Training an AI eye on the moon
2021-07-12
(Press-News.org) A Moon-scanning method that can automatically classify important lunar features from telescope images could significantly improve the efficiency of selecting sites for exploration.
There is more than meets the eye to picking a landing or exploration site on the Moon. The visible area of the lunar surface is larger than Russia and is pockmarked by thousands of craters and crisscrossed by canyon-like rilles. The choice of future landing and exploration sites may come down to the most promising prospective locations for construction, minerals or potential energy resources. However, scanning by eye across such a large area, looking for features perhaps a few hundred meters across, is laborious and often inaccurate, which makes it difficult to pick optimal areas for exploration.
Siyuan Chen, Xin Gao and Shuyu Sun, along with colleagues from The Chinese University of Hong Kong, have now applied machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate the identification of prospective lunar landing and exploration areas.
"We are looking for lunar features like craters and rilles, which are thought to be hotspots for energy resources like uranium and helium-3 -- a promising resource for nuclear fusion," says Chen. "Both have been detected in Moon craters and could be useful resources for replenishing spacecraft fuel."
Machine learning is a very effective technique for training an AI model to look for certain features on its own. The first problem faced by Chen and his colleagues was that there was no labeled dataset for rilles that could be used to train their model.
"We overcame this challenge by constructing our own training dataset with annotations for both craters and rilles," says Chen. "To do this, we used an approach called transfer learning to pretrain our rille model on a surface crack dataset with some fine tuning using actual rille masks. Previous approaches require manual annotation for at least part of the input images --our approach does not require human intervention and so allowed us to construct a large high-quality dataset."
The next challenge was developing a computational approach that could be used to identify both craters and rilles at the same time, something that had not been done before.
"This is a pixel-to-pixel problem for which we need to accurately mask the craters and rilles in a lunar image," says Chen. "We solved this problem by constructing a deep learning framework called high-resolution-moon-net, which has two independent networks that share the same network architecture to identify craters and rilles simultaneously."
The team's approach achieved precision as high as 83.7 percent, higher than existing state-of-the-art methods for crater detection.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-12
Smoking among young teens has become an increasingly challenging and costly public healthcare issue. Despite legislation to prevent the marketing of tobacco products to children, tobacco companies have shrewdly adapted their advertising tactics to circumvent the ban and maintain their access to this impressionable--and growing--market share.
How they do it is the subject of a recent study led by Dr. Yael Bar-Zeev at Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU)'s Braun School of Public Health and Community Medicine at HU-Hadassah Medical Center. She also serves as Chair ...
2021-07-12
Forest clearance in Southeast Asia is accelerating, leading to unprecedented increases in carbon emissions, according to new research.
The findings, revealed by a research team including University of Leeds academics, show that forests are being cut down at increasingly higher altitudes and on steeper slopes in order to make way for agricultural intensification.
As a result, more than 400 million metric tons of carbon are released into the atmosphere every year as forests are cleared in the region, with that emissions figure increasing in recent ...
2021-07-12
A Sussex team - including university mathematicians - have created a new modelling toolkit which predicts the impact of COVID-19 at a local level with unprecedented accuracy. The details are published in the International Journal of Epidemiology, and are available for other local authorities to use online, just as the UK looks as though it may head into another wave of infections.
The study used the local Sussex hospital and healthcare daily COVID-19 situation reports, including admissions, discharges, bed occupancy and deaths.
Through the pandemic, the newly-published modelling has been used by local NHS and public ...
2021-07-12
Humans can easily identify sweet-tasting foods - and with pleasure. However, many carnivorous animals lack this ability, and whether birds, descendants of meat-eating dinosaurs, can taste sweet was previously unclear. An international team of researchers led by Max Planck Institute for Ornithology including Dr Simon SIN from Research Division for Ecology and Biodiversity, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), has now shown that songbirds, a group containing over 4,000 species, can sense sweetness regardless of their primary diets. The study highlights a specific event in the songbird ancestors ...
2021-07-12
In the vicinity of black holes, space is so warped that even light rays may curve around them several times. This phenomenon may enable us to see multiple versions of the same thing. While this has been known for decades, only now do we have an exact, mathematical expression, thanks to Albert Sneppen, student at the Niels Bohr Institute. The result, which even is more useful in realistic black holes, has just been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
You have probably heard of black holes -- the marvelous lumps of gravity from which not even light can escape. You may also have heard that space itself and even time behave oddly near black holes; space is warped.
In the vicinity of a black hole, space ...
2021-07-12
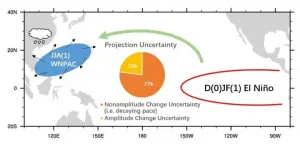
The impact of El Nino on East Asian climate under a warmer climate will be dominated by the change in El Nino decaying pace, according to a new paper published by a research team based in the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
The western North Pacific anomalous anticyclone (WNPAC) is a low-level atmospheric circulation system, linking up El Nino events with East Asian -western Pacific summer climate. The WNPAC can persist from El Nino mature phase in boreal winter to the upcoming summer, bringing abundant moisture to enhance the precipitation over East Asia. How the WNPAC will change in the future concerns millions of ...
2021-07-12
July 12, New Delhi - Women who received free meals in primary school have children with improved linear growth, according to a new study by researchers at the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI).
India is home to the highest number of undernourished children and the largest school feeding program in the world--the Mid-Day Meal (MDM) scheme--yet long-term program benefits on nutrition are unknown. As school feeding programs target children outside the highest-return "first 1000-days" window spanning from conception until a child's second birthday, they have not been a focal point in the global agenda to address stunting. School meals benefit education and nutrition in participants, but ...
2021-07-12
Ecologists from the Conservation Forensics Laboratory of the Research Division for Ecology and Biodiversity at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) have applied stable isotope techniques to determine whether birds in the pet trade are captive or wild-caught, a key piece of evidence required in many cases to determine whether a trade is legal or not. They have applied this technique to the yellow-crested cockatoo (Cacatua sulphurea, YCC), a critically endangered species from Indonesia/Timor-Leste with a global population of fewer than 2,500, according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Threatened by overexploitation for the pet trade, Hong Kong has a sizeable ...
2021-07-12
July 12, 2021-- A new study sheds light on how the specter of dementia and chronic pain reduce people's desire to live into older ages. Among Norwegians 60 years of age and older the desire to live into advanced ages was significantly reduced by hypothetical adverse life scenarios with the strongest effect caused by dementia and chronic pain, according to research conducted at the Robert N. Butler Columbia Aging Center based at the Columbia Mailman School of Public Health.
The paper is among the first to study Preferred Life Expectancy (PLE) based on hypothetical health and living conditions. The findings are published ...
2021-07-12
A new University of Arizona Health Sciences study found women on hormone therapy were up to 58% less likely to develop neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease, and reduction of risk varied by type and route of hormone therapy and duration of use. The findings could lead to the development of a precision medicine approach to preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
The study, published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions, found that women who underwent menopausal hormone therapy for six years or greater were 79% less likely to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Training an AI eye on the moon