(Press-News.org) A team of geneticists and archaeologists from Ireland, France, Iran, Germany, and Austria has sequenced the DNA from a 1,600-year-old sheep mummy from an ancient Iranian salt mine, Chehrābād. This remarkable specimen has revealed sheep husbandry practices of the ancient Near East, as well as underlining how natural mummification can affect DNA degradation.
The incredible findings have just been published in the international, peer-reviewed journal Biology Letters.
The salt mine of Chehrābād is known to preserve biological material. Indeed, it is in this mine that human remains of the famed "Salt Men" were recovered, dessicated by the salt-rich environment. The new research confirms that this natural mummification process - where water is removed from a corpse, preserving soft tissues that would otherwise be degraded - also conserved animal remains.
The research team, led by geneticists from Trinity College Dublin, exploited this by extracting DNA from a small cutting of mummified skin from a leg recovered in the mine.
While ancient DNA is usually damaged and fragmented, the team found that the sheep mummy DNA was extremely well-preserved; with longer fragment lengths and less damage that would usually be associated with such an ancient age. The group attributes this to the mummification process, with the salt mine providing conditions ideal for preservation of animal tissues and DNA.
The salt mine's influence was also seen in the microorganisms present in the sheep leg skin. Salt-loving archaea and bacteria dominated the microbial profile - also known as the metagenome - and may have also contributed to the preservation of the tissue.
The mummified animal was genetically similar to modern sheep breeds from the region, which suggests that there has been a continuity of ancestry of sheep in Iran since at least 1,600 years ago.
The team also exploited the sheep's DNA preservation to investigate genes associated with a woolly fleece and a fat-tail - two important economic traits in sheep. Some wild sheep - the asiatic mouflon - are characterised by a "hairy" coat, much different to the woolly coats seen in many domestic sheep today. Fat-tailed sheep are also common in Asia and Africa, where they are valued in cooking, and where they may be well-adapted to arid climates.
The team built a genetic impression of the sheep and discovered that the mummy lacked the gene variant associated with a woolly coat, while fibre analysis using Scanning Electron Microscopy found the microscopic details of the hair fibres consistent with hairy or mixed coat breeds. Intriguingly, the mummy carried genetic variants associated with fat-tailed breeds, suggesting the sheep was similar to the hairy-coated, fat-tailed sheep seen in Iran today.
"Mummified remains are quite rare so little empirical evidence was known about the survival of ancient DNA in these tissues prior to this study," says Conor Rossi, PhD candidate in Trinity's School of Genetics and Microbiology, and the lead author of the paper.
"The astounding integrity of the DNA was not like anything we had encountered from ancient bones and teeth before. This DNA preservation, coupled with the unique metagenomic profile, is an indication of how fundamental the environment is to tissue and DNA decay dynamics.
Dr Kevin G Daly, also from Trinity's School of Genetics and Microbiology, supervised the study. He added:
"Using a combination of genetic and microscopic approaches, our team managed to create a genetic picture of what sheep breeds in Iran 1,600 years ago may have looked like and how they may have been used.
"Using cross-disciplinary approaches we can learn about what ancient cultures valued in animals, and this study shows us that the people of Sasanian-era Iran may have managed flocks of sheep specialised for meat consumption, suggesting well developed husbandry practices."
INFORMATION:
Survival for a baby born with a birth defect - otherwise known as a congenital anomaly - is a "post-code lottery", according to scientists from 74 countries.
A study published today in The Lancet, led by researchers from King's College London, examined the risk of mortality for nearly 4000 babies born with birth defects in 264 hospitals around the world. The study found babies born with birth defects involving the intestinal tract have a two in five chance of dying in a low-income country compared to one in five in a middle-income country and one in twenty in a high-income country.
Gastroschisis, a birth defect where the baby is born with ...
A global study provides up-to-date estimates for the effect of alcohol consumption on cancers worldwide. It suggests that 4% of all newly diagnosed cancers in 2020 may be associated with drinking alcohol, with men accounting for more than three quarters of those cases.
Risky and heavy drinking was estimated to contribute the highest number of cancer cases, but moderate drinking - the equivalent of around two daily drinks - was estimated to lead to more than 103,000 cases in 2020, almost 1 in 7 of all alcohol-associated cases.
The proportion of new cancer cases associated with alcohol varied widely between world regions, with the lowest found in Northern Africa and Western Asia, and the highest in ...
COVID-19 is marked by heightened inflammation and abnormal clotting in the blood vessels, particularly in the lungs, and is believed to contribute to progression to severe disease and death. New trial results show that administering a full dose of a standard blood thinner early to moderately ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 could halt the thrombo-inflammation process and reduce the risk of severe disease and death.
The study, led by investigators at St. Michael's Hospital, a site of Unity Health Toronto, and the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, is available as ...
A scientific team has shown that the release of neurotransmitters in the brain is impaired in patients with schizophrenia who have a rare, single-gene mutation known to predispose people to a range of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Significantly, the results from the research with human-derived neurons validated previous and new experiments that found the same major decrease in neurotransmitter release and synaptic signaling in genetically engineered human neurons with the same genetic variant - the deletion of neurexin 1 (NRXN1). NRXN1 is a protein-coding gene at the synapse, a cellular junction that ...
WACO, Texas (July 13, 2021) - Climate change mitigation efforts have led to shifts from fossil-fuel dependence to large-scale renewable energy. However, renewable energy sources require significant land and could come at a cost to ecosystems. A new study led by Ryan McManamay, Ph.D., assistant professor of environmental science at Baylor University, evaluates potential conflicts between alternative energy strategies and biodiversity conservation.
The study, published in Biological Conservation, evaluates potential tradeoffs between climate benefits ...
Cancer survivors ages 18 to 64 faced fewer financial barriers to health care after the Affordable Care Act was implemented than they did before the landmark law took effect, University of Michigan researchers found.
In fact, they believe the ACA helped the financial burden (problems related to the cost of medical care) for younger cancer survivors fall to its lowest estimated levels in 20 years.
"There has been a lot of talk about the ACA affecting people who don't have the Medicare safety net," said Christopher Su, M.D., a clinical fellow in the division of hematology and oncology at Michigan Medicine and the first author of the paper. "We were able to drill down to that and show that it did make a difference to younger cancer ...
The COVID-19 pandemic and the situations of stress and sadness associated with it have not significantly increased the prevalence of depression and anxiety among participants in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil) who live in the city of São Paulo.
ELSA-Brazil has been monitoring the overall health of 15,000 civil servants at six public universities and research centers in Brazil since 2008. The survey on mental health during the pandemic was conducted in São Paulo and involved 2,117 members of the staff of the University of São Paulo (USP) - in active service or retired - who are participants in the nationwide study and aged 50-80.
The survey is supported by São Paulo Research Foundation ...
In early March 2020, the University of Washington became the first four-year U.S. university to transition to online-only classes due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Many researchers predicted severe consequences of these physical distancing measures. To understand how this change affected college students' mental health, UW researchers surveyed 147 UW students over the 2020 spring quarter, which began shortly after the university transitioned to online-only classes. The team compared the students' responses to a previous survey of 253 students in spring quarter 2019.
The researchers didn't see much change in average levels of students' depressive symptoms, anxiety, stress or loneliness between 2019 and 2020 or between the beginning and the end of spring quarter ...
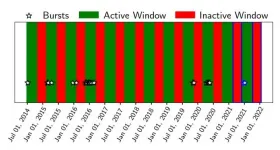
Magnetars are bizarre objects -- massive, spinning neutron stars with magnetic fields among the most powerful known, capable of shooting off brief bursts of radio waves so bright they're visible across the universe.
A team of astrophysicists has now found another peculiarity of magnetars: They can emit bursts of low energy gamma rays in a pattern never before seen in any other astronomical object.
It's unclear why this should be, but magnetars themselves are poorly understood, with dozens of theories about how they produce radio and gamma ray bursts. The recognition of this unusual pattern of gamma ray activity ...
Bacterial vaginosis is the most common and recurrent gynecological condition affecting nearly 30% of women between the ages of 15 and 44, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A University of Arizona Health Sciences-led study recently identified a specific bacteria family and uncovered how it contributes to bacterial vaginosis, paving the way for new insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Led by Melissa Herbst-Kralovetz, PhD, a member of the BIO5 Institute and associate professor of basic medical sciences at the College of Medicine - Phoenix, researchers found that members of the Veillonellaceae bacteria family contribute to an increase in inflammation and cell death, and alter the acidity of the cervical microenvironment. These changes support bacterial ...