(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - Direct farm marketing efforts, such as farmers markets and roadside stands, are more successful in communities with more nonprofits, social enterprises and creative industries, according to a team including Cornell University researchers, who created a nationwide database of assets to help municipalities craft community-specific development plans.
While many municipalities seek to encourage direct-to-consumer (DTC) marketing - an important factor in farmers' livelihoods - the success of their efforts hinges on a wide array of community resources, or capital assets, with natural and cultural assets correlating most strongly with farmers' success, the research found.
To explore differences between communities, Todd Schmit, associate professor in the Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management, and colleagues at Colorado State University and the University of Missouri created a database of assets for every county in the United States, breaking down these community resources in six areas: built, cultural, financial, human, natural and social.
"There's a broad acceptance of the idea that sustainable community development is dependent on this array of capital assets. But when it comes to measuring those capitals, the literature is all over the place," Schmit said. "Some studies will use educational attainment to measure human capital, but others will use food security, or access to medical care. We thought, why not measure all of those things?"
To create their composite database, Schmit and his colleagues gathered data on dozens of factors, such as: the number of manufacturing establishments; the number of owner-occupied housing units without a mortgage; and acreage of farmland. All data came from publicly available sources such as the U.S. Census and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Then they used their new database to evaluate DTC farm marketing against community capital stocks in an article published July 2 in the journal Food Policy: "Measuring Stocks of Community Wealth and Their Association With Food Systems Efforts in Rural and Urban Places."
They found, as expected, that high levels of natural capital, especially farmland, correlated positively with DTC farm marketing. But they also found a positive association with cultural capital: Communities with more nonprofits, social enterprises and creative industries help farmers prosper in direct marketing.
"Art-centric businesses, museums, theaters, symphonies, architecture firms - there was a very complementary effect," Schmit said. "Maybe farmers markets are hosting musicians or art vendors and that's making the farmers market a bigger draw for consumers? Or maybe because people are coming to communities to visit an art gallery or go to a museum, they're saying, 'Well, let's head over to the farmers market, too, and make a day of it.'"
Schmit said he hopes the new database will be helpful for community planners and other researchers studying a variety of issues important for regional development.
"With this paper, we wanted to showcase an application of these capital stocks, but our bigger purpose is to provide this data for others to use in whatever application they want: obesity, child nutrition programs, infrastructure investment planning, conservation protection," he said. "We want people to use this data."
Co-author Becca Jablonski, a Cornell alum and an associate professor of agricultural and resource economics at Colorado State University, hopes the database will enable researchers and planners to craft economic development policies that are more successful because they are community-specific.
"Often policymakers set strategies to support community economic development at the federal level without full consideration of the fact that different types of programs and initiatives will have different impacts in different places based on the comparative advantage of a particular place - what they do better than other places," Jablonski said. "We hope that this database of the stocks of community assets can help decision-makers more thoughtfully reflect on their unique strengths and opportunities."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by a grant from the USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
AMHERST, Mass. - Humans have known for over two thousand years that shipworms, a worm-like mollusk, are responsible for damage to wooden boats, docks, dikes and piers. Yet new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst published in Frontiers in Microbiology reveals that we still don't know the most basic thing about them: how they eat.
"It's unbelievable," says Reuben Shipway, adjunct assistant professor in microbiology at UMass Amherst, research fellow at the Centre for Enzyme Innovation at the University of Portsmouth, UK, and one of the paper's authors. "The ancient Greeks wrote about them, Christopher Columbus lost his fleet due to what he called 'the havoc which the worm had wrought,' and, today, shipworms cause billions of dollars of damage a year."
Shipworms ...
Middle- to older-aged adults who ate at least three servings of whole grains daily had smaller increases in waist size, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels over time compared to those who ate less than one-half serving per day, according to new research.
Published July 13, 2021, in the Journal of Nutrition, the study by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University examined how whole- and refined-grain intake over time impacted five risk factors of heart disease: Waist size, blood pressure, blood sugar, triglyceride, and HDL ("good") cholesterol.
Using data from the Framingham Heart Study Offspring ...
Philadelphia, July 13, 2021 - Consumers may have less trust in food processes that they don't understand, and animal-based foods may be subject to more uninformed scrutiny than other foods due to consumers' perception of higher risk. Dairy producers can benefit from understanding how consumers interpret unfamiliar terms and claims on dairy product labels. In a new END ...
New research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln has shown that the mutations arising in the COVID-19-causing SARS-CoV-2 virus seem to run in the family -- or at least the genus of coronaviruses most dangerous to humans.
After comparing the early evolution of SARS-CoV-2 against that of its closest relatives, the betacoronaviruses, the Nebraska team found that SARS-CoV-2 mutations are occurring in essentially the same locations, both genetically and structurally.
The mutational similarities between SARS-CoV-2 and its predecessors, including the human-infecting SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV, could help inform predictions of how the COVID-causing virus will continue to evolve, the researchers ...
Amsterdam, July 13, 2021 - Mass spectrometry has emerged as an important analytical tool for gaining a better understanding of mechanisms underlying Huntington's disease (HD), alongside the increased availability of cell and animal models of the disease. This END ...
YorkU pain research finds what you say in the first minute after a vaccine can be key in reducing a child's future distress
New study finds it's not just what say, but when you say it that can keep preschoolers calmer during vaccinations
TORONTO, July 13, 2021 - As we look forward to a fall with hopefully one of the most important vaccination uptakes of children in a generation, a new study provides insights to help parents with reducing post-vaccination distress in younger kids. The study, published in END ...
WASHINGTON--In cities and towns across the United States, neighborhoods with more Black, Hispanic and Asian residents experience hotter temperatures during summer heatwaves than nearby white residents, a new study finds. It is the first to show that the trend, documented in some major cities, is widespread, even in small towns, nationwide.
According to the new nationwide study, these racial disparities exist because non-white neighborhoods tend to be more densely built up with buildings and pavement that trap heat and have fewer trees to cool the landscape.
"Urban climate is different from temperatures outside the city," said co-author Susanne Benz, an ...
Antimicrobials are used to kill or slow the growth of bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms. They can be in the form of antibiotics, used to treat bodily infections, or as an additive or coating on commercial products used to keep germs at bay. These life-saving tools are essential to preventing and treating infections in humans, animals and plants, but they also pose a global threat to public health when microorganisms develop resistance to them, a concept known as antimicrobial resistance.
One of the main drivers of antimicrobial resistance is the misuse and overuse of antimicrobial agents, which includes silver nanoparticles, ...
The COVID-19 pandemic caused an unprecedented disruption to health care delivery, with resources shifted toward telehealth services and mass viral testing. While early studies in the pandemic highlighted differences in health care utilization among patients with commercial insurance, data from publicly insured or uninsured "safety-net" patient populations continue to emerge.
A recent study from researchers at the University of Minnesota and Hennepin Healthcare Research Institute (HHRI) is among the first to examine how different socio-demographic groups used telehealth, outpatient (i.e., clinic), emergency department and inpatient (i.e., hospital) care to test for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. ...
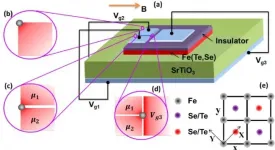
In particle physics, a Majorana Fermion is charge neutral and its antiparticle is just itself. In condensed matter physics, a Majorana zero mode (MZM) is a quasi-particle excitation, which appears in the surfaces or edges of topological superconductors. Unlike the ordinary particles or quasi-particles that obey boson or fermion statistics, MZM obeys non-abelian statistics, a key property that makes MZM the building block for realizing topological quantum computation. Currently major experimental efforts focus on heterostructures made of superconductors and spin-orbit coupled systems (such as semiconducting nano-wires and topological insulators), where evidences of MZMs have been found. Unambiguous detection and manipulation of MZMs in these heterostructures, ...