Supermarket model to guide safer shopping amid pandemic
2021-07-13
(Press-News.org) A Skoltech team has developed a model for assessing infection risks for supermarket customers. The researchers believe that their model will help formulate scientifically backed rules for safe shopping during the pandemic. The paper was published in PLOS One.
The team included professor Maxim Fedorov, who serves as Skoltech's Vice President for Artificial Intelligence and Mathematical Modeling, and a research group led by professor Nikolai Brilliantov -- the Director of the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE).
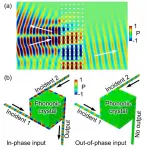
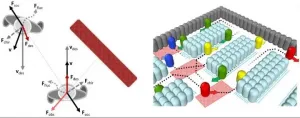
The composite model presented in the paper incorporates a social forces model that describes customer motions and interactions with other shoppers or obstacles and is known to realistically reproduce waiting lines and congestions in confined spaces, such as stairs, and customers' behavior during emergency evacuation. The approach is based on calculating several "forces" (see image), each describing a customer's tendency to maintain a comfortable speed, approach a target, avoid obstacles, etc.
Other components describe the purchasing strategy and retail space layout. Customers are known to behave differently, depending on the place they visit: a small shop, a supermarket, or a cafe. The team used customer behavior scenarios specific to supermarkets and several layouts with varying numbers of intersections and bottleneck widths. Finally, the team proposed a model of infection transmission by virus-containing aerosol droplets.
The researchers used their composite model in multivariate numerical simulations to assess infection risks depending on several factors, such as average customer density, social distancing, behavior scenarios, use of masks, and retail space geometry. It turned out that the infection rate is primarily determined by social distancing, and to a much lesser extent, by the supermarket layout or customer strategy.
Curiously enough, the team discovered that increasing customer density has only a slight positive effect on sales, so filling the store to the limit makes little sense not just epidemiologically but economically, too.
"The functional version of our model, which we have made publicly available, can be used to assess the effects of various factors on the risk of infection. For example, you can optimize a store's operations in the pandemic environment by controlling customer flow, relocating specific items, and reconfiguring the retail area. Although our selection of layouts did not reveal a noticeable effect of space configuration on infection spread, geometry may be an important factor in other cases," Alexey Tsukanov, a co-author of the paper, comments.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-13
LEXINGTON, Ky. (July 13, 2021) -- A recently published study co-authored by University of Kentucky Sanders-Brown Center on Aging researcher Justin Miller, Ph.D., identifies 11 rare candidate variants for Alzheimer's disease. Researchers found 19 different families in Utah that suffered from Alzheimer's disease more frequently than what is considered normal.
Miller, an assistant professor in the UK College of Medicine, was a co-first author for the study published in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia. The work was started at another university, however, some of the computational work was done after Miller arrived at UK in March.
For the study, genetic sequencing was conducted on two cousins from each of the 19 families. Miller says they then identified genetic variants that were shared ...
2021-07-13
Automation of technology has reshaped both the way in which we work and how we tackle problems. Thanks to the progress made in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) over the last few years, it is now possible to leave several tasks in the hands to machines and algorithms.
To highlight these advances, in the July 2021 issue, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica features six articles covering innovative applications of AI that can make our lives easier.
The first article, authored by researchers from Virginia Tech Mechanical Engineering Department ASIM Lab, USA, delves into an interesting mixture of topics: intelligent cars, machine learning, and electroencephalography (EEG). Self-driving cars have ...
2021-07-13
The concept of topological phases have not only revolutionized our understanding of physics or materials, but also brought about new possibilities for applications. Recent advances in higher-order topological insulators show that multiple forms of topological states can exist at boundaries of different dimensions, which greatly enriched the potentials for diverse applications. Interesting, the topological phases can also be implemented in artificial structures in photonics, electromagnetism, and acoustics.
A recent work co-led by Dr. Guancong Ma from Hong Kong Baptist University and Dr. Ying Wu from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology explored the controlling sound propagation with topological modes at different dimensions. They designed and built ...
2021-07-13
One in ten school-aged children in Australia have a current diagnosis of asthma. Every year, there are around 40,000 asthma hospitalisations and over 40 per cent of these are in children aged younger than 14 years old.
Approximately 80 per cent of these asthma-related hospital presentations are potentially avoidable through a standardised comprehensive care pathway for children with asthma.
These preventative measures include the use of evidence-based clinical guidelines, ensuring that there is an asthma action plan in place; regular follow-up with GP; provision of asthma education to parents/carers; and establishing ...
2021-07-13
A research group has produced fresh insights about the release of oxygen in lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for more robust and safer high-energy-density batteries.
Next-generation batteries that store more energy are critical if society is to achieve the UN's Sustainable Development Goals and realize carbon neutrality. However, the higher the energy density, the higher the likelihood of thermal runaway - the overheating of batteries that can sometimes result in a battery exploding.
Oxygen released from cathode active material is a trigger for thermal runaway, yet our knowledge of this process is insufficient.
Researchers from Tohoku University ...
2021-07-13
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common liver disorder worldwide and is present in approximately 25 percent of the world's population. Over 90 percent of obese, 60 percent of diabetic, and up to 20 percent of normal-weight people develop it. A key feature of the condition is the accumulation of fat in the liver. A liver can remain fatty without disturbing normal function; however, fat accumulations may progress into a so-called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - an aggressive form of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease combined with inflammation and sometimes fibrosis. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis can lead to further complications such as liver cirrhosis, primary liver ...
2021-07-13
Every year, thousands of dogs end up in a shelter in the Netherlands. Experts expect an increase in this number in the upcoming period, when people go back to the office after working from home during the corona crisis. Despite the good care of staff and volunteers, the shelter can be a turbulent experience for dogs. Researchers at Utrecht University investigated if dogs can adapt to their new environment based on their nocturnal activity.
Janneke van der Laan and fellow researchers from Utrecht University's Faculty of Veterinary Medicine compared the nocturnal activity of 29 shelter dogs and 29 pet dogs in their own homes - similar in breed, age and sex - with the help of night cameras and a small activity tracker on ...
2021-07-13
A KAIST research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, ...
2021-07-13
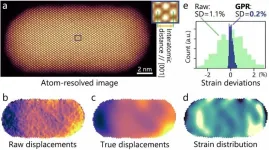
Ishikawa, Japan - Sometimes, a material's property, such as magnetism and catalysis, can change drastically owing to nothing more than minute changes in the separation between its atoms, commonly referred to as "local strains" in the parlance of materials science. A precise measurement of such local strains is, therefore, important to materials scientists.
One powerful technique employed for this purpose is "high-angle annular dark-field imaging" (HAADF), an approach within scanning transmission electron microscopy (a technique for mapping the position of atoms ...
2021-07-13
Museum specimens held in natural history collections around the world represent a wealth of underutilized genetic information due to the poor state of preservation of the DNA, which often makes it difficult to sequence. An international team, led by researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the Museum of Natural History of the City of Geneva (MHN), has optimized a method developed for analyzing ancient DNA to identify the relationships between species on a deep evolutionary scale. This work is published in the journal Genome Biology and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Supermarket model to guide safer shopping amid pandemic