INFORMATION:
Theoretical model able to reliably predict low-temperature properties of compounds
A paper by Kazan Federal University appeared in early access in Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids.
2021-07-12
(Press-News.org) Co-authors Bulat Galimzyanov and Anatolii Mokshin (Department of Computational Physics) have developed a unique model that allows for a universal interpretation of experimental data on viscosity for systems of different types, while also proposing an alternative method for classifying materials based on a unified temperature scale.
The publication was funded by Russian Science Foundation's grant 'Theoretical, simulation and experimental studies of physical and mechanical features of amorphous systems with inhomogeneous local viscoelastic properties', guided by Professor Mokshin.
Using the developed viscosity model, scientists processed experimental data obtained for thirty different types of systems: from simple quartz glass to complex organic compounds such as salol and propylene carbonate.
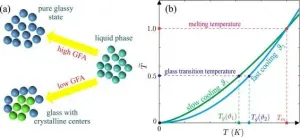
"The model reproduces quite accurately the experimental temperature dependences of the viscosity of such materials both near the melting point and near the glass transition temperature, below which the system freezes while still preserving the liquid structure. At the same time, the model uses only two adjustable parameters. In comparison, other existing models use at least three of such parameters. Therefore, this model can be used to more accurately predict the low-temperature physical parameters of materials based on high-temperature characteristics such as thermal conductivity and entropy at the melting point," comments Associate Professor Galimzyanov.
The results were obtained using an original method of temperature scaling.
"Earlier, we have developed a method to scale the temperature and the phase diagram of various types of systems. This gave a toll to compare the experimental temperature dependences of the viscosity of systems regardless of their preparation conditions. This temperature scale formed the basis of the developed viscosity model, which made it possible to minimize the number of adjustable parameters and improve the accuracy of data approximation," adds Anatolii Mokshin.
The research contributes to making corrections to the existing methods of classification for glass-forming materials and to establishing a unified viscosity model for various types of compounds.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study sheds light on precise personalized hepatocellular carcinoma medicine
2021-07-12
A research group led by Prof. PIAO Hailong from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) identified hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) subtypes with distinctive metabolic phenotypes through bioinformatics and machine learning methods, and elucidated the potential mechanisms based on a metabolite-protein interaction network and multi-omics data.
The study, published in Advanced Science on July 11, provides insights guiding precise personalized HCC medicine.
Metabolic reprogramming, which can promote rapid cell proliferation by regulating energy and nutrient metabolism, is considered to be one hallmark of cancer. It can impact other biological processes through complex metabolite-protein ...
Want to avoid running overuse injuries? Don't lean forward so much, says CU Denver study
2021-07-12
The ubiquitous overuse injuries that nag runners may stem from an unlikely culprit: how far you lean forward.
Trunk flexion, the angle at which a runner bends forward from the hip, can range wildly--runners have self-reported angles of approximately -2 degrees to upward of 25. A new study from the END ...
Heart risk 'calculators' overlook increased risk for people of South Asian ancestry
2021-07-12
DALLAS, July 12, 2021 -- People of South Asian ancestry have more than double the risk of developing heart disease compared to people of European ancestry, yet clinical risk assessment calculators used to guide decisions about preventing or treating heart disease may fail to account for the increased risk, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation.
About a quarter of the world's population (1.8 billion people) are of South Asian descent, and prior research has shown South Asians experience higher rates of heart disease compared to people of most other ethnicities.
To better understand the variables surrounding the heart disease risk for people of South Asian ancestry, researchers evaluated ...
Innovative gene therapy 'reprograms' cells to reverse neurological deficiencies
2021-07-12
A novel method of gene therapy is helping children born with a rare genetic disorder called AADC deficiency that causes severe physical and developmental disabilities. The study, led by researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, offers new hope to those living with incurable genetic and neurodegenerative diseases.
Research findings are published online in the journal Nature Communications.
This study describes the findings from the targeted delivery of gene therapy to midbrain to treat a rare ...
USC researchers discover better way to identify DNA variants
2021-07-12
USC researchers have achieved a better way to identify elusive DNA variants responsible for genetic changes affecting cell functions and diseases.
Using computational biology tools, scientists at the university's Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences studied "variable-number tandem repeats" (VNTR) in DNA. VNTRs are stretches of DNA made of a short pattern of nucleotides repeated over and over, like a plaid pattern shirt. Though they comprise but 3% of the human genome, the repetitive DNA governs how some genes are encoded and levels of proteins are produced in a cell, and account for most of the structural variation.
Current methods do not accurately detect the variations in genes in some repetitive ...
Scientists blueprint bacterial enzyme believed to "stealthily" suppress immune response
2021-07-12
Scientists have produced the first fine-detail molecular blueprints of a bacterial enzyme known as Lit, which is suspected to play a "stealthy" role in the progression of infection by reducing the immune response.
Blueprints such as these allow drug designers to uncover potential weaknesses in bacterial arsenals as they seek to develop new therapeutics that may help us win the war against antibiotic resistance.
The study, led by scientists from the School of Biochemistry and Immunology and the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) at Trinity College Dublin, has just been published by leading international journal Nature Communications.
Lipoproteins and their role in ...
A Trojan horse could help get drugs past our brain's tough border patrol
2021-07-12
Sclerosis, Parkinson's Disease, Alzheimer's and epilepsy are but a few of the central nervous system disorders. They are also very difficult to treat, since the brain is protected by the blood-brain barrier.
The blood-brain barrier works as a border wall between the blood and the brain, allowing just certain molecules to enter the brain. And whereas water and oxygen can get through, as can other substances such as alcohol and coffee. But it does block more than 99 percent of potentially neuroprotective compounds from reaching their targets in the brain.
Now, ...
Just 25 mega-cities produce 52% of the world's urban greenhouse gas emissions
2021-07-12
In 2015, 170 countries worldwide adopted the Paris Agreement, with the goal limiting the average global temperature increase to 1.5°C. Following the agreement, many countries and cities proposed targets for greenhouse gas mitigation. However, the UNEP Emissions Gap Report 2020 shows that, without drastic and strict actions to mitigate the climate crisis, we are still heading for a temperature increase of more than 3°C by the end of the 21st century.
A new study published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Cities presents the first global balance sheet of greenhouse gasses (GHGs) emitted by major cities around the world. The aim was to research and monitor the effectiveness of historical GHG reduction ...
Addressing social needs may help mitigate distress and improve the health of women with cancer
2021-07-12
A new study published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, has identified unmet social needs in women with gynecologic cancer that could be addressed to improve care for patients and lessen disparities. For example, identifying patients who reported needing help with reading hospital materials resulted in the use of a cancer care navigator who provided patient education and support, facilitating physician-patient communication and adherence to care recommendations.
The prospective survey-based ...
Oncotarget: Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia" which reported that the authors evaluated the therapeutic potential of the highly-selective MNK1/2 inhibitor Tomivosertib on AML cells.
Tomivosertib was highly effective at blocking eIF4E phosphorylation on serine 209 in AML cells.
Moreover, combination of Tomivosertib and Venetoclax resulted in synergistic anti-leukemic responses in AML cell lines.
Mass spectrometry studies identified novel putative MNK1/2 interactors, while in parallel studies we demonstrated that MNK2 - RAPTOR - mTOR complexes are not disrupted by Tomivosertib.
Overall, these Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Theoretical model able to reliably predict low-temperature properties of compoundsA paper by Kazan Federal University appeared in early access in Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids.