How learning Braille changes brain structure over time
White matter reorganizes at specific time points to meet the needs of the brain
2021-07-12
(Press-News.org) Learning changes the brain, but when learning Braille different brain regions strengthen their connections at varied rates and time frames. A new study published in JNeurosci highlights the dynamic nature of learning-induced brain plasticity.
Learning new skills alters the brain's white matter, the nerve fibers connecting brain regions. When people learn to read tactile Braille, their somatosensory and visual cortices reorganize to accommodate the new demands. Prior studies only examined white matter before and after training, so the exact time course of the changes was not known.
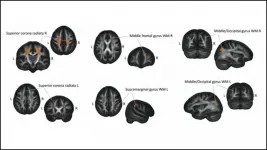
Molendowska and Matuszewski et al. used diffusion MRI to measure changes in the white matter strength of sighted adults as they learned Braille over the course of eight months. They took measurements at five time points: before the training, three times during, and once after. White matter in somatosensory areas strengthened steadily over the course of the training. But white matter in the visual cortex did not reorganize until halfway through the training, the point where the Braille words start to take on semantic meaning. White matter in both regions went back to the pre-training level two and a half months after the training ended. These results demonstrate white matter reorganizes itself across regions and different timeframes to meet the brain's needs.
INFORMATION:
Paper title: Temporal Dynamics of Brain White Matter Plasticity in Sighted Subjects During Tactile Braille Learning - a Longitudinal Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience's first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors' changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-12
Imagine sitting out in the sun, reading a digital screen as thin as paper, but seeing the same image quality as if you were indoors. Thanks to research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, it could soon be a reality. A new type of reflective screen - sometimes described as 'electronic paper' - offers optimal colour display, while using ambient light to keep energy consumption to a minimum.
Traditional digital screens use a backlight to illuminate the text or images displayed upon them. This is fine indoors, but we've all experienced the difficulties of viewing such screens in bright sunshine. Reflective screens, however, attempt to use the ambient light, mimicking the way our eyes respond to natural paper.
"For reflective screens to compete with the energy-intensive ...
2021-07-12
Smoking among young teens has become an increasingly challenging and costly public healthcare issue. Despite legislation to prevent the marketing of tobacco products to children, tobacco companies have shrewdly adapted their advertising tactics to circumvent the ban and maintain their access to this impressionable--and growing--market share.
How they do it is the subject of a recent study led by Dr. Yael Bar-Zeev at Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU)'s Braun School of Public Health and Community Medicine at HU-Hadassah Medical Center. She also serves as Chair of the Israeli Association for Smoking Cessation and Prevention, and teamed up with colleagues at HU and George Washington University. They published their findings in Nicotine and Tobacco Research.
Their study ...
2021-07-12
July 12, 2021 - Transitions between healthcare sites - such as from the hospital to home or to a skilled nursing facility - carry known risks to patient safety. Many programs have attempted to improve continuity of care during transitions, but it remains difficult to establish and compare the benefits of these complex interventions. An update on patient-centered approaches to transitional care research and implementation is presented in a supplement to the August issue of Medical Care, sponsored by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). Medical Care is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters ...
2021-07-12
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a new technique that can alter plant metabolism. Tested in tobacco plants, the technique showed that it could reduce harmful chemical compounds, including some that are carcinogenic. The findings could be used to improve the health benefits of crops.
"A number of techniques can be used to successfully reduce specific chemical compounds, or alkaloids, in plants such as tobacco, but research has shown that some of these techniques can increase other harmful chemical compounds while reducing the target compound," said De-Yu Xie, professor of plant and microbial biology at NC State and the corresponding author of a paper describing the research. "Our technology ...
2021-07-12
Snowmelt - the surface runoff from melting snow - is an essential water resource for communities and ecosystems. But extreme snow melt, which occurs when snow melts too rapidly over a short amount of time, can be destructive and deadly, causing floods, landslides and dam failures.
To better understand the processes that drive such rapid melting, researchers set out to map extreme snowmelt events over the last 30 years. Their findings are published in a new paper in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
"When we talk about snowmelt, people want to know the basic numbers, just like the weather, but no one has ever provided anything like that before. It's like if nobody told you the maximum and minimum temperature or record temperature in your city," said study co-author ...
2021-07-12
The transportation sector is the largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, and a lot of attention has been devoted to electric passenger vehicles and their potential to help reduce those emissions.
But with the rise of online shopping and just-in-time shipping, electric delivery fleets have emerged as another opportunity to reduce the transportation sector's environmental impact.
Though EVs represent a small fraction of delivery vehicles today, the number is growing. In 2019, Amazon announced plans to obtain 100,000 electric delivery vehicles. UPS has ordered 10,000 of them and FedEx plans to be fully electric by 2040.
Now, a study from University of Michigan ...
2021-07-12
New Brunswick, NJ--Children and adolescents with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) who are treated initially with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) and glucocorticoids have reduced risk for serious short-term outcomes, including cardiovascular dysfunction, than those who receive an initial treatment of IVIG alone, a new study finds.
MIS-C is a rare but serious--and sometimes fatal--condition associated with COVID-19, in which different body organs or systems become inflamed, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes, or gastrointestinal system. It can occur weeks after having COVID-19 and even if the child or caregivers did not know the child had been infected.
The new study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, analyzed treatment ...
2021-07-12
Taken together, the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microbes that live in our intestines form the gut microbiome, which plays a key role in the health of people and animals. In new research from the University of Minnesota, University of Notre Dame and Duke University, scientists found that genetics nearly always plays a role in the composition of the gut microbiome of wild baboons.
"In humans, research has shown that family members share a significant portion of microbes in their gut, but it's hard to answer if our microbiome is shaped more by nature, such as those ...
2021-07-12
A team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine found that a screening method known as untargeted metabolomics profiling can improve the diagnostic rate for inborn errors of metabolism, a group of rare genetic conditions, by about seven-fold when compared to the traditional metabolic screening approach.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, shows that untargeted metabolomics identifies many more disorders of greater variety as compared to traditional methods, including disorders for which there was not a clinically available biochemical test. The researchers hope that adoption of metabolomics to screen for inborn errors of metabolism will result in a more rapid, more efficient ...
2021-07-12
The sharp eyes of an eagle, the extraordinary hearing of an owl - to successfully find food, the eyes and ears of birds have adapted optimally to their living conditions. Until now, the sense of smell has played a rather subordinate role. When meadows are freshly mowed, storks often appear there to search for snails and frogs. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Animal Behavior in Radolfzell and the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Mainz have now studied the birds' behavior and discovered that the storks are attracted by the smell of the mown grass. Only storks that were downwind and could thus perceive the smell reacted to the mowing. The scientists also sprayed a meadow with a spray of green leaf scents released during mowing. Storks appeared here as well. This ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How learning Braille changes brain structure over time
White matter reorganizes at specific time points to meet the needs of the brain