Revealing the mystery behind the threat of non-alcoholic liver disease
2021-07-13
(Press-News.org) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common liver disorder worldwide and is present in approximately 25 percent of the world's population. Over 90 percent of obese, 60 percent of diabetic, and up to 20 percent of normal-weight people develop it. A key feature of the condition is the accumulation of fat in the liver. A liver can remain fatty without disturbing normal function; however, fat accumulations may progress into a so-called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - an aggressive form of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease combined with inflammation and sometimes fibrosis. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis can lead to further complications such as liver cirrhosis, primary liver cancer and eventually death.
Liver fibrosis is a strong predictor of long-term mortality in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The mechanisms underlying the progression from the comparatively benign fatty liver state to advanced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis are incompletely understood. "Understanding the mechanism by which this condition becomes life threatening is key in our quest for the discovery of therapeutic solutions and preventative measures," said Stephan Herzig.
Loss of identity results in dysfunction
The researchers used comparative genomics to analyze mechanisms that control the development and specialized functions of the most abundant cell type in the liver, the hepatocyte. "Our results demonstrated that during progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, hepatocytes suffer from partial identity loss, they are re-programmed," explained Anne Loft, first co-author of the article.
The hepatocyte reprogramming is tightly controlled by a network of proteins acting as molecular switches, so-called 'transcription factors'. Their activity results in the dysfunction of hepatocytes. The network of transcription factors that controls this process also plays a role in fibrosis progression. "These findings are important because they unravel the cellular mechanisms underlying non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Knowing about the role of the protein networks and the identity loss of hepatocytes gives us potential intervention targets for the development of effective therapies" says Ana Alfaro, first co-author of the article.
Future work
Based on these findings, it will now be possible to develop novel approaches to effectively target certain nodes in the protein network to prevent disease progression or even revert existing fibrosis, something that is still not possible to-date.
INFORMATION:
About the people
Stephan Herzig is Director of the Helmholtz Diabetes Center at Helmholtz Zentrum München. He holds the Chair for Molecular Metabolic Control at the Technical University of Munich and an Honorary Chair at Heidelberg University. Anne Loft and Ana Alfaro are first co-authors of the study at Helmholtz Zentrum München. All are part of the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD).
Helmholtz Zentrum München
Helmholtz Zentrum München is a research center with the mission to discover personalized medical solutions for the prevention and therapy of environmentally-induced diseases and promote a healthier society in a rapidly changing world. It investigates major diseases which develop from the interaction of lifestyle, environmental factors and personal genetic background, focusing particularly on diabetes mellitus, allergies and chronic lung diseases. Helmholtz Zentrum München is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,500 staff members. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany with more than 43,000 employees at 18 research centers.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-13
Every year, thousands of dogs end up in a shelter in the Netherlands. Experts expect an increase in this number in the upcoming period, when people go back to the office after working from home during the corona crisis. Despite the good care of staff and volunteers, the shelter can be a turbulent experience for dogs. Researchers at Utrecht University investigated if dogs can adapt to their new environment based on their nocturnal activity.
Janneke van der Laan and fellow researchers from Utrecht University's Faculty of Veterinary Medicine compared the nocturnal activity of 29 shelter dogs and 29 pet dogs in their own homes - similar in breed, age and sex - with the help of night cameras and a small activity tracker on ...
2021-07-13
A KAIST research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, ...
2021-07-13
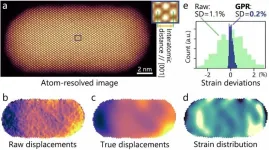
Ishikawa, Japan - Sometimes, a material's property, such as magnetism and catalysis, can change drastically owing to nothing more than minute changes in the separation between its atoms, commonly referred to as "local strains" in the parlance of materials science. A precise measurement of such local strains is, therefore, important to materials scientists.
One powerful technique employed for this purpose is "high-angle annular dark-field imaging" (HAADF), an approach within scanning transmission electron microscopy (a technique for mapping the position of atoms ...
2021-07-13
Museum specimens held in natural history collections around the world represent a wealth of underutilized genetic information due to the poor state of preservation of the DNA, which often makes it difficult to sequence. An international team, led by researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the Museum of Natural History of the City of Geneva (MHN), has optimized a method developed for analyzing ancient DNA to identify the relationships between species on a deep evolutionary scale. This work is published in the journal Genome Biology and ...
2021-07-13
Australian reptiles face serious conservation threats from illegal poaching fueled by international demand and the exotic pet trade.
In a new study in Animal Conservation, researchers from the University of Adelaide and the Monitor Conservation Research Society (Monitor) investigated the extent of illegal trade in a well-known Australian lizard: the shingleback, also known as the bobtail or sleepy lizard.
Using government records, media reports, and online advertisements, the researchers found clear evidence that many shinglebacks have been illegally poached from the wild and are smuggled overseas to be traded as pets.
Author and PhD Candidate Adam Toomes from the University of Adelaide says: ...
2021-07-13
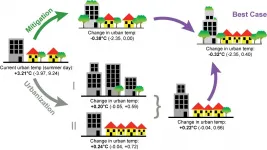
Low-income neighborhoods and communities with higher Black, Hispanic and Asian populations experience significantly more urban heat than wealthier and predominantly white neighborhoods within a vast majority of populous U.S. counties, according new research from the University of California San Diego's School of Global Policy and Strategy.
The analysis of remotely-sensed land surface temperature measurements of 1,056 U.S. counties, which have ten or more census districts, was recently published in the journal END ...
2021-07-13
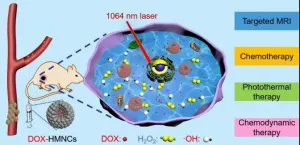
As a minimally invasive method for cancer therapy at precise locations, NIR-induced photothermal therapy (PTT) has drawn extensively attention. The therapeutic mechanism is the use of photothermal agents (PTAs) in the treatment of tumors,and its therapeutic effect happens only at the tumor site where both light-absorbent and localized laser radiation coexist.
The development of PTAs with NIR-II absorbance, ranging from 1000nm to 1700 nm, can efficiently improve their penetrating ability and therapeutic effects because of their high penetration depth in the body. Howerever, several disadvantages are associated with these NIR-II responsive PTAs for their ...
2021-07-13
Over the past years, graphene oxide membranes have been mainly studied for water desalination and dye separation. However, membranes have a wide range of applications such as the food industry. A research group led by Aaron Morelos-Gomez of Shinshu University's Global Aqua Innovation Center investigated the application of graphene oxide membranes for milk which typically creates dense foulant layers on polymeric membranes.
Graphene oxide membranes have the advantage to create a porous foulant layer, therefore, their filtration performance can be maintained better than commercial polymeric membranes. The unique chemical and ...
2021-07-13
Clinician well-being is imperative to providing high-quality patient care, yet clinician burnout continues to increase, especially over the last year due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Four leading cardiovascular organizations - the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, the European Society of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation - are calling for global action to improve clinician well-being in a joint opinion paper published today.
"Over the last several decades, there have been significant changes in health care with the expansion of technology, regulatory burden and clerical task loads. These developments have come at a cost to the ...
2021-07-13
A new population-based study looking at nearly 30 years of billing data demonstrates that sex-based differences in Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP) payments exists for Canadian ophthalmologists.
A team led by researchers and clinicians from the Donald K. Johnson Eye Institute, part of the Krembil Research Institute at University Health Network (UHN), studied 22,389 Ontario physicians across three decades and found a significant payment gap between female and male ophthalmologists even after accounting for age, and some practice differences. This disparity was more pronounced among ophthalmologists when compared to other surgical, medical procedural and medical non-procedural specialty groups.
"This is real and robust ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Revealing the mystery behind the threat of non-alcoholic liver disease