(Press-News.org) For 30 years, University of Tokyo Associate Professor Hisayoshi Nozaki has traveled an hour west of Tokyo to visit the Sagami River and collect algal samples to understand how living things evolved different sexes. Through new analysis of samples collected in 2007 and 2013 from dam lakes along the river, Lake Sagami and Lake Tsukui, researchers identified a species of freshwater algae that evolved three different sexes, all of which can breed in pairs with each other.
This phenomenon of three sexes is slightly different from hermaphroditism. In species that normally have two sexes, a hermaphroditic individual who can produce both the male and female sex cells usually exists due to unusual gene expression. Many plants and some invertebrate species have three sexes due to normal gene expression, but this is the first time a species of algae or fungi has been identified with three sexes.
The threes sexes of the Pleodorina starrii algae are male, female, and a third sex that researchers call bisexual in reference to the fact that it can produce both male and female sex cells in a single genotype and exists due to normal expression of the species' genes. These algae are 32- or 64-celled organisms and have small mobile (male) and large immobile (female) sex cells.
"It seems very uncommon to find a species with three sexes, but in natural conditions, I think it may not be so rare," said Nozaki, the last author of the research paper published in Evolution.
Evoluntionarily ancient living things have sex cells that are similar in appearance and known as plus or minus, rather than male or female. More recently evolved species usually have dramatic differences between the sex cells, like the large egg and small spermatozoa of humans.
Nozaki and his colleagues are interested in Pleodorina starrii because it and its close evolutionary cousins use different sex systems, so they are useful models to study the genetics of how sex evolved. P. starrii had been identified decades prior, but had not been studied in detail.
In the lab, researchers can watch green P. starrii cells grow in spherical colonies with other individuals of their sex. Male colonies are recognizable by the clear packets of sperm they release into the water. The sperm packets swim until they hit a female colony, then split up into individual sperm cells that enter individual female cells and combine to produce a new generation.
Researchers separate colonies and then deprive them of nutrients to force them to reproduce sexually. In isolation, colonies reproduce asexually, forming cloned colonies of their same genotype. Isolated colonies of one sex can be mixed with isolated colonies of another sex and the ratio of their offsprings' sexes can be useful clues for researchers to understand the genetics of sex determination.
In 2006, Nozaki and other University of Tokyo experts were the first to find a male-specific gene in P. starrii, which they named OTOKOGI, a Japanese word meaning "manly." In 2010, they found a group of female-only genes and named them HIBOTAN, or "scarlet peony," after a 1960s film franchise where the lead female character had a red flower tattoo.
After genetic analysis and more mating trials, researchers eventually concluded that P. starrii has a "bisexual-factor" gene that is likely located on a chromosome separate from the OTOKOGI and HIBOTAN sex genes. Cells in genetically bisexual P. starrii possess both OTOKOGI and bisexual-factor genes, but they can produce normal male or female colonies when they reproduce sexually with other P. starrii colonies.
Genetically male P. starrii have only the OTOKOGI male-type gene and genetically female can have either only the female-type HIBOTAN genes or both HIBOTAN and the bisexual-factor genes.
More experiments are needed to understand genes in more detail, but researchers suspect that the bisexual factor may only be active in the presence of the "manly" OTOKOGI.
"This finding was possible because of our very long-term experience of going on field collection trips and our practice growing and studying algae. Continued, long-term studies are very important to unveil the true nature of species in the natural world," Nozaki commented.
INFORMATION:
Research Publication
Kohei Takahashi, Hiroko Kawai-Toyooka, Ryo Ootsuki, Takashi Hamaji, Yuki Tsuchikane, Hiroyuki Sekimoto, Tetsuya Higashiyama, and Hisayoshi Nozaki. 12 July 2021. Three sex phenotypes in a haploid algal species give insights into the evolutionary transition to a self-compatible mating system. Evolution. DOI: 10.1111/evo.14306
https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.14306
Related Links
Laboratory of Origin of Eukaryote Biodiversity (Japanese only): http://www.bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~tayousei/index.html
Department of Biological Sciences: http://www.bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/english/
Graduate School of Science: https://www.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Research Contact
Associate Professor Hisayoshi Nozaki
Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033
Tel: +81-03-5841-4271
Email: nozaki@bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press Officer Contact
Ms. Caitlin Devor
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 133-8654, JAPAN
Tel: +81-080-9707-8178
Email: press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at http://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
Funders
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
China's first meteorological satellite launched in 1988. It was named Fengyun, which roughly translates to "wind and cloud". Since then, 17 more Fengyun meteorological satellites were launched, with seven still in operation, to monitor Earth's wind, clouds and, more recently, extreme weather events such as hurricanes and wildfires. With more than 30 years of Earth observational data freely available to international partners, the Fengyun Meteorological Satellite program works as part of Earth's operational observation system, along with the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration satellites and Europe's polar orbiting meteorological satellite series to provide ...
RUDN University mathematicians have developed a model for calculating the density of 5G stations needed to achieve the required network parameters. The results are published in Computer Communications.
Network slicing (NS) is one of the key technologies that the new 5G communication standard relies on. Several virtual networks, or layers, are deployed on the same physical infrastructure (the same base stations). Each layer is allocated to a separate group of users, devices, or applications. To slice the network, one need the NR (New Radio) technology, which operates on millimetre waves. Most of the research in this area is aimed at creating an infrastructure of NR stations ...
"All living beings, including us, depend on photosynthesis," says Prof. Wataru Sakamoto of the Institute of Plant Science and Resources at Okayama University, Japan, as he begins to explain the core concepts behind a recent breakthrough in understanding plant physiology, which he was involved in. "Photosynthesis produces the energy needed to sustain plants and the oxygen we breathe. This reaction occurs in two steps, the first of which involves capturing light energy
and producing oxygen. This step takes place in a cell organelle in the plant cells called the chloroplast: specifically, ...
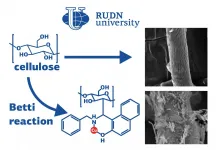
RUDN and Shahid Beheshti University (SBU) chemist proposed a protocol for converting cellulose into a catalyst for the synthesis of oxadiazoles. The new approach makes the catalyst 3 times more stable compared to the same catalyst obtained by the traditional method. The results are published in Carbohydrate Polymers
One of the directions of green chemistry is the biopolymers functionalization. Chemists modify polymers obtained from plants and animals -- they add functional molecular groups to them to get useful substances. For example, the catalysts for oxadiazoles synthesis are created from cellulose. They are necessary to produce polymers, dyes, medicines, and photographic ...
Tel Aviv University's new and groundbreaking technology inspires hope among people who have lost their sense of touch in the nerves of a limb following amputation or injury. The technology involves a tiny sensor that is implanted in the nerve of the injured limb, for example in the finger, and is connected directly to a healthy nerve. Each time the limb touches an object, the sensor is activated and conducts an electric current to the functioning nerve, which recreates the feeling of touch. The researchers emphasize that this is a tested and safe technology that is suited to the human body and could be implanted anywhere inside of it once clinical trials will be done.
The technology was developed under the leadership of a team of experts from Tel Aviv University: Dr. Ben M. Maoz, ...
For quite some time, farmers and researchers have been focusing on how to bind carbon to soil. Doing so makes food crops more nutritious and increases yields.
However, because carbon is converted into CO2 when it enters the atmosphere, there is a significant climate benefit to capturing carbon in soil as well.
Too much carbon finds its way into the atmosphere. Should we fail to reverse this unfortunate trend, we will fail to achieve the Paris Agreement's goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 40 percent by 2030, according to CONCITO, Denmark's Green Think Tank.
As such, it is important to find new ways of sequestering carbon in soil. This ...
A Moon-scanning method that can automatically classify important lunar features from telescope images could significantly improve the efficiency of selecting sites for exploration.
There is more than meets the eye to picking a landing or exploration site on the Moon. The visible area of the lunar surface is larger than Russia and is pockmarked by thousands of craters and crisscrossed by canyon-like rilles. The choice of future landing and exploration sites may come down to the most promising prospective locations for construction, minerals or potential energy resources. However, scanning by eye across such a large area, looking for features perhaps a few hundred meters across, is laborious and often inaccurate, which makes it difficult ...
Smoking among young teens has become an increasingly challenging and costly public healthcare issue. Despite legislation to prevent the marketing of tobacco products to children, tobacco companies have shrewdly adapted their advertising tactics to circumvent the ban and maintain their access to this impressionable--and growing--market share.
How they do it is the subject of a recent study led by Dr. Yael Bar-Zeev at Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU)'s Braun School of Public Health and Community Medicine at HU-Hadassah Medical Center. She also serves as Chair ...
Forest clearance in Southeast Asia is accelerating, leading to unprecedented increases in carbon emissions, according to new research.
The findings, revealed by a research team including University of Leeds academics, show that forests are being cut down at increasingly higher altitudes and on steeper slopes in order to make way for agricultural intensification.
As a result, more than 400 million metric tons of carbon are released into the atmosphere every year as forests are cleared in the region, with that emissions figure increasing in recent ...
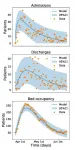
A Sussex team - including university mathematicians - have created a new modelling toolkit which predicts the impact of COVID-19 at a local level with unprecedented accuracy. The details are published in the International Journal of Epidemiology, and are available for other local authorities to use online, just as the UK looks as though it may head into another wave of infections.
The study used the local Sussex hospital and healthcare daily COVID-19 situation reports, including admissions, discharges, bed occupancy and deaths.
Through the pandemic, the newly-published modelling has been used by local NHS and public ...