(Press-News.org) A new University of Iowa study suggests that metabolism of plant-based dietary substances by specific gut bacteria, which are lacking in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), may provide protection against the disease.
The study led by Ashutosh Mangalam, PhD, UI associate professor of pathology, shows that a diet rich in isoflavone, a phytoestrogen or plant-based compound that resembles estrogen, protects against multiple sclerosis-like symptoms in a mouse model of the disease. Importantly, the isoflavone diet was only protective when the mice had gut microbes capable of breaking down the isoflavones. The findings were published July 9 in Science Advances.
"Interestingly, previous human studies have demonstrated that patients with multiple sclerosis lack these bacteria compared to individuals without MS," Mangalam says. "Our new study provides evidence that the combination of dietary isoflavones and these isoflavone metabolizing gut bacteria may serve as a potential treatment for MS."
Isoflavones are found in soybeans, peanuts, chickpeas and other legumes. The study also found that mice fed the isoflavone diet have a microbiome that is similar to the microbiome found in healthy people and includes the bacteria which can metabolize isoflavones. Conversely, a diet lacking isoflavones promotes a microbiome in mice which is similar to one observed in patients with MS and lacks beneficial bacteria that can metabolize isoflavone.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease of the brain and spinal cord where the immune system attacks the protective coating surrounding nerve fibers. The symptoms of this disease include muscles weakness, balance issues, and problems with vision and thinking. While there are treatments that slow down the disease, there is currently no cure for MS.
Although the exact cause of MS is unknown, a complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors are thought to initiate the disease. Recently, the gut microbiome--the trillions of gut bacteria the live inside human intestines--has emerged as a potential environmental factor that contributes to MS. In prior work, Mangalam and colleagues demonstrated that there are significant differences between the gut microbes of patients with MS and people without MS. Specifically, patients with MS lacked bacteria that are able to metabolize isoflavones. Although role of gut microbiome in human diseases such as MS is being appreciated, the mechanism through which these gut bacteria might influence the disease is poorly understood.
In the current study, Mangalam's team, including first author Samantha Jensen, a UI graduate student in immunology, found that the bacteria that are lacking in patients with MS are able to suppress inflammation in a mouse model of MS. The team compared the effects of an isoflavone diet and an isoflavone-free diet on disease in the mouse model of MS. They found that the isoflavone diet led to disease protection. However, when the team placed the mice on the isoflavone diet but removed the isoflavone-metabolizing gut bacteria, the isoflavone diet was no longer able to protect against MS-like symptoms. When the bacteria were reintroduced, the protective effect of the isoflavone diet was restored. Furthermore, the team was able to show that a specific isoflavone metabolite called equol, which is produced by the gut bacteria from isoflavone, is also able to provide protection against disease.
"This study suggests that an isoflavone diet may be protective so long as the isoflavone metabolizing gut bacteria are present in the intestines," say Mangalam, who also is a member of the Iowa Neuroscience institute and Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported in part by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and the Roy J. Carver Charitable Trust.
In addition to Mangalam and Jensen, the team included UI scientists Shailesh Shahi and Stephanie Peterson; Katherine Gibson-Corley at Vanderbilt University; Nicole Cady at the University of Michigan; and Arnav Gupta at the KK Birla in Goa.
MORGANTOWN, W.Va.--Just as helicopter traffic reporters use their "bird's eye view" to route drivers around roadblocks safely, radiation oncologists treating a variety of cancers can use new guidelines developed by a West Virginia University researcher to reduce mistakes in data transfer and more safely treat their patients.
Ramon Alfredo Siochi--the director of medical physics at WVU--led a task group to help ensure the accuracy of data that dictates a cancer patient's radiation therapy. The measures he and his colleagues recommended in their new report safeguard against medical errors in a treatment that more than half of all cancer patients receive.
"The most common mistake that happens in radiation oncology is the transfer of information from one system to another," Siochi, ...
How we sense texture has long been a mystery. It is known that nerves attached to the fingertip skin are responsible for sensing different surfaces, but how they do it is not well understood. Rodents perform texture sensing through their whiskers. Like human fingertips, whiskers perform multiple tasks, sensing proximity and shape of objects, as well as surface textures.
Mathematicians from the University of Bristol's Department of Engineering Mathematics, worked with neuroscientists from the University of Tuebingen in Germany, to understand how the motion of a whisker across a surface translates texture information into neural signals that can be perceived by the brain.
By carrying out high ...
Scientists have found new evidence of menopause in killer whales - raising fascinating questions about how and why it evolved.
Most animals breed throughout their lives. Only humans and four whale species are known to experience menopause, and scientists have long been puzzled about why this occurs.
Killer whales are a diverse species made up of multiple separate ecotypes (different types within a species) across the world's oceans that differ in their prey specialisation and patterns of social behaviour.
Previous studies have found menopause in an ecotype called "resident" killer whales whose social structure appears to favour "grandmothering" (females using their energy and knowledge ...
When a doctor gives a patient antibiotics for a bacterial infection, they usually require them to finish the entire treatment, even when symptoms go away. This is to ensure the drugs kill off any remaining bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Visiting Scientist Raffaella Sordella investigated a similar problem that occurs in some lung cancers.
Approximately 15% of non-small cell lung cancers have a mutation in a growth receptor called EGFR, causing tumor cells to grow uncontrollably. Researchers developed an effective drug that inhibits EGFR and ...
A Skoltech team has developed a model for assessing infection risks for supermarket customers. The researchers believe that their model will help formulate scientifically backed rules for safe shopping during the pandemic. The paper was published in PLOS One.
The team included professor Maxim Fedorov, who serves as Skoltech's Vice President for Artificial Intelligence and Mathematical Modeling, and a research group led by professor Nikolai Brilliantov -- the Director of the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE).
The composite model presented in the paper incorporates ...
LEXINGTON, Ky. (July 13, 2021) -- A recently published study co-authored by University of Kentucky Sanders-Brown Center on Aging researcher Justin Miller, Ph.D., identifies 11 rare candidate variants for Alzheimer's disease. Researchers found 19 different families in Utah that suffered from Alzheimer's disease more frequently than what is considered normal.
Miller, an assistant professor in the UK College of Medicine, was a co-first author for the study published in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia. The work was started at another university, however, some of the computational work was done after Miller arrived at UK in March.
For the study, genetic sequencing was conducted on two cousins from each of the 19 families. Miller says they then identified genetic variants that were shared ...
Automation of technology has reshaped both the way in which we work and how we tackle problems. Thanks to the progress made in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) over the last few years, it is now possible to leave several tasks in the hands to machines and algorithms.
To highlight these advances, in the July 2021 issue, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica features six articles covering innovative applications of AI that can make our lives easier.
The first article, authored by researchers from Virginia Tech Mechanical Engineering Department ASIM Lab, USA, delves into an interesting mixture of topics: intelligent cars, machine learning, and electroencephalography (EEG). Self-driving cars have ...
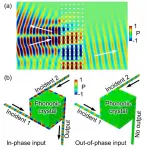
The concept of topological phases have not only revolutionized our understanding of physics or materials, but also brought about new possibilities for applications. Recent advances in higher-order topological insulators show that multiple forms of topological states can exist at boundaries of different dimensions, which greatly enriched the potentials for diverse applications. Interesting, the topological phases can also be implemented in artificial structures in photonics, electromagnetism, and acoustics.
A recent work co-led by Dr. Guancong Ma from Hong Kong Baptist University and Dr. Ying Wu from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology explored the controlling sound propagation with topological modes at different dimensions. They designed and built ...
One in ten school-aged children in Australia have a current diagnosis of asthma. Every year, there are around 40,000 asthma hospitalisations and over 40 per cent of these are in children aged younger than 14 years old.
Approximately 80 per cent of these asthma-related hospital presentations are potentially avoidable through a standardised comprehensive care pathway for children with asthma.
These preventative measures include the use of evidence-based clinical guidelines, ensuring that there is an asthma action plan in place; regular follow-up with GP; provision of asthma education to parents/carers; and establishing ...
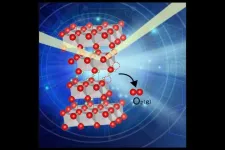
A research group has produced fresh insights about the release of oxygen in lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for more robust and safer high-energy-density batteries.
Next-generation batteries that store more energy are critical if society is to achieve the UN's Sustainable Development Goals and realize carbon neutrality. However, the higher the energy density, the higher the likelihood of thermal runaway - the overheating of batteries that can sometimes result in a battery exploding.
Oxygen released from cathode active material is a trigger for thermal runaway, yet our knowledge of this process is insufficient.
Researchers from Tohoku University ...