(Press-News.org) Research from the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis has found a missing piece in the puzzle of optical quantum computing.
Jung-Tsung Shen, associate professor in the Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering, has developed a deterministic, high-fidelity two-bit quantum logic gate that takes advantage of a new form of light. This new logic gate is orders of magnitude more efficient than the current technology.
"In the ideal case, the fidelity can be as high as 97%," Shen said.
His research was published in May 2021 in the journal Physical Review A.
The potential of quantum computers is bound to the unusual properties of superposition -- the ability of a quantum system to contain many distinct properties, or states, at the same time -- and entanglement -- two particles acting as if they are correlated in a non-classical manner, despite being physically removed from each other.
Where voltage determines the value of a bit (a 1 or a 0) in a classical computer, researchers often use individual electrons as "qubits," the quantum equivalent. Electrons have several traits that suit them well to the task: they are easily manipulated by an electric or magnetic field and they interact with each other. Interaction is a benefit when you need two bits to be entangled -- letting the wilderness of quantum mechanics manifest.
But their propensity to interact is also a problem. Everything from stray magnetic fields to power lines can influence electrons, making them hard to truly control.
For the past two decades, however, some scientists have been trying to use photons as qubits instead of electrons. "If computers are going to have a true impact, we need to look into creating the platform using light," Shen said.
Photons have no charge, which can lead to the opposite problems: they do not interact with the environment like electrons, but they also do not interact with each other. It has also been challenging to engineer and to create ad hoc (effective) inter-photon interactions. Or so traditional thinking went.
Less than a decade ago, scientists working on this problem discovered that, even if they weren't entangled as they entered a logic gate, the act of measuring the two photons when they exited led them to behave as if they had been. The unique features of measurement are another wild manifestation of quantum mechanics.
"Quantum mechanics is not difficult, but it's full of surprises," Shen said.
The measurement discovery was groundbreaking, but not quite game-changing. That's because for every 1,000,000 photons, only one pair became entangled. Researchers have since been more successful, but, Shen said, "It's still not good enough for a computer," which has to carry out millions to billions of operations per second.
Shen was able to build a two-bit quantum logic gate with such efficiency because of the discovery of a new class of quantum photonic states -- photonic dimers, photons entangled in both space and frequency. His prediction of their existence was experimentally validated in 2013, and he has since been finding applications for this new form of light.
When a single photon enters a logic gate, nothing notable happens -- it goes in and comes out. But when there are two photons, "That's when we predicted the two can make a new state, photonic dimers. It turns out this new state is crucial."
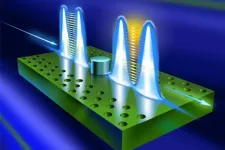
High-fidelity, two-bit logic gate, designed by Jung-Tsung Shen.
Mathematically, there are many ways to design a logic gate for two-bit operations. These different designs are called equivalent. The specific logic gate that Shen and his research group designed is the controlled-phase gate (or controlled-Z gate). The principal function of the controlled-phase gate is that the two photons that come out are in the negative state of the two photons that went in.
"In classical circuits, there is no minus sign," Shen said. "But in quantum computing, it turns out the minus sign exists and is crucial."
When two independent photons (representing two optical qubits) enter the logic gate, "The design of the logic gate is such that the two photons can form a photonic dimer," Shen said. "It turns out the new quantum photonic state is crucial as it enables the output state to have the correct sign that is essential to the optical logic operations."
Shen has been working with the University of Michigan to test his design, which is a solid-state logic gate -- one that can operate under moderate conditions. So far, he says, results seem positive.
Shen says this result, while baffling to most, is clear as day to those in the know.
"It's like a puzzle," he said. "It may be complicated to do, but once it's done, just by glancing at it, you will know it's correct."
INFORMATION:
Irvine, Calif., June 29, 2021 - Fireworks are synonymous in the United States with the celebration of Independence Day and other special events, but the colorful displays have caused a growing risk to public safety in recent years, according to a study by environmental health researchers at the University of California, Irvine.
Relying on real-time air quality measurements crowdsourced from a network of more than 750 automated sensors distributed throughout California, scientists from UCI's Program in Public Health found that short-term, extremely high-particulate-matter air pollution from the widespread ...
This lobster tale begins a few years ago when the proprietor of a northeastern seafood restaurant publicly asserted that exposing lobsters to a little cannabis prior to cooking produced notable changes in their behavior and a less dramatic scene in the kitchen for all concerned, which was the Maine thing.
In a paper published online June 29, 2021 in the journal Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, a team led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, report on efforts to answer that burning, boiling and baked question. They obtained live lobsters (Homarus americanus) from a supermarket and exposed the crustaceans to up to 60 minutes of vaporized Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) -- the principle psychoactive component of cannabis -- then ...
June 29, 2021 - Nutley, NJ - Scientists from the Hackensack Meridian Center for Discovery and Innovation, working with collaborators from across the globe, uncovered the mechanism of action of a novel anti-tuberculosis drug that they have helped develop.
The new findings show how the enzyme inhibitor triaza-coumarin, or TA-C, is metabolized by the TB germs, which makes it effective in inhibiting the disease from within, like in a "Trojan horse" attack, according to the new paper in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"This is a promising new direction of research," said Thomas Dick, member of the CDI faculty. "We are hoping this work can make a difference in the ongoing fight against TB."
"The scientists at the CDI who specialize in ...
For many years, researchers have been focused on developing technologies that can help us fight the imminent climate change crisis. They have one goal in common: finding sustainable energy sources that can replace the environmentally toxic fossil fuels. "Photocatalysts" that drive an artificial process that replicates photosynthesis (in which solar energy is converted to useful materials) are promising in this regard, given that we are able to develop the technology needed for them. Crystalline materials, such as strontium titanate (SrTiO3), which can serve as "photocatalysts" in solar devices, can lead us in the direction.
SrTiO3 is attractive owing to various other reasons ...
Basic needs of disaster- and conflict-impacted refugees are often met by humanitarian relief goods and services, and until now little was known about how refugees create economic livelihood beyond immediate relief.
A new exploratory case study from Portland State University Associate Professor of Management Theodore Khoury reveals how Syrian refugees in the Za'atari camp reached beyond basic disaster relief support and leveraged social capital to create informal economic systems that helped improve their quality of life. The study, "Towards a theory of informal supply networks: An?exploratory case study of the Za'atari refugee camp," is published in the Journal of Operations Management and co-authored by ...
PHILADELPHIA - The use of e-cigarettes, or vaping, causes serious damage to the lungs. After the novel coronavirus responsible for the respiratory disease COVID-19 emerged last year, there have been ongoing concerns about how vaping might impact risk of infection and severity of symptoms. Some evidence shows an increased risk of COVID-19 among those who vape. Research also shows a higher COVID-19 mortality rate in men compared to women, and men are more likely to vape than women. However, there is no evidence to link these two observations.
New research from Jefferson sheds light on this by showing that exposure to e-cigarette vapor increases levels of the coronavirus receptor in the lungs ...
A 50% rise in the level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere could reduce rainfall in the Amazon as much as or even more than substitution of the entire forest by pasture. The rise in CO2 would reduce the amount of water vapor emitted by the forest, leading to a 12% annual drop in the volume of rainfall, while total deforestation would reduce rainfall by 9%.
These estimates are presented in a study published in Biogeosciences by scientists affiliated with the National Space Research Institute (INPE), the University of São Paulo (USP) and the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil, and with Munich Technical University (TUM) in Germany.
“CO2 is a basic input for photosynthesis, so when it increases in the atmosphere, plant physiology ...
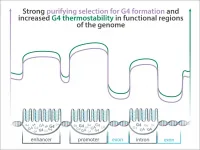
Some regions of the human genome where the DNA can fold into unusual three-dimensional structures called G-quadruplexes (G4s) show signs that they are preserved by natural selection. When G4s are located in the regulatory sequences that control how genes are expressed or in other functional, but non-protein coding, regions of the genome, they are maintained by selection, are more common, and their unusual structures are more stable, according to a new study. Conversely, the structures are less common, less stable, and evolve neutrally outside of these regions, including within the protein-coding regions of genes themselves.
Together, these ...
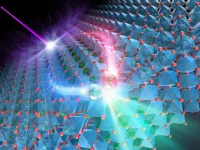
A two-dimensional alloy material -- made from five metals as opposed to the traditional two -- has been developed by a collaboration between researchers at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis and researchers at the College of Engineering at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
And, in a first for such a material, it has been shown to act as an excellent catalyst for reducing CO2, into CO, with potential applications in environmental remediation.
The research, from the lab of Rohan Mishra, assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science at ...
A team of neuroscientists at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology led by Baher Ibrahim and Dr. Daniel Llano published a study in eLife that furthers our understanding of how the brain perceives everyday sensory inputs.
"There is a traditional idea that the way that we experience the world is sort of like a movie being played on a projector. All the sensory information that is coming in is being played on our cerebral cortex and that's how we see things and hear things," said Llano, a Beckman researcher and associate professor in the Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology at the University of Illinois ...