New evidence of an anomalous phase of matter brings energy-efficient technologies closer
2021-07-14
(Press-News.org) Researchers have found evidence for an anomalous phase of matter that was predicted to exist in the 1960s. Harnessing its properties could pave the way to new technologies able to share information without energy losses. These results are reported in the journal Science Advances.
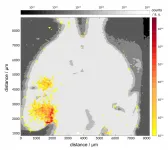
While investigating a quantum material, the researchers from the University of Cambridge who led the study observed the presence of unexpectedly fast waves of energy rippling through the material when they exposed it to short and intense laser pulses. They were able to make these observations by using a microscopic speed camera that can track small and very fast movement on a scale that is challenging with many other techniques. This technique probes the material with two light pulses: the first one disturbs it and creates waves - or oscillations - propagating outward in concentric circles, in the same way as dropping a rock into a pond; the second light pulse takes a snapshot of these waves at various times. Put together, these images allowed them to look at how these waves behave, and to understand their 'speed limit.'
"At room temperature, these waves move at a hundredth of the speed of light, much faster than we would expect in a normal material. But when we go to higher temperatures, it is as if the pond has frozen," explained first author Hope Bretscher, who carried out this research at Cambridge's Cavendish Laboratory. "We don't see these waves moving away from the rock at all. We spent a long time searching for why such bizarre behaviour could occur."
The only explanation that seemed to fit all the experimental observations was that the material hosts, at room temperature, an "excitonic insulator" phase of matter, which while theoretically predicted, had eluded detection for decades.
"In an excitonic insulator, the observed waves of energy are supported by charge neutral particles that can move at electron-like velocities. Importantly, these particles could transport information without being hindered by the dissipation mechanisms that, in most common materials, affect charged particles like electrons," said Dr Akshay Rao from the Cavendish Laboratory, who led the research. "This property could provide a simpler route toward room-temperature, energy-saving computation than that of superconductivity."
The Cambridge team then worked with theorists around the world to develop a model about how this excitonic insulating phase exists, and why these waves behave in this way.
"Theorists predicted the existence of this anomalous phase decades ago, but the experimental challenges to see evidence of this has meant that only now we are able to apply previously developed frameworks to provide a better picture of how it behaves in a real material," commented Yuta Murakami, from the Tokyo Institute of Technology, who collaborated on the study.
"The dissipationless energy transfer challenges our current understanding of transport in quantum materials and opens theorists' imaginations to new ways for their future manipulation," said collaborator Denis Golež, from the Jozef Stefan Institute and University of Ljubljana.
"This work puts us a step closer toward achieving some incredibly energy-efficient applications that can harness this property, including in computers." concluded Dr Rao.
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Hope M. Bretscher et al. 'Imaging the coherent propagation of collective modes in the excitonic insulator Ta2NiSe5 at room temperature', Science Advances (July 2021). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd6147
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-14
In lab tests, Imperial researchers have created a metal-based molecule that inhibits the build-up of a peptide associated with Alzheimer's disease.
A peptide is a fragment of a protein, and one of the key hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease is the build-up of a specific peptide known as amyloid-β. The team demonstrated that with the aid of ultrasound, their molecule can cross the blood-brain barrier in mice, targeting the part of the brain where the damaging peptide most often accumulates.
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia, affecting approximately 50 million people worldwide. There is a pressing need to develop drugs ...
2021-07-14
Pioneering 'printed metal' procedure to create bespoke treatment for early knee osteoarthritis set to be trialled in the UK following MHRA approval.
World's first 3D printed high tibial osteotomy (HTO) device and procedure developed at University of Bath given approval for UK trials
Bespoke titanium alloy HTO implants that fit perfectly are designed to reduce discomfort for knee osteoarthritis patients
Sophisticated 3D scanning aims to make surgery quicker and safer
New TOKA process could make earlier intervention possible - saving patients decades of pain before surgery becomes viable
Intro
A ...
2021-07-14
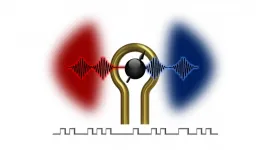
Many of us swing through gates every day -- points of entry and exit to a space like a garden, park or subway. Electronics have gates too. These control the flow of information from one place to another by means of an electrical signal. Unlike a garden gate, these gates require control of their opening and closing many times faster than the blink of an eye.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Chicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering have devised a unique means of achieving effective gate operation with a form of information processing called electromagnonics. Their pivotal discovery allows real-time control of information transfer between microwave photons and magnons. And it could result in a new generation ...
2021-07-14
An important new study by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has yielded critical fresh insights into the lithium production process and how it relates to long-term environmental sustainability, particularly in the area of transportation with batteries and electric vehicles.
The paper, "Energy, Greenhouse Gas, and Water Life Cycle Analysis of Lithium Carbonate and Lithium Hydroxide Monohydrate from Brine and Ore Resources and Their Use in Lithium Ion Battery Cathodes and Lithium Ion Batteries," in the journal ...
2021-07-14
Prof. PAN Jianwei and Prof. ZHANG Jun from University of Science of Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with Prof. CHU Tao's group from Zhejiang University, realized the fastest and miniaturized real-time quantum random number generator (QRNG) with the record-breaking output rate of 18.8 Gbps by combing a state-of-the-art photonic integrated chip with the optimized real-time post processing. The study was published in Applied Physics Letters on June 29.
Random number exists in many fields such as information security and cryptology industries. Different from other random number generators, QRNG, as the key part in quantum communication system, embraces the characteristics ...
2021-07-14
Prof. DU Jiangfeng, Prof. RONG Xing, and their colleagues from the Key Laboratory of Micromagnetic Resonance, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), set the most stringent laboratory constraint on the exotic spin- and velocity-dependent interaction at the micrometer scale. This study was published in Physical Review Letters.
The search for dark matter, dark energy, and extra forces is important for the understanding of the existence of the matter that accounts for about a quarter of the universe, but little progress has been made. It is necessary to theoretically and experimentally find particles outside the Standard Model, a tradition ...
2021-07-14
Shells of tamarind, a tropical fruit consumed worldwide, are discarded during food production. As they are bulky, tamarind shells take up a considerable amount of space in landfills where they are disposed as agricultural waste.
However, a team of international scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has found a way to deal with the problem. By processing the tamarind shells which are rich in carbon, the scientists converted the waste material into carbon nanosheets, which are a key component of supercapacitors - energy storage devices that are used in automobiles, buses, electric vehicles, trains, and elevators.
The study reflects ...
2021-07-14
Osaka, Japan - When things get too much, we're often advised to "take a load off," but when it comes to bone maintenance, doing the opposite can be a good thing. Researchers from Japan have discovered some key mechanisms of how physical load stimulates bone growth.
In a study published July 13, 2021 at 11 a.m. ET in Cell Reports, researchers from the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center Research Institute have revealed that the expression of the peptide osteocrin (OSTN) is influenced by load - decreasing when load is reduced, and increasing when it is added.
Bones and skeletal muscles are strengthened by the load associated with exercise, preventing bone and muscle atrophy, and maintaining bone and muscle strength is important for maintaining physical activity. ...
2021-07-14
Researchers from Kumamoto University, Japan have found that a component derived from turmeric essential oil, aromatic turmerone (ar-turmerone), and its derivatives act directly on dopaminergic nerves to create a neuroprotective effect on tissue cultures of a Parkinson's disease model. This appears to be due to enhanced cellular antioxidant potency from the activation of Nrf2. The researchers believe that the ar-turmerone derivatives identified in this study can be used as new therapeutic agents for Parkinson's disease.
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the ...
2021-07-14
When it comes to the medicinal and therapeutic properties of Cannabis sativa, an unsolved mystery is whether there exists an "entourage effect," whereby the pain-relieving effects of the plant as a whole are greater than any of its individual parts. New research from the University of Arizona Health Sciences has found evidence that favors the entourage effect theory and positions Cannabis terpenes, the part of the plant that provides flavor and aroma, as a promising new target for pain therapies that would require lower doses and produce fewer side effects.
"A lot of people are taking cannabis and cannabinoids for pain," said lead researcher John Streicher, PhD, a member ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New evidence of an anomalous phase of matter brings energy-efficient technologies closer