studying one such theory, using ultra-cold neutrons. Named 'Gravity Resonance Spectroscopy' (GRS), their approach could bring researchers ...
Scientists have discovered how plants manage to live alongside each other in places that are dark and shady.
Moderate shade or even the threat of shade - detected by phytochrome photoreceptors - causes plants to elongate to try to outgrow the competition.
But in the deep gloom of a dense forest or a cramped crop canopy where resources and photosynthesis are limited, this strategy doesn't work. In these conditions it would be a waste of energy and detrimental to survival to elongate stems because seedlings would never be able to over-grow larger neighbours.
So how do plants prevent elongated growth under deep shade conditions? The secret lies in their internal clocks, says the research collaboration from the John Innes Centre ...
NEW YORK (June 29, 2021)--In a new paper published in the journal Vaccine: X, public health experts from Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, the University of Oslo, and Spark Street Advisors highlight actions to accelerate access to vaccines globally. The paper reviews the vaccine research and development process and proposes areas where reforms could increase access, speed time to market and decrease costs--from R&D to manufacturing and regulation to the management of incentives like patents and public funding.
The COVID-19 ...
A process that uses heat to change the arrangement of molecular rings on a chemical chain creates 3D-printable gels with a variety of functional properties, according to a Dartmouth study.
The researchers describe the new process as "kinetic trapping." Molecular stoppers--or speed bumps--regulate the number of rings going onto a polymer chain and also control ring distributions. When the rings are bunched up, they store kinetic energy that can be released, much like when a compressed spring is released.
Researchers in the Ke Functional Materials Group use heat to change the distribution of rings and then use moisture ...
DURHAM, N.C. - Combining structural biology and computation, a Duke-led team of researchers has identified how multiple mutations on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein independently create variants that are more transmissible and potentially resistant to antibodies.
By acquiring mutations on the spike protein, one such variant gained the ability to leap from humans to minks and back to humans. Other variants -- including Alpha, which first appeared in the United Kingdom, Beta, which appeared in South Africa, and Gamma, first identified in Brazil - independently developed spike mutations that enhanced their ability to spread rapidly in human ...
Aerospace engineering faculty member Melkior Ornik is also a mathematician, a history buff, and a strong believer in integrity when it comes to using hard science in public discussions. So, when a story popped up in his news feed about a pair of researchers who developed a statistical method to analyze datasets and used it to purportedly refute the number of Holocaust victims from a concentration camp in Croatia, it naturally caught his attention.
Ornik is a professor in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. He proceeded to study the research in depth and used the method to re-analyze the same data from the United ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers are taking a close look at rare cases of inflammation of the heart muscle, or myocarditis, in young men who developed symptoms shortly after receiving the second dose of the Moderna or Pfizer messenger RNA (mRNA) COVID-19 vaccines. Several recent studies suggest that health care professionals should watch for hypersensitivity myocarditis as a rare adverse reaction to being vaccinated for COVID-19. However, researchers stress that this awareness should not diminish overall confidence in vaccination during the current pandemic.
While reports of post-vaccine myocarditis ...
Using real-time deformability cytometry, researchers at the Max-Planck-Zentrum für Physik und Medizin in Erlangen were able to show for the first time: Covid-19 significantly changes the size and stiffness of red and white blood cells - sometimes over months. These results may help to explain why some affected people continue to complain of symptoms long after an infection (long Covid).
Shortness of breath, fatigue and headaches: some patients still struggle with the long-term effects of a severe infection by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus after six months or more. This post Covid-19 syndrome, also called long covid, is still not properly understood. What is clear is that -- during the ...
In two journal articles, a University of Houston biomedical researcher reports a step forward in diagnosing intestinal diseases, including colorectal cancer, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease using stool proteins. The current gold standard for colon cancer testing measures blood (hemoglobin) present in stool, and tests for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measure levels of calprotectin, a protein that detects inflammation in the intestines.
"The unique aspect of both research reports is that we are looking at stool samples comprehensively, ...