(Press-News.org) July 8, 2021 - Women with recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) experience frustration related to their treatment - particularly the risks from repeated use of antibiotics, according to a focus group study in The Journal of Urology®, Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"This study was prompted by our experience treating countless women with recurrent UTIs referred to our specialized Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery center," comments senior author Ja-Hong Kim, MD, of UCLA Center of Women's Pelvic Health. "The vast majority were understandably dissatisfied with their care pathway, which was primarily antibiotic-focused with minimal effort spent on patient education and prevention strategies."
Lead author Victoria C.S. Scott, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Beverly Hills, Calif adds, "It's important for patients with this chronic condition to feel empowered in sharing their concerns with physicians regarding their health, quality of life and medical treatment and for physicians to respond to these concerns."
New strategies needed 'to minimize and target antibiotic use'
More than half of women will develop a UTI sometime during their lives, and about one-fourth experience recurrent UTIs. Episodes of UTI have a major impact on patients' lives - including pain and other symptoms, reduced quality of life, and repeated courses of antibiotics for prevention and treatment.
"In our experience, many patients labelled with recurrent UTI are either misdiagnosed or mistreated without following the guidelines set forth by specialty societies," says Dr. Kim. "It became clear that a paradigm shift in recurrent UTI management was needed, starting with patient-centered research to assess gaps in the current UTI treatment algorithm." The researchers performed a series of focus groups, with a total of 29 patients participating.
Analysis of the discussions identified several themes related to negative effects associated with antibiotic use. The women were well aware of the risks of developing antibiotic resistance and collateral damage from overuse or inappropriate use of antibiotics. Some patients developed infection with antibiotic-resistant C. difficile bacteria, in one case leading to hospitalization.
The patients also voiced concern about taking antibiotics when they didn't have an infection. Many believed they had been given antibiotics for other causes of urinary symptoms - particularly overactive bladder, which commonly occurs in women with recurrent UTIs but causes less-severe symptoms.
Other themes centered on resentment of the medical profession. The women expressed irritation with physicians for "throwing antibiotics" at them without presenting other, non-antibiotic options for treating recurrent UTIs. They also felt the medical profession underestimated the impact of recurrent UTIs on their lives. The women felt an urgent need for more research on non-antibiotic options, with a special interest in "natural" or "alternative" treatments for prevention of recurrent UTIs.
However, some women shared they were satisfied with their care - particularly those treated by a physician specializing in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery. Patients were more likely to be satisfied if they felt their doctor understood their problems and had a system for rapid diagnosis and treatment when UTI episodes occurred.
"Physicians must investigate patients' recurrent UTI experiences and their perceptions of antibiotics during counseling to address their concern over antibiotic overuse," says Dr. Scott. The researchers follow and recommend a strategy of delaying antibiotics until urine culture results are available - as endorsed by the American Urological Association (AUA) and other specialty societies.
Dr. Kim concludes: "There are exciting research developments underway, including the utilization of point-of-care rapid diagnostic assays to accurately and selectively treat UTIs as well as studies to understand the impact of vaginal microbiome on voiding dysfunction. We hope these efforts will pave the way to improved patient experience."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Fear and Frustration among Women with Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections: Findings from Patient Focus Groups."
DOI: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001843
About The Journal of Urology®
The Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA), and the most widely read and highly cited journal in the field, The Journal of Urology® brings solid coverage of the clinically relevant content needed to stay at the forefront of the dynamic field of urology. This premier journal presents investigative studies on critical areas of research and practice, survey articles providing brief editorial comments on the best and most important urology literature worldwide and practice-oriented reports on significant clinical observations. The Journal of Urology® covers the wide scope of urology, including pediatric urology, urologic cancers, renal transplantation, male infertility, urinary tract stones, female urology and neurourology.
About the American Urological Association
Founded in 1902 and headquartered near Baltimore, Maryland, the American Urological Association is a leading advocate for the specialty of urology, and has nearly 24,000 members throughout the world. The AUA is a premier urologic association, providing invaluable support to the urologic community as it pursues its mission of fostering the highest standards of urologic care through education, research and the formulation of health care policy. To learn more about the AUA visit: http://www.auanet.org.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2020 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,200 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
Ibaraki, Japan - Most kids dream of growing up to be astronauts; but the downside of spending extended amounts of time in low gravity is that astronauts' muscles tend to shrink and weaken through disuse. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a protein that affects how muscles respond to space flight.
In a study published in June 2021 in Communications Biology, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that nuclear factor E2-related factor 2, or NRF2, helps keep muscles from becoming weak in low gravity.
Muscle atrophy, or weakening, is a common feature of disease and aging. It can also occur after a long period of inactivity, such as during space flight, when astronauts don't need to use their muscles as much as they do on Earth to support ...
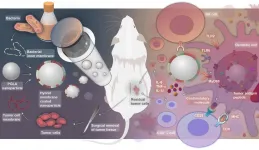
Thanks to the rapid development of nanotechnology, a research team led by Profs. NIE Guangjun, WU Yan and ZHAO Yuliang from the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently designed personalized tumor vaccines based on bacterial cytoplasmic membranes and cell membranes from resected tumor tissue. This work was published in Science Translational Medicine.
Cancer vaccines are an effective anti-tumor therapeutic option that utilize tumor antigens to stimulate patients' immune response and specifically kill tumor cells. Postoperative recurrence and metastasis after surgery can thus be effectively inhibited by the activated immune system. Therefore, ...
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a method for secure communication that uses quantum mechanics to encrypt information. While the security of QKD is unbreakable in principle, if it is incorrectly implemented, vital information could still be stolen by attackers. These are known as side-channel attacks, where the attackers exploit weaknesses in the setup of the information system to eavesdrop on the exchange of secret keys.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have developed two methods, one theoretical and one experimental, to ensure that QKD communications cannot be attacked in this way. The first is an ultra-secure cryptography protocol that can be deployed in any communication network that needs long-term ...
Researchers at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), have developed the Families Sharing Health Assessment and Risk Evaluation (SHARE) workbook, which helps people use their family history to assess their risk for heart disease, diabetes, breast cancer and colorectal cancer.
Since 2012, Laura Koehly, Ph.D., and her research team have measured the accessibility and usability of the workbook by working with communities and continually updating the workbook to address issues. Koehly is the chief of the Social ...
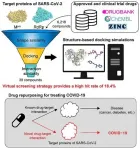
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of ...
Washington, DC (July 6, 2021) --The International Whaling Commission (IWC) was founded to regulate whaling. Today, it also increasingly focuses on the value of live whales for planetary health. A new workshop report confirms the great ecological value of whales to help mitigate climate change, transport nutrients, enhance marine productivity, and promote biodiversity in marine ecosystems.
The world's leading experts gathered for a three-day workshop in April that was co-hosted by the IWC and the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). The meeting came in response to a 2016 IWC resolution, introduced by the government of Chile, to compile scientific information about the ecological roles of cetaceans (whales and dolphins).
The workshop discussions ...
Researchers at the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan show that excessive blood pressure reduction for acute intracerebral hemorrhage is risky in people with decreased kidney function
Suita, Japan -- Stroke and chronic kidney disease are both difficult to handle in their own rights, but having a stroke when your kidneys are already poor is more than just double the trouble. A new study led by Kazunori Toyoda at the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center (NCVC) in Japan shows that excessive blood pressure reduction for acute intracerebral hemorrhage can have dire consequences when kidney function is low. The study was published in the scientific journal Neurology®.
Intracerebral hemorrhage is a disease for which effective treatment is expected ...
Rare-earth compounds have fascinated researchers for decades due to the unique quantum properties they display, which have so far remained totally out of reach of everyday compounds. One of the most remarkable and exotic properties of those materials is the emergence of exotic superconducting states, and particularly the superconducting states required to build future topological quantum computers. While these specific rare-earth compounds, known as heavy fermion superconductors, have been known for decades, making usable quantum technologies out of them has remained a critically ...
A new study suggests sea discoloration data obtained from satellite images as a novel criterion in predicting if eruption looms for an underwater volcano.
There have been frequent eruptions of submarine volcanoes in recent years. The past two years alone recorded the explosions of Anak Krakatau in Indonesia, White Island in New Zealand, and Nishinoshima Island in Japan. Observing signs of volcanic unrest is crucial in providing life-saving information and ensuring that air and maritime travel are safe in the area.
Although predicting when a volcano will erupt can be difficult as each behaves differently, scientists are on the lookout for these telltale signs: heightened seismic activity, expansion of magma pools, increases in volcanic gas release, ...
A pioneering cultivation strategy that recreates a mangrove environment in the lab has enabled identification of novel bacteria residing in Red Sea mangroves and will help improve understanding of mangrove ecosystem stability, resilience and sustainability.
Mangroves are highly productive, dominant coastal ecosystems that line between 60-70 percent of the world's tropical and subtropical coastlines. They harbor diverse microbial communities thought to make up 80 percent of the ecosystem's biomass. Many of the microbial species, families and taxa are unknown to science.
The cultivation strategy was developed by a team of KAUST researchers, including Fatmah Sefrji and Ramona Marasco.
"Red Sea mangroves are particularly interesting because they represent an extreme and unique ...