INFORMATION:
Article Title: The role of race and scientific trust on support for COVID-19 social distancing measures in the United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0254127
The role of race and scientific trust on support for COVID-19 social distancing
2021-07-09
(Press-News.org) Trust in science - but not trust in politicians or the media - significantly raises support across US racial groups for COVID-19 social distancing.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
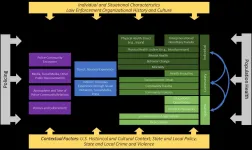
Study model explores impact of police action on population health
2021-07-09
A specific police action, an arrest or a shooting, has an immediate and direct effect on the individuals involved, but how far and wide do the reverberations of that action spread through the community? What are the health consequences for a specific, though not necessarily geographically defined, population?
The authors of a new UW-led study looking into these questions write that because law enforcement directly interacts with a large number of people, "policing may be a conspicuous yet not-well understood driver of population health."
Understanding how law enforcement impacts the mental, physical, social and structural health and wellbeing of a community is a complex challenge, involving many academic and research ...
Neonatal meningitis: the immaturity of microbiota and epithelial barriers implicated
2021-07-09
Meningitis is associated with high mortality and frequently causes severe sequelae. Newborn infants are particularly susceptible to this type of infection; they develop meningitis 30 times more often than the general population. Group B streptococcus (GBS) bacteria are the most common cause of neonatal meningitis, but they are rarely responsible for disease in adults. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur, in collaboration with Inserm, Université de Paris and Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital (AP-HP), set out to explain neonatal susceptibility to GBS meningitis. In a mouse model, they demonstrated that the immaturity of both the gut microbiota and epithelial barriers such as the gut and choroid plexus play a role in the susceptibility of newborn infants to bacterial meningitis caused by ...
Sensitivity of the Delta variant to sera from convalescent and vaccinated individuals
2021-07-09
The Delta variant was detected for the first time in India in October 2020 and has since spread throughout the world. It is now dominant in many countries and regions (India, the UK, Portugal, Russia, etc.) and is predicted to be the most prevalent variant in Europe within weeks or months. Epidemiological studies have shown that the Delta variant is more transmissible than other variants. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur (CNRS joint unit), in collaboration with Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou (part of the Paris Public Hospital Network or AP-HP), Orléans Regional Hospital and Strasbourg University Hospital, studied the sensitivity of the Delta variant ...
Dying cells protect their neighbors to maintain tissue integrity
2021-07-09
To enable tissue renewal, human tissues constantly eliminate millions of cells, without jeopardizing tissue integrity, form and connectivity. The mechanisms involved in maintaining this integrity remain unknown. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur and the CNRS today revealed a new process which allows eliminated cells to temporarily protect their neighbors from cell death, thereby maintaining tissue integrity. This protective mechanism is vital, and if disrupted can lead to a temporary loss of connectivity. The scientists observed that when the mechanism is deactivated, the simultaneous elimination of ...
Huge volcanic eruption disrupted climate but not human evolution
2021-07-09
New Brunswick, N.J. (July 9, 2021) -- A massive volcanic eruption in Indonesia about 74,000 years ago likely caused severe climate disruption in many areas of the globe, but early human populations were sheltered from the worst effects, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The findings appear in the journal PNAS.
The eruption of the Toba volcano was the largest volcanic eruption in the past two million years, but its impacts on climate and human evolution have been unclear. Resolving this debate is important for understanding environmental changes during a key interval in human evolution.
"We were able to use a large number of climate model simulations to resolve what seemed like a paradox," said lead author Benjamin Black, an assistant professor in the Department ...
New 3D printable phase-changing composites can regulate temperatures inside buildings
2021-07-09
Changing climate patterns have left millions of people vulnerable to weather extremes. As temperature fluctuations become more commonplace around the world, conventional power-guzzling cooling and heating systems need a more innovative, energy-efficient alternative, and in turn, lessen the burden on already struggling power grids.
In a new study, researchers at Texas A&M University have created novel 3D printable phase-change material (PCM) composites that can regulate ambient temperatures inside buildings using a simpler and cost-effective manufacturing process. Furthermore, these composites can be added to building materials, like paint, or 3D printed as decorative home accents to seamlessly integrate into different indoor environments.
"The ability to integrate phase-change materials ...
Combining gamification, cash incentive increases veterans' exercise
2021-07-09
We know that turning goals into a game can increase people's physical activity. We also know that financial incentives can be effective, especially when they're framed in a way where people lose money if they don't reach their goals. But a new Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania study adds to evidence that combining the two can result in significant gains.
Researchers affiliated with Penn Medicine's Center for Health Care Innovation showed that a group of veterans who were overweight or obese and receiving care from a Philadelphia hospital were able to increase their daily step counts by more than 1,200, on average, when their personalized goals were paired with a game in which they received support from a buddy, all while they stood ...
Disparities in vaccine acceptance among adults in China
2021-07-09
What The Study Did: This survey study examined disparities in COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and approaches to improve vaccination rates among adults in China.
Authors: Jingjing Ma, Ph.D., of Peking University in Beijing, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1466)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked ...
Changes in care delivery during COVID-19
2021-07-09
What The Study Did: Researchers characterized clinical content of ambulatory care among office-based compared with telemedicine visits in the United States before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: G. Caleb Alexander, M.D., M.S., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1529)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is ...
Researchers examine burden of electronic health record on primary care clinicians
2021-07-09
Primary care clinicians face a heavy administrative burden, spending significantly more time using the electronic health record (EHR) than their counterparts in other specialties. With studies demonstrating high rates of burnout among primary care clinicians, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and collaborators set out to examine how different types of primary care clinicians interface with the EHR. They found that general internal medicine and family medicine clinicians spent an average of two hours actively using the EHR each day, while general pediatric clinicians actively ...