(Press-News.org) In 2015, 170 countries worldwide adopted the Paris Agreement, with the goal limiting the average global temperature increase to 1.5°C. Following the agreement, many countries and cities proposed targets for greenhouse gas mitigation. However, the UNEP Emissions Gap Report 2020 shows that, without drastic and strict actions to mitigate the climate crisis, we are still heading for a temperature increase of more than 3°C by the end of the 21st century.
A new study published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Cities presents the first global balance sheet of greenhouse gasses (GHGs) emitted by major cities around the world. The aim was to research and monitor the effectiveness of historical GHG reduction policies implemented by 167 globally distributed cities that are at different developmental stages.
While only covering 2% of the Earth's surface, cities are big contributors to the climate crisis. But current urban GHG mitigation targets are not sufficient to achieve global climate change targets by the end of this century. "Nowadays, more than 50% of the global population resides in cities. Cities are reported to be responsible for more than 70% of GHG emissions, and they share a big responsibility for the decarbonization of the global economy. Current inventory methods used by cities vary globally, making it hard to assess and compare the progress of emission mitigation over time and space," says co-author Dr Shaoqing Chen, of Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Key findings
1. The top 25 cities accounted for 52% of the total urban GHG emissions.
2. Cities in Europe, Australia, and the US had significantly higher per capita emissions than cities in developing areas.
3. Stationary energy and transportation were the two main sources of emissions.
4. Of the 42 cities that had time-series traceable data, 30 decreased the annual GHG emissions over the study period. Though in several cities, there was an increase in emissions.
5. 113 out of the 167 set varying types of GHG emission reduction targets, while 40 have set carbon neutrality goals.
The biggest polluters
First, the authors conducted sector-level GHG emission inventories of the 167 cities - from metropolitan areas such as Durban, South Africa, to cities such as Milan, Italy. Then, they analyzed and compared the carbon reduction progresses of the cities based on the emission inventories recorded in different years (from 2012 to 2016). Lastly, they assessed the cities' short-, mid-, and long-term carbon mitigation goals. The cities were chosen from 53 countries (in North and South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Oceania) and were selected based on representativeness in urban sizes and regional distribution. The degree of development was distinguished based on whether they belonged to developed and developing countries according to the UN classification criteria.
The results showed that both developed and developing countries have cities with high total GHG emissions, but that megacities in Asia (such as Shanghai in China and Tokyo in Japan) were especially important emitters. The inventory of per capita emissions showed that cities in Europe, the US, and Australia had significantly higher emissions than most cities in developing countries. China, classified here as a developing country, also had several cities where per capita emissions matched those of developed countries. It is important to note that many developed countries outsource high carbon production chains to China, which increases export-related emissions for the latter.
The researchers also identified some of the most important sources of greenhouse gas emissions. "Breaking down the emissions by sector can inform us what actions should be prioritized to reduce emissions from buildings, transportation, industrial processes and other sources," says Chen. Stationary energy - which includes emissions from fuel combustion and electricity use in residential and institutional buildings, commercial buildings, and industrial buildings - contributed between 60 and 80% of total emissions in North American and European cities. In one third of the cities, more than 30% of total GHG emissions were from on-road transportation. Meanwhile, less than 15% of total emissions came from railways, waterways, and aviation.
Lastly, the findings show that the levels of emissions increase and decrease varied between the cities over the study period. For 30 cities, there was a clear emission decrease between 2012 and 2016. The top four cities with the largest per capita reduction were Oslo, Houston, Seattle, and Bogotá. The top four cities with the largest per capita emissions increase were Rio de Janeiro, Curitiba, Johannesburg, and Venice.
Policy recommendations
Of the 167 cities, 113 have set varying types of GHG emission reduction targets, while 40 have set carbon neutrality goals. But this study joins many other reports and research that show that we are a long way off achieving the goals set by the Paris Agreement.
Chen and colleagues make three key policy recommendations. First: "Key emitting sectors should be identified and targeted for more effective mitigation strategies. For example, the differences in the roles that stationary energy use, transportation, household energy use, and waste treatments play for cities should be assessed."
Second, development of methodologically consistent global GHG emission inventories is also needed, to track the effectiveness of urban GHG reductions policies. Lastly: "Cities should set more ambitious and easily-traceable mitigation goals. At a certain stage, carbon intensity is a useful indicator showing the decarbonization of the economy and provides better flexibility for cities of fast economic growth and increase in emission. But in the long run, switching from intensity mitigation targets to absolute mitigation targets is essential to achieve global carbon neutrality by 2050."
INFORMATION:
A new study published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, has identified unmet social needs in women with gynecologic cancer that could be addressed to improve care for patients and lessen disparities. For example, identifying patients who reported needing help with reading hospital materials resulted in the use of a cancer care navigator who provided patient education and support, facilitating physician-patient communication and adherence to care recommendations.
The prospective survey-based ...
Oncotarget published "Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia" which reported that the authors evaluated the therapeutic potential of the highly-selective MNK1/2 inhibitor Tomivosertib on AML cells.
Tomivosertib was highly effective at blocking eIF4E phosphorylation on serine 209 in AML cells.
Moreover, combination of Tomivosertib and Venetoclax resulted in synergistic anti-leukemic responses in AML cell lines.
Mass spectrometry studies identified novel putative MNK1/2 interactors, while in parallel studies we demonstrated that MNK2 - RAPTOR - mTOR complexes are not disrupted by Tomivosertib.
Overall, these Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent ...
Oncotarget published "Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates Tau Post-translational modifications and cytoskeletal network" which reported that the chemical modulators of Tau PTMs, such as kinase inhibitors and antibody-based therapeutics, have been developed, but natural compounds, as modulators of Tau PTMs are not much explored.
These authors applied biophysical and biochemical techniques like fluorescence kinetics, oligomerization analysis and transmission electron microscopy to investigate the impact of EGCG on Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG inhibited methyl glyoxal -induced Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG potently inhibited MG-induced advanced glycation endproducts formation in neuroblastoma cells as well modulated the localization ...
Oncotarget published "A novel E2F1-regulated lncRNA, LAPAS1, is required for S phase progression and cell proliferation" which reported that long non-coding RNAs are major regulators of many cellular processes, including cell cycle progression and cell proliferation.
Inhibition of LAPAS1 expression increases the percentage of S phase cells, and its silencing in synchronized cells delays their progression through S phase.
In agreement with its suggested role in cell cycle progression, prolonged inhibition of LAPAS1 attenuates proliferation of human cancer cells.
Importantly, knockdown of SPNS2 rescues the effect of LAPAS1 silencing on cell cycle ...
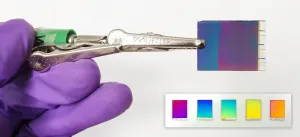
Imagine sitting out in the sun, reading a digital screen as thin as paper, but seeing the same image quality as if you were indoors. Thanks to research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, it could soon be a reality. A new type of reflective screen - sometimes described as 'electronic paper' - offers optimal colour display, while using ambient light to keep energy consumption to a minimum.
Traditional digital screens use a backlight to illuminate the text or images displayed upon them. This is fine indoors, but we've all experienced the difficulties of viewing such screens in bright sunshine. Reflective screens, however, attempt to use the ambient light, mimicking the way our eyes ...
Researchers have identified a specialized protein that appears to help prevent tumor cells from entering the bloodstream and spreading to other parts of the body.
"We have discovered that this protein, TRPM7, senses the pressure of fluid flowing in the circulation and stops the cells from spreading through the vascular system," said Kaustav Bera, a Johns Hopkins University PhD candidate in chemical and biomolecular engineering and a lead author of the study, which was done with colleagues at the University of Alberta and Universitat Pompeu Fabra.
"We found that metastatic tumor cells have markedly reduced levels of this sensor protein, and that is why they ...
Men over 60 with low-risk prostate cancer could spend ten years with no active treatment, have a better sex life as a result, yet still be very unlikely to die from the disease, new research has found.
The findings come from two new studies looking at 'active surveillance' of prostate cancer - when the disease is closely monitored but not treated - presented at the European Association of Urology congress, EAU21, today.
The first uses data from Sweden's National Prostate Cancer Register, which has information on virtually every man diagnosed with the disease in that country since 1998 - 23,649 of whom went on active surveillance. ...
Care homes need to be vigilant for outbreaks of COVID-19, even after residents have received two doses of the vaccine, according to new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year.
Long-term care facilities, such as care homes with elderly residents with multiple underlying conditions, are at high risk of COVID-19 outbreaks and many vaccination campaigns have initially focused on care home residents and the staff looking after them. An outbreak in a French care home, however, raises questions about how effective the vaccine is in the elderly.
Martin Martinot, of ...
COVID-19 outbreaks in French nursing homes almost certainly started in staff - and none of measures put in place stopped the virus from taking hold, new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year, shows.
Residents of long-term care facilities represent a small fraction of the general population but account for a disproportionate number of SARS-CoV-2-related deaths in many countries.
In France, 5,203 outbreaks (of 1 case or more) were reported in nursing homes during the first wave of COVID-19. In the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, there were 651 outbreaks, 3,885 residents had confirmed COVID-19 infection and 1,772 ...
The flu vaccine may provide vital protection against COVID-19, new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year, concludes.
An analysis of patient data from around the world strongly suggests that the annual flu shot reduces the risk of stroke, sepsis and DVT in patients with COVID-19. Patients with COVID-19 who had been vaccinated against flu were also less likely to visit the emergency department and be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU).
Immunising the world against COVID-19 is a daunting challenge and, although production and distribution of vaccines increases daily, some countries are not expected to vaccinate large numbers of their population ...