(Press-News.org) The city park may be an artificial ecosystem but it plays a key role in the environment and our health, the first global assessment of the microbiome in city parks has found.
The study, published in END
Every spot of green space counts
An international study of parks and gardens finds even the humble roadside verge plays an important role in the environment and for our health
2021-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
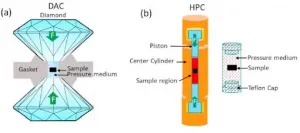
Reviewing pressure effects on iron-based high-temperature superconductors
2021-07-12
The discovery of iron-based superconductors with a relatively high transition temperature Tc in 2008 opened a new chapter in the development of high-temperature superconductivity.
The following decade saw a 'research boom' in superconductivity, with remarkable achievements in the theory, experiments and applications of iron-based superconductors, and in our understanding of the fundamental mechanism of superconductivity.
A UOW paper published last month reviews progress on high-pressure studies on properties of iron-based superconductor (ISBC) families.
FLEET PhD student Lina Sang (University of Wollongong) was first author on the Materials Today Physics review paper, investigating ...
Two-thirds of romantic couples start out as friends, study finds
2021-07-12
Movies and television often show romance sparking when two strangers meet. Real-life couples, however, are far more likely to begin as friends. Two-thirds of romantic relationships start out platonically, a new study in Social Psychological and Personality Science finds.
This friends-first initiation of romance is often overlooked by researchers. Examining a sample of previous studies on how relationships begin, the authors found that nearly 75 percent focused on the spark of romance between strangers. Only eight percent centered on romance that develops among friends over time.
"There are a lot of people ...
Ecosystem destruction endangers local soy agriculture in Brazil
2021-07-12
Destroying tropical ecosystems and replacing them with soybeans and other crops has immediate and devastating consequences for soybeans, according to new peer-reviewed research in the journal World Development. With 35.8 million hectare currently under soy cultivation in Brazil, extreme heat--which adjacent tropical forests help keep in check--has reduced soybean income by an average of approximately US$100 per hectare per year.
The study, Conserving the Cerrado and Amazon biomes of Brazil protects the soy economy from damaging warming, shows that protecting the Amazon and Cerrado can prevent the sort of high temperatures that damages the productivity of crops--estimated to cost the sector US$3.55 billion.
Another recent study found annual agricultural losses associated ...
Study reveals ways to preserve employee morale during cost-cutting
2021-07-12
PULLMAN, Wash. - After cutbacks and layoffs, remaining employees were more likely to feel they were treated fairly if the companies invested in them - and morale was less likely to plunge, according to new research.
Those investments can include training for workers, team-building exercises or improving company culture. Even keeping workloads manageable after layoffs can help employees' job attitudes, according to the Journal of Organizational Behavior study.
"Whenever possible, cost-cutting is best combined with signals that people remain the firm's most prized asset," said Jeff Joireman, the study's co-author and a professor in Washington State University's Carson College of Business.
Researchers reviewed 137 previous studies examining job attitudes before, during and after cost-cutting ...
Humans can learn from animals and insects about impact of climate change
2021-07-12
If we pay closer attention to how birds, rabbits and termites transform their local living spaces in response to varying climate conditions, we could become much better at predicting what impact climate change will have on them in future.
This is according to a group of researchers* from the Universities of Montana and Wyoming in the United States, the University of Tours in France and Stellenbosch University (SU) in South Africa. They examined how animals' ability to respond to climate change likely depends on how well they modify their habitats, such as the way they build nests and burrows.
The findings of their study were published recently in the high-impact journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution.
"It's crucial that we continuously improve our ability to predict and mitigate the ...
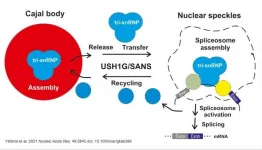
Remarkable new insights into the pathology of Usher syndrome
2021-07-12
Human Usher syndrome (USH) is the most common form of hereditary deaf-blindness. Sufferers can be deaf from birth, suffer from balance disorders, and eventually lose their eyesight as the disease progresses. For some 25 years now, the research group led by Professor Uwe Wolfrum of the Institute of Molecular Physiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has been conducting research into Usher syndrome. Working in cooperation with the group headed up by Professor Reinhard Lührmann at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen, his team has now identified a novel pathomechanism leading to Usher syndrome. They have discovered that the Usher syndrome type 1G protein SANS plays a crucial role in regulating ...
Giving a "tandem" boost to solar-powered water splitting
2021-07-12
Turning away from fossil fuels is necessary if we are to avert an environmental crisis due to global warming. Both industry and academia have been focusing heavily on hydrogen as a feasible clean alternative. Hydrogen is practically inexhaustible and when used to generate energy, only produces water vapor. However, to realize a truly eco-friendly hydrogen society, we need to be able to mass-produce hydrogen cleanly in the first place.
One way to do that is by splitting water via "artificial photosynthesis," a process in which materials called "photocatalysts" leverage solar energy to produce oxygen and hydrogen from water. However, the available photocatalysts are not yet where they need to be to make solar-powered water splitting economically feasible and scalable. ...
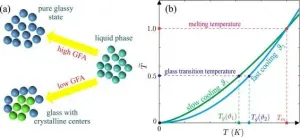
Theoretical model able to reliably predict low-temperature properties of compounds
2021-07-12
Co-authors Bulat Galimzyanov and Anatolii Mokshin (Department of Computational Physics) have developed a unique model that allows for a universal interpretation of experimental data on viscosity for systems of different types, while also proposing an alternative method for classifying materials based on a unified temperature scale.
The publication was funded by Russian Science Foundation's grant 'Theoretical, simulation and experimental studies of physical and mechanical features of amorphous systems with inhomogeneous local viscoelastic properties', guided by Professor Mokshin.
Using the developed viscosity model, scientists processed experimental data obtained for thirty different ...
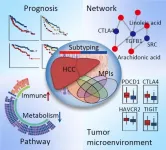
Study sheds light on precise personalized hepatocellular carcinoma medicine
2021-07-12
A research group led by Prof. PIAO Hailong from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) identified hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) subtypes with distinctive metabolic phenotypes through bioinformatics and machine learning methods, and elucidated the potential mechanisms based on a metabolite-protein interaction network and multi-omics data.
The study, published in Advanced Science on July 11, provides insights guiding precise personalized HCC medicine.
Metabolic reprogramming, which can promote rapid cell proliferation by regulating energy and nutrient metabolism, is considered to be one hallmark of cancer. It can impact other biological processes through complex metabolite-protein ...
Want to avoid running overuse injuries? Don't lean forward so much, says CU Denver study
2021-07-12
The ubiquitous overuse injuries that nag runners may stem from an unlikely culprit: how far you lean forward.
Trunk flexion, the angle at which a runner bends forward from the hip, can range wildly--runners have self-reported angles of approximately -2 degrees to upward of 25. A new study from the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
[Press-News.org] Every spot of green space countsAn international study of parks and gardens finds even the humble roadside verge plays an important role in the environment and for our health