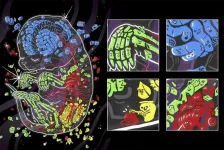
(Press-News.org) A new technique called sci-Space, combined with data from other technologies, could lead to four-dimensional atlases of gene expression across diverse cells during embryonic development of mammals.
Such atlases would map how the gene transcripts in individual cells reflect the passage of time, cell lineages, cell migration, and location on the developing embryo. They would also help illuminate the spatial regulation of gene expression.
Mammalian embryonic development is a remarkable phenomenon: a fertilized egg divides repeatedly and turns, in a matter of weeks or months, into a complex organism capable of a myriad of physiological processes and composed of a variety of cells, tissues, organs, anatomical structures.
A better understanding of how mammals form before birth -- particularly the prenatal spatial patterns of gene expression at a single-cell level during embryonic development -- could advance biomedical and veterinary research on a variety of conditions. These range from inherited disorders to congenital malformations and developmental delays. Understanding how organs originate might also assist future regenerative medicine efforts.
An international team led by scientists at UW Medicine, Howard Hughes Medical Institute and the Brotman Baty Institute for Precision Medicine in Seattle demonstrated the proof-of-concept of their sci-Space technique in mouse embryos.
Their results are published in the July 2 edition of Science. The lead authors are Sanjay R. Srivatsan of the Department of Genome Sciences at the University of Washington School of Medicine, and Mary C. Regier of the UW Department of Bioengineering.
The senior authors are Jay Shendure, UW Medicine professor of genome sciences, and director of the Brotman Baty Institute, and an investigator at the Allan Discovery Center for Cell Lineage Tracing; Kelly R. Stevens, UW assistant professor of bioengineering; and Cole Trapnell, associate professor of genome sciences. Regier and Stevens are also investigators at the UW Medicine Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Research.
The researchers observed the orchestration of genes in 120,000 cell nuclei. All the body's somatic cells contain the same DNA code. The researchers captured information on which genes were turned on or off in these nuclei as mouse embryos took shape. The scientists also investigated how cells' locations in an embryo affected which genes were activated during development.
This technique builds on previous work in which these scientists and other groups developed ways of conducting whole-organism profiling of gene expression and DNA-code accessibility, in thousands of single cells, during embryonic development. They did so to track the emergence and trajectory of various cell types.
How cells are organized spatially - what physical positions they take as an embryo forms - is critical to normal development. Misplacements, disruptions, or cells not showing at the right time in the right spot can cause serious problems or even prenatal death.
However, gaining knowledge on spatial patterns of gene expression has been technically difficult. It has been unwieldy to assay gene transcripts of individual cells over wide swaths of the embryo. This limited the scientific understanding of how spatial organization influences gene expression and, consequently, why which cell types form where, or how neighboring groups of cells influence each other's future roles.
The scientists on the present study had earlier developed a method to label cell nuclei, a technique they called sci-Plex. They then went on to index single-cell RNA sequencing, with a method called sci-RNA-sequencing.
Now, with sci-Space, by analyzing spatial coordinates and cell gene transcripts the scientists identified thousands of genes whose expression was anatomically patterned. For example, certain genetic profiles emerged in neurons in the brain and spinal cord and others in cardiac muscle cells in the heart.
The scientists also used spatial and gene profile information to annotate subtypes of cells. For example, while both blood vessel cells and heart muscle might both express the gene for a particular growth factor, only the heart muscle cells produced certain growth factor receptors.
The researchers also observed that cell types varied greatly in the extent of their spatial patterning of gene expression. For example, connective tissue progenitor cells showed a relatively large proportion of spatially restricted gene expression. This observation suggests that subtypes of these cells behave in a position-dependent manner throughout the body.
To measure the power of spatial position on a cell type's gene transcript profile, the researchers also calculated the physical distance between cells and the angular distance of their gene expression profiles.
"For many cell types, as the physical distance between cells increased, so did the angular distance between their transcriptomes," the researchers noted in their paper. However, they added that this trend varied considerably. It was most pronounced in certain brain and spinal cord cells.
The genetic transcript profiles of some other cell types were highly influenced by their position in the developing embryo. Among these are certain cartilage cells, which become part of the scaffolding for bones of the head and face.
The researchers also studied gene expression dynamics that took place as part of brain cell differentiation and migration during mouse embryonic development. The researchers examined how various brain cell trajectories were anatomically distributed. The researchers did so by using the Allen Institute's Anatomical Reference Brain Atlas as a guide.
"Cells from each trajectory overwhelmingly occupied distinct brain regions," the researchers noted. They also observed gradients of developmental maturity in different regions of the brain. These gradients revealed both known and new patterns of migration.
In the future, the researchers hope sci-Space will be further applied to serial sections that span the entire mouse embryo and that cover many points of time.
INFORMATION:
The recently reported research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Brotman Baty Institute, Paul G. Allen Frontiers Foundation, and Washington Research Foundation.
Quantum computers promise great advances in many fields - from cryptography to the simulation of protein folding. Yet, which physical system works best to build the underlying quantum bits is still an open question. Unlike regular bits in your computer, these so-called qubits cannot only take the values 0 and 1, but also mixtures of the two. While this potentially makes them very useful, they also become very unstable.
One approach to solve this problem bets on topological qubits that encode the information in their spatial arrangement. That could provide a more stable ...
Current rates of plastic emissions globally may trigger effects that we will not be able to reverse, argues a new study by researchers from Sweden, Norway and Germany published on July 2nd in Science. According to the authors, plastic pollution is a global threat, and actions to drastically reduce emissions of plastic to the environment are "the rational policy response".
Plastic is found everywhere on the planet: from deserts and mountaintops to deep oceans and Arctic snow. As of 2016, estimates of global emissions of plastic to the world's lakes, rivers and ...
Scientists have long searched in vain for a class of brain cells that could explain the visceral flash of recognition that we feel when we see a very familiar face, like that of our grandmothers. But the proposed "grandmother neuron"--a single cell at the crossroads of sensory perception and memory, capable of prioritizing an important face over the rabble--remained elusive.
Now, new research reveals a class of neurons in the brain's temporal pole region that links face perception to long-term memory. It's not quite the apocryphal grandmother neuron--rather than a single ...
The COVID-19 catastrophe in India has resulted in more than 30 million people infected with the virus and nearly 400,000 deaths, though experts are concerned that the figures most likely are much higher. Meanwhile, another public health crisis has emerged along with COVID-19: the widespread misuse of antibiotics.
During India's first surge of COVID-19, antibiotic sales soared, suggesting the drugs were used to treat mild and moderate cases of COVID-19, according to research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such use is considered inappropriate because antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, not viral infections such as COVID-19, and overuse increases the risk ...
Fifteen years ago, UC Santa Barbara electrical and materials professor John Bowers pioneered a method for integrating a laser onto a silicon wafer. The technology has since been widely deployed in combination with other silicon photonics devices to replace the copper-wire interconnects that formerly linked servers at data centers, dramatically increasing energy efficiency -- an important endeavor at a time when data traffic is growing by roughly 25% per year.
For several years, the Bowers group has collaborated with the group of Tobias J. Kippenberg at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), within the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Direct On-Chip Digital Optical ...
Optical frequency combs consist of light frequencies made of equidistant laser lines. They have already revolutionized the fields of frequency metrology, timing and spectroscopy. The discovery of ''soliton microcombs'' by Professor Tobias Kippenberg's lab at EPFL in the past decade has enabled frequency combs to be generated on chip. In this scheme, a single-frequency laser is converted into ultra-short pulses called dissipative Kerr solitons.
Soliton microcombs are chip-scale frequency combs that are compact, consume low power, and exhibit broad bandwidth. Combined with large spacing of comb "teeth", microcombs are uniquely ...
Conversations between seriously ill people, their families and palliative care specialists lead to better quality-of-life. Understanding what happens during these conversations - and particularly how they vary by cultural, clinical, and situational contexts - is essential to guide healthcare communication improvement efforts. To gain true understanding, new methods to study conversations in large, inclusive, and multi-site epidemiological studies are required. A new computer model offers an automated and valid tool for such large-scale scientific analyses.
Research results on this model were published today in PLOS ONE.
Developed by a team of computer scientists, clinicians and engineers at the University of Vermont, the approach - called CODYM ...
A study by Stanford University School of Medicine investigators hints that people with COVID-19 may experience milder symptoms if certain cells of their immune systems "remember" previous encounters with seasonal coronaviruses -- the ones that cause about a quarter of the common colds kids get.
These immune cells are better equipped to mobilize quickly against SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus responsible for COVID-19, if they've already met its gentler cousins, the scientists concluded.
The findings may help explain why some people, particularly children, seem much more resilient than others to infection by SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. They also might make it possible ...
Scientists have developed a new technology to detect a wider variety of T cells that recognize coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2. The technology revealed that killer T cells capable of recognizing epitopes conserved across all coronaviruses are much more abundant in COVID-19 patients with mild disease versus those with more severe illness, suggesting a protective role for these broad-affinity T cells. The ability to distinguish T cells based on their affinities to SARS-CoV-2 could help scientists elucidate the disparity in COVID-19 outcomes and determine which COVID-19 patients will or will not exhibit a successful immune response ...
In a new Editorial, Peter Heeger, Christian Larsen, and Dorry Segev discuss recent evidence - including a recent Science Immunology study by Hector Rincon-Arevalo and colleagues - that points to a diminished immune response to COVID-19 vaccines among organ transplant recipients and others on immunosuppressive drug regimens. The authors note that this presents challenges at both the individual and population levels, since current vaccine protocols may not provide adequate protection to immunosuppressed patients - who could, in turn, become reservoirs for new and dangerous variants of the virus. As such, Heeger, Larsen, and Segev argue that developing vaccination strategies for transplant recipients should be a high priority in the next wave of research focused on fighting COVID-19. ...