G-quadruplex-forming DNA molecules enhance enzymatic activity of myoglobin
2021-07-01
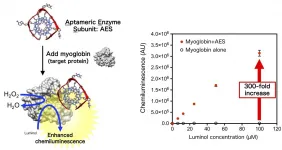
(Press-News.org) A collaboration led by Distinguished Professor Dr. Kazunori Ikebukuro from Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT), Japan, discovered that G-quadruplex (G4)-forming DNA binds myoglobin through a parallel-type G4 structure. Through the G4 binding, the enzymatic activity of myoglobin increases over 300-fold compared to that of myoglobin alone (Figure). This finding indicates that DNA may work as a carrier of genetic information in living organisms and act as a regulator of unknown biological phenomena.
"Aptamers" are nucleic acid-based synthetic ligands that can be used against many target molecules with high affinity and specificity. Some aptamers that bind to proteins are reported as specific ligands and biological function regulators. Dr. Ikebukuro and his group have developed many DNA aptamers that bind proteins, especially enzymes. In addition, they developed the aptameric enzyme modulator--aptameric enzyme subunit (AES), which can inhibit enzymatic activities. The current challenge for the group is to create novel aptamers that upregulate the catalytic activity of enzymes.
The collaborative team of TUAT, RIKEN (Japan), DENSO CORPORATION (Japan), and the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill (USA) succeeded in developing a new AES that increases the peroxidase activity of myoglobin. As myoglobin contains a heme as a cofactor, the research team found that a region near the heme-binding site can be positively charged. "We hypothesized that this region is likely to interact with negative charges of the DNA oligonucleotides derived from its sugar-phosphate backbone, which may lead to an enhancing effect on the enzymatic activity," said Dr. Ikebukuro.
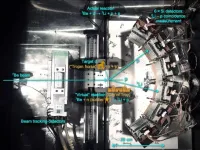
The chemiluminescence measurements in their study showed that the AES specifically enhanced the peroxidase activity of myoglobin by up to 300-fold compared to that of myoglobin alone (Figure). Further, the AES bound to myoglobin strongly at the heme in myoglobin, as expected (Figure). The structural analyses by NMR and spectroscopic observation revealed the AES folded into a parallel-type G-quadruplex structure.
"Our study has revealed that DNA can potentially work as a regulator of protein's functions in the cell. On the other hand, because the AES produces a dramatically enhanced chemiluminescent signal, it could also offer a new strategy for future biosensor application studies," Dr. Ikebukuro added.
INFORMATION:
For more information about the Ikebukuro Tsugawa Asano laboratory, please visit http://web.tuat.ac.jp/~tanpaku/index_E.html
Original publication:
G-quadruplex-forming aptamer enhances the peroxidase activity of myoglobin against luminol
Nucleic Acid Research, gkab388
URL https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab388
Kaori Tsukakoshi1,†, Yasuko Yamagishi1,†, Mana Kanazashi2, Kenta Nakama1, Daiki Oshikawa1, Nasa Savory1, Akimasa Matsugami3, Fumiaki Hayashi3, Jinhee Lee4, Taiki Saito1, Koji Sode4, Kanjana Khunathai2, Hitoshi Kuno2, Kazunori Ikebukuro1, *
1 Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo, 184-8588, Japan
2 DENSO CORPORATION, 1-1 Showa-cho, Kariya, Aichi, 448-8661, Japan
3 Advanced NMR Application and Platform Team, NMR Research and Collaboration Group, NMR Science and Development Division, RIKEN SPring-8 Center, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi, Yokohama, Kanagawa 230-0045, Japan
4 Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and North Carolina State University, Chapel Hill, NC 27599, USA
†: The authors equally contributed to this work
*: Corresponding author
About Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT):
TUAT is a distinguished university in Japan dedicated to science and technology. TUAT focuses on agriculture and engineering that form the foundation of industry, and promotes education and research fields that incorporate them. Boasting a history of over 140 years since our founding in 1874, TUAT continues to boldly take on new challenges and steadily promote fields. With high ethics, TUAT fulfills social responsibility in the capacity of transmitting science and technology information towards the construction of a sustainable society where both human beings and nature can thrive in a symbiotic relationship. For more information, please visit http://www.tuat.ac.jp/en/.
Contact: Kazunori Ikebukuro, Ph.D.
Professor
Department of Biotechnology and Life Science,
Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-01
Zeolites are extremely porous materials: Ten grams can have an internal surface area the size of a soccer field. Their cavities make them useful in catalyzing chemical reactions and thus saving energy. An international research team has now made new findings regarding the role of water molecules in these processes. One important application is the conversion of biomass into biofuel.
Fuel made from biomass is considered to be climate-neutral, although energy is still needed to produce it: The desired chemical reactions require high levels of temperature and pressure.
"If ...
2021-07-01
WASHINGTON -- If you've ever tried to capture a sunset with your smartphone, you know that the colors don't always match what you see in real life. Researchers are coming closer to solving this problem with a new set of algorithms that make it possible to record and display color in digital images in a much more realistic fashion.
"When we see a beautiful scene, we want to record it and share it with others," said Min Qiu, leader of the Laboratory of Photonics and Instrumentation for Nano Technology (PAINT) at Westlake University in China. "But we don't want to see a digital photo or video with the wrong colors. Our new algorithms can help digital camera and electronic display developers better adapt their ...
2021-07-01
There is a significant discrepancy between theoretical and observed amounts of lithium in our universe. This is known as the cosmological lithium problem, and it has plagued cosmologists for decades. Now, researchers have reduced this discrepancy by around 10%, thanks to a new experiment on the nuclear processes responsible for the creation of lithium. This research could point the way to a more complete understanding of the early universe.
There is a famous saying that, "In theory, theory and practice are the same. In practice, they are not." This holds true in every academic domain, but it's especially common in cosmology, the study of the entire ...
2021-07-01
A wonder of nature
As a human cell begins division, its 23 chromosomes duplicate into identical copies that remain joined at a region called the centromere. Here lies the kinetochore, a complicated assembly of proteins that binds to thread-like structures, the microtubules. As mitosis progresses, the kinetochore gives green light to the microtubules to tear the DNA copies apart, towards the new forming cells. "The kinetochore is a beautiful, flawless machine: You almost never lose a chromosome in a normal cell!", says Musacchio. "We already know the proteins that constitute it, yet important questions about how the kinetochore works are still open: How does it rebuild itself during chromosome replication? ...
2021-07-01
Researchers at the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku, Finland, study insect biodiversity particularly in Amazonia and Africa. In their studies, they have discovered hundreds of species previously unknown to science. Many of them are exciting in their size, appearance, or living habits.
"The species we have discovered show what magnificent surprises the Earth's rainforests can contain. The newly discovered Dolichomitus meii wasp is particularly interesting for its large size and unique colouring. With a quick glance, its body looks black but glitters electric blue in light. Moreover, its wings are golden yellow. Therefore, you could say it's like a flying jewel," says Postdoctoral Researcher Diego Pádua from the Instituto Nacional ...
2021-07-01
Contrary to what science once suggested, older people with a declining sense of smell do not have comprehensively dampened olfactory ability for odors in general - it simply depends upon the type of odor. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen reached this conclusion after examining a large group of older Danes' and their intensity perception of common food odours.
That grandpa and grandma aren't as good at smelling as they once were, is something that many can relate to. And, it has also been scientifically demonstrated. One's sense of smell gradually begins to decline from about the age of 55. Until now, it was believed that one's sense of smell broadly ...
2021-07-01
Plastic waste is considered one of the biggest environmental problems of our time. IASS researchers surveyed consumers in Germany about their use of plastic packaging. Their research reveals that fundamental changes in infrastructures and lifestyles, as well as cultural and economic transformation processes, are needed to make zero-waste shopping the norm.
96 percent of the German population consider it important to reduce packaging waste. Nevertheless, the private end consumption of packaging in Germany has increased continuously since 2009. At 3.2 million tons in 2018, the amount of plastic packaging waste generated by end consumers in Germany ...
2021-07-01
One year after infection by SARS-CoV-2, most people maintain anti-Spike antibodies regardless of the severity of their symptoms, according to a study with healthcare workers co-led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), the Catalan Health Institute (ICS) and the Jordi Gol Institute (IDIAP JG), with the collaboration of the Daniel Bravo Andreu Private Foundation. The results suggest that vaccine-generated immunity will also be long-lasting.
One of the key questions to better predict the pandemic's evolution is the duration of natural immunity. A growing number of studies suggest that most people generate a humoral ...
2021-07-01
The eruption of the Laacher See volcano in the Eifel, a low mountain range in western Germany, is one of Central Europe's largest eruptions over the past 100,000 years. The eruption ejected around 20 cubic kilometers of tephra and the eruption column is believed to have reached at least 20 kilometers in height, comparable to the Pinatubo eruption in the Philippines in 1991. Technical advances in combination with tree remains buried in the course of the eruption now enabled an international research team to accurately date the event. Accordingly, the eruption of the Laacher See volcano occurred 13,077 years ago and thus 126 years earlier than previously assumed. This sheds new light on the climate history of the entire North ...
2021-07-01
Scientists at the University of Helsinki have found an essential factor from the extracellular matrix that regulates functionality of the breast tissue for instance during pregnancy.
Extracellular matrix (ECM) has previously been recognised as an important element for the growth of various epithelial cells, but rather as a scaffold. A new study shows that ECM can also regulate the function of epithelial cells.
Our tissues constitute of differentiated cell types, which perform specific tasks that are tightly controlled. Normal growth and functioning of tissues is possible only when the various differentiated cell types interact appropriately. Differentiation and function of breast epithelium is guided by a group of cells responsive for estrogen and progesterone hormones. In the recent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] G-quadruplex-forming DNA molecules enhance enzymatic activity of myoglobin