Scientists blueprint bacterial enzyme believed to "stealthily" suppress immune response
2021-07-12
(Press-News.org) Scientists have produced the first fine-detail molecular blueprints of a bacterial enzyme known as Lit, which is suspected to play a "stealthy" role in the progression of infection by reducing the immune response.
Blueprints such as these allow drug designers to uncover potential weaknesses in bacterial arsenals as they seek to develop new therapeutics that may help us win the war against antibiotic resistance.
The study, led by scientists from the School of Biochemistry and Immunology and the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) at Trinity College Dublin, has just been published by leading international journal Nature Communications.
Lipoproteins and their role in bacterial infection
Lipoproteins serve diverse functions in the bacterial cell. Some are essential for survival while some play an important role by engaging with the innate immune response of the host.
The growing list of enzymes responsible for building lipoproteins includes the recently discovered Lit (lipoprotein intramolecular transacylase), which creates a specific lipoprotein that "cools the immune response" - raising the likelihood that Lit enables the bacteria to gain a foothold in the host by stealth.
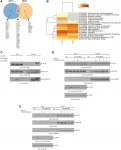
With a view to understanding how Lit functions at the molecular level, the Trinity-led team has just produced Lit's all-important, high-resolution crystal structure from Bacillus cereus - a common bacteria found in soil and food.
Combined with other analytical techniques, molecular dynamics simulations and quantum mechanics approaches, the team now has a detailed understanding of how it functions.
Professor Martin Caffrey, Fellow Emeritus (Trinity and TBSI), is the senior author of the research. Underlining its significance and potential societal impact, he said:
"We believe Lit is very likely a virulence factor, negatively impacting host immune response to infection. As such, it could well turn out to be an important target for the development of critically needed antibiotics against which resistance is much less likely to evolve. And it is no exaggeration to say that antibiotic resistance poses a genuine, growing threat to our society.
"With a high-resolution crystal structure and a strong foundation for understanding how it functions in bacterial cells, we are in a similar position to where we were four years ago when we published similar work concerning a related lipoprotein processing enzyme, known as lipoprotein signal peptidase II (or LspA). LspA is currently under intense scrutiny as an antibiotic target by several research groups - including ours in TBSI - and by a number of pharmaceutical companies."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by funding from Science Foundation Ireland, the Irish Research Council, the German Research Foundation, the European Union 's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sk?odowska-Curie grants agreement, and the Northern Ireland Department of Agriculture, Environment and Rural Affairs.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-12
Sclerosis, Parkinson's Disease, Alzheimer's and epilepsy are but a few of the central nervous system disorders. They are also very difficult to treat, since the brain is protected by the blood-brain barrier.
The blood-brain barrier works as a border wall between the blood and the brain, allowing just certain molecules to enter the brain. And whereas water and oxygen can get through, as can other substances such as alcohol and coffee. But it does block more than 99 percent of potentially neuroprotective compounds from reaching their targets in the brain.
Now, ...
2021-07-12
In 2015, 170 countries worldwide adopted the Paris Agreement, with the goal limiting the average global temperature increase to 1.5°C. Following the agreement, many countries and cities proposed targets for greenhouse gas mitigation. However, the UNEP Emissions Gap Report 2020 shows that, without drastic and strict actions to mitigate the climate crisis, we are still heading for a temperature increase of more than 3°C by the end of the 21st century.
A new study published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Cities presents the first global balance sheet of greenhouse gasses (GHGs) emitted by major cities around the world. The aim was to research and monitor the effectiveness of historical GHG reduction ...
2021-07-12
A new study published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, has identified unmet social needs in women with gynecologic cancer that could be addressed to improve care for patients and lessen disparities. For example, identifying patients who reported needing help with reading hospital materials resulted in the use of a cancer care navigator who provided patient education and support, facilitating physician-patient communication and adherence to care recommendations.
The prospective survey-based ...
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia" which reported that the authors evaluated the therapeutic potential of the highly-selective MNK1/2 inhibitor Tomivosertib on AML cells.
Tomivosertib was highly effective at blocking eIF4E phosphorylation on serine 209 in AML cells.
Moreover, combination of Tomivosertib and Venetoclax resulted in synergistic anti-leukemic responses in AML cell lines.
Mass spectrometry studies identified novel putative MNK1/2 interactors, while in parallel studies we demonstrated that MNK2 - RAPTOR - mTOR complexes are not disrupted by Tomivosertib.
Overall, these Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent ...
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates Tau Post-translational modifications and cytoskeletal network" which reported that the chemical modulators of Tau PTMs, such as kinase inhibitors and antibody-based therapeutics, have been developed, but natural compounds, as modulators of Tau PTMs are not much explored.
These authors applied biophysical and biochemical techniques like fluorescence kinetics, oligomerization analysis and transmission electron microscopy to investigate the impact of EGCG on Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG inhibited methyl glyoxal -induced Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG potently inhibited MG-induced advanced glycation endproducts formation in neuroblastoma cells as well modulated the localization ...
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "A novel E2F1-regulated lncRNA, LAPAS1, is required for S phase progression and cell proliferation" which reported that long non-coding RNAs are major regulators of many cellular processes, including cell cycle progression and cell proliferation.
Inhibition of LAPAS1 expression increases the percentage of S phase cells, and its silencing in synchronized cells delays their progression through S phase.
In agreement with its suggested role in cell cycle progression, prolonged inhibition of LAPAS1 attenuates proliferation of human cancer cells.
Importantly, knockdown of SPNS2 rescues the effect of LAPAS1 silencing on cell cycle ...
2021-07-12
Imagine sitting out in the sun, reading a digital screen as thin as paper, but seeing the same image quality as if you were indoors. Thanks to research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, it could soon be a reality. A new type of reflective screen - sometimes described as 'electronic paper' - offers optimal colour display, while using ambient light to keep energy consumption to a minimum.
Traditional digital screens use a backlight to illuminate the text or images displayed upon them. This is fine indoors, but we've all experienced the difficulties of viewing such screens in bright sunshine. Reflective screens, however, attempt to use the ambient light, mimicking the way our eyes ...
2021-07-12
Researchers have identified a specialized protein that appears to help prevent tumor cells from entering the bloodstream and spreading to other parts of the body.
"We have discovered that this protein, TRPM7, senses the pressure of fluid flowing in the circulation and stops the cells from spreading through the vascular system," said Kaustav Bera, a Johns Hopkins University PhD candidate in chemical and biomolecular engineering and a lead author of the study, which was done with colleagues at the University of Alberta and Universitat Pompeu Fabra.
"We found that metastatic tumor cells have markedly reduced levels of this sensor protein, and that is why they ...
2021-07-12
Men over 60 with low-risk prostate cancer could spend ten years with no active treatment, have a better sex life as a result, yet still be very unlikely to die from the disease, new research has found.
The findings come from two new studies looking at 'active surveillance' of prostate cancer - when the disease is closely monitored but not treated - presented at the European Association of Urology congress, EAU21, today.
The first uses data from Sweden's National Prostate Cancer Register, which has information on virtually every man diagnosed with the disease in that country since 1998 - 23,649 of whom went on active surveillance. ...
2021-07-12
Care homes need to be vigilant for outbreaks of COVID-19, even after residents have received two doses of the vaccine, according to new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year.
Long-term care facilities, such as care homes with elderly residents with multiple underlying conditions, are at high risk of COVID-19 outbreaks and many vaccination campaigns have initially focused on care home residents and the staff looking after them. An outbreak in a French care home, however, raises questions about how effective the vaccine is in the elderly.
Martin Martinot, of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists blueprint bacterial enzyme believed to "stealthily" suppress immune response