(Press-News.org) An international team of scientists has used high-powered X-rays at the European Synchrotron, the ESRF, to show how an extinct South African 200-million-year-old dinosaur, Heterodontosaurus tucki, breathed. The study is published in eLife on 6 July 2021.
In 2016, scientists from the Evolutionary Studies Institute at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa, came to the ESRF, the European Synchrotron in Grenoble, France, the brightest synchrotron light source, for an exceptional study: to scan the complete skeleton of a small, 200-million-year-old plant-eating dinosaur. The dinosaur specimen is the most complete fossil ever discovered of a species known as Heterodontosaurus tucki. The fossil was found in 2009 in the Eastern Cape of South Africa by study co-author, Billy de Klerk of the Albany Museum, Makhanda, South Africa. "A farmer friend of mine called my attention to the specimen" says de Klerk, "and when I saw it I immediately knew we had something special on our hands."
Fast forward some years: the team of scientists, using scans and new algorithm developed by ESRF scientists to virtually reconstruct the skeleton of Heterodontosaurus in unprecedented detail, and thus show how this extinct dinosaur breathed. "This specimen represents a turning point in understanding how dinosaurs evolved" explains Viktor Radermacher, corresponding author, South African PhD now at the University of Minnesota, US.
Not all animals use the same techniques and organs to breathe. Humans expand and contract their lungs. Birds have air sacs outside their lungs that pump oxygen in, and their lungs don't actually move. For a long time, paleontologists assumed that all dinosaurs breathed like birds, since they had similar breathing anatomy. This study, however, found that Heterodontosaurus did not--it instead had paddle-shaped ribs and small, toothpick-like bones, and expanded both its chest and belly in order to breathe.
Heterodontosaurus is one of the oldest and first-evolving Ornithischians, the group that includes favourites like Triceratops, Stegosaurus, and duckbilled dinosaurs. Heterodontosaurus lived in the early Jurassic period, about 200 million years ago, surviving an extinction at the end of the prior Triassic period. Understanding how this dinosaur breathed could also help paleontologists figure out what biological features allowed certain dinosaurs to survive or caused them to go extinct.
"We've long known that the skeletons of ornithischian dinosaurs were radically different from those of other dinosaurs," explains Richard Butler, from the School of Geography, Earth, and Environmental Sciences, University of Birmingham, UK. "This amazing new fossil helps us understand why ornithischians were so distinctive and successful", he adds.
This study is the result of a long-standing collaboration between palaeontologists based in South Africa and at the ESRF, where non-invasive techniques have been developped specifically for palaeontological studies. "You could only do this study with a synchrotron" says Vincent Fernandez, scientist at the Natural History Museum in London, UK, co-author of the study and former ESRF scientist. "The characteristics of the ESRF's X-rays, combined with its high energy beamline configuration, made scanning this complete turkey-sized dinosaur possible".
This is a perfect example of the diversity of life on Earth. "The takeaway message is that there are many ways to breathe," Radermacher said. "And the really interesting thing about life on earth is that we all have different strategies to do the same thing, and we've just identified a new strategy of breathing."
"Studies like this highlight how South Africa's fossil record once again helps us understand evolutionary origins" said senior author Jonah Choiniere, Professor at the Evolutionary Studies Institute, University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa.
INFORMATION:
Scientists Contact:
Viktor Radermacher, corresponding author, University of Mineesota, US - viktorsaurus91@gmail.com - US cell number: +1 6123254785
Whatsapp: +27 761278242
Vincent Fernandez, former scientist at the ESRF, now at the Natural History Museum, London, UK, co-author - v.fernandez@nhm.ac.uk - +33 6 95 57 68 96
Supports:
Authors Viktor Radermacher, Kimberley Chapelle, and Jonah Choiniere were supported by grants from the NRF-African Origins Platform, Centre of Excellence in Palaeosciences, and the Palaeontological Scientific Trust. South African participation in the ESRF, the European synchrotron, is supported by the NRF and DSI.
At the end of life, people may have to rely on others for help with showering, dressing and going to the toilet. This loss of privacy and independence can be confronting and difficult.
Now Australian occupational therapy (OT) researchers have interviewed 18 people receiving palliative care about how they feel about losing independence with self-care, specifically their intimate hygiene, as function declines with disease progression.
The study aims to raise awareness of how to provide better care for people at the end of life.
Lead researcher Dr Deidre Morgan, a Flinders University occupational ...
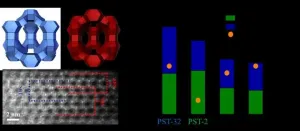
A research team at POSTECH has uncovered a promising new zeolite, anticipated to be a turning point for the oil refining and petrochemical industries. This research was recently published in the scientific journal Science on July 2, 2021.
The team of researchers led by Suk Bong Hong, a professor in the Division of Environmental Science and Engineering at POSTECH, synthesized two thermally stable three-dimensional (3D) large-pore (12-ring)1 zeolites - PST-32 (POSTECH No. 32) and PST-2, the hypothetical SBS/SBT intergrowth structure2 - by using the "multiple inorganic cation" and the "charge density mismatch" synthetic strategies, respectively. The research team identified their structures by using both powder X-ray diffraction ...
New research in BMC Cancer has shown myelosuppressive chemotherapy destabilises gut microbiome in patients with solid organ cancers.
The study from SAHMRI and Flinders University assessed the gut health of men and women who underwent conventional chemotherapy on cancers, such as breast and lung cancer, without exposure to antibiotics.
"We know that myelosuppressive chemotherapy reduces white blood cell count significantly during the first seven to 10 days of treatment, making the body more vulnerable to infection," says lead author Dr Lito Papanicolas, an infectious diseases expert and clinical microbiologist.
"In this study we focused on how much the individual's microbiome changed over this period, when the ...
Scientists at UC San Francisco have shown that gene-edited cellular therapeutics can be used to successfully treat cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases, potentially paving the way for developing less expensive cellular therapies to treat diseases for which there are currently few viable options.
The study, in mice, is the first in the emerging field of regenerative cell therapy to show that products from specially engineered induced pluripotent stem cells called "HIP" cells can successfully be employed to treat major diseases while evading the ...
A 15-year reciprocal transplant study on Guam's native cycad tree, Cycas micronesica, by the Plant Physiology Laboratory at the University of Guam's Western Pacific Tropical Research Center has revealed that acute adaptation to local soil conditions occurs among the tree population and is important in the survival rate of transplanted cycads. The results show that 70% to 100% of cycads that were transplanted in local conditions survived versus less than 10% that were transplanted in foreign conditions. The article describing the study has been published in the peer-reviewed journal Diversity (doi: 10.3390/d13060237).
Transplantation ...
Vertical greenery 'planted' on the exterior of buildings may help to buffer people against stress, a Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) study has found.
The benefits of nature on mental health and for wellbeing have long been recognised, and now a team of NTU Singapore psychologists has used Virtual Reality (VR) to examine whether vertical greenery has a stress buffering effect (ability to moderate the detrimental consequences of stress) in an urban environment.
Using VR headsets, 111 participants were asked to walk down a virtual street for five minutes. Participants were randomly assigned to either a street that featured rows of planted greenery (e.g., on balconies, walls, and pillars of buildings), ...
Attention training in young people with autism can lead to significant improvements in academic performance, according to a new study.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham in the UK along with institutions in São Paolo, in Brazil, tested a computer programme designed to train basic attention skills among a group of autistic children aged between eight and 14 years old.
They found participants achieved improvements in maths, reading, writing and overall attention both immediately after undergoing the training and at a three-month follow up assessment. Their results are published in Autism Research.
Lead researcher, Dr Carmel Mevorach, in the University of Birmingham's Centre for Human Brain Health, and School of Psychology, says: "It's ...
The urgency to remember a dangerous experience requires the brain to make a series of potentially dangerous moves: Neurons and other brain cells snap open their DNA in numerous locations--more than previously realized, according to a new study--to provide quick access to genetic instructions for the mechanisms of memory storage.
The extent of these DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in multiple key brain regions is surprising and concerning, said study senior author Li-Huei Tsai, Picower Professor of Neuroscience at MIT and director of The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, because while the breaks are routinely repaired, that process may become more flawed and fragile with age. Tsai's lab has shown that lingering DSBs are associated with neurodegeneration ...
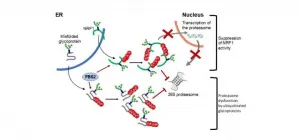
Peptide: N-glycanase (NGLY1) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme for removing N-linked glycans (N-glycans) from glycoproteins and is involved in proteostasis of N-glycoproteins in the cytosol. In 2012, a rare genetic disorder called NGLY1 deficiency was discovered by an exome analysis. Symptoms in patients with NGLY1 deficiency include global developmental delay, hypotonia, hypo/alacrima, movement disorder, scoliosis, abnormal liver, brain functions and peripheral neuropathy. Unfortunately, no therapeutic treatment is currently available to this devastating ...
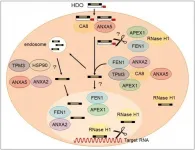
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find proteins that bind to and regulate tocopherol-conjugated heteroduplex oligonucleotides during gene silencing
Tokyo, Japan - Gene silencing therapies are used to interfere with, or "silence", the expression of genes that are associated with disorders. Now, a team at TMDU has uncovered some of the cellular mechanisms by which the silencing therapies act in cells.
Antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapies use small strands of DNA or RNA that are antisense, or complementary, to the associated gene to interfere with its expression. ASO therapies are already available for some diseases, particularly neurological disorders, but their use is at a very ...