Looking beyond the numbers to see pandemic's effect on nursing home residents
2021-07-15
(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- Nursing homes throughout the United States have been devastated by the COVID-19 pandemic with many perceptions and misperceptions but little documentation about what has happened on a day-by -day basis to residents in these facilities. A study from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine research scientists is one of the first to describe and identify patterns in the course of COVID-19 in the typically frail individuals who reside in nursing homes.
Much has been written about number of deaths, vaccine uptake and other topics related to the impact of COVID on nursing homes, yet prior to the Regenstrief-IU School of Medicine study, there has been little known about how the disease has clinically affected individuals residing in nursing homes. A full understanding of the disease burden and trajectories of COVID-19 in nursing home residents - those who died and those who survived COVID - will aid medical and public health professionals immediately, will help them prepare for outbreaks of variants and may inform efforts to confront outbreaks of other diseases.
"When the COVID outbreak occurred, we [physicians who care for nursing home residents] didn't know, because we weren't armed with knowledge or clinical experience, what to expect - who would do well and who wouldn't," said Regenstrief Institute Research Scientist Kathleen Unroe, M.D., senior author of the study. "This is a population that by their very need to reside in a nursing home, has complex medical conditions and is at high risk. And it's a different population than younger adults. For example, some older adults may not experience fever in response to infection; persons with dementia may be unable to report symptoms."
The researchers studied the electronic medical records (EMRs) of 74 nursing home residents infected with COVID of whom half were women, 57 percent were Caucasian and 43 percent were African American. One third (25) died; with 23 of the deaths considered related to COVID-19 infection. Hypertension was the most common comorbidity (81 percent) followed by dementia (51 percent), diabetes (50 percent) and non-dementia mental illness (43 percent). The most common symptoms were fever, hypoxia (low oxygen level in the blood), anorexia, and fatigue/malaise. None reported headaches. The duration of symptoms was extended, with an average of more than three weeks.
The 74 nursing home residents with COVID-19 infection appeared to fall into four disease trajectory categories:
minimal to no symptoms (17)
residents who survived but experienced significant symptoms (32),
residents who died after a rapidly progressive course (less than seven days) (5)
residents who died after a prolonged course with significant symptom burden (20)
"For many of nursing home residents who survive COVID-19, the duration of symptoms is long and arduous; most will survive the disease but may not get back to baseline," said Dr. Unroe. "The effect of COVID on nursing home residents goes beyond the mortality numbers we saw."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Dr. Unroe, authors of "COVID-19 Disease Trajectories Among Nursing Home Residents," published online ahead of print in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, are corresponding author Regenstrief Institute Research Scientist and IU School of Medicine faculty member Jennifer Carnahan, M.D., MPH, MA, and IU School of Medicine student Lauren Albert. Additional co-authors are Kristi M Lieb M.D.; Kamal Wagle M.D., MPH; Ellen Kaehr M.D., all of IU School of Medicine and Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health's National Institute on Aging (K23AG062797) and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (1E1CMS331488).
About Regenstrief Institute
Founded in 1969 in Indianapolis, the Regenstrief Institute is a local, national and global leader dedicated to a world where better information empowers people to end disease and realize true health. A key research partner to Indiana University, Regenstrief and its research scientists are responsible for a growing number of major healthcare innovations and studies. Examples range from the development of global health information technology standards that enable the use and interoperability of electronic health records to improving patient-physician communications, to creating models of care that inform practice and improve the lives of patients around the globe.
Sam Regenstrief, a nationally successful entrepreneur from Connersville, Indiana, founded the institute with the goal of making healthcare more efficient and accessible for everyone. His vision continues to guide the institute's research mission.
About IU School of Medicine
IU School of Medicine is the largest medical school in the U.S. and is annually ranked among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. The school offers high-quality medical education, access to leading medical research and rich campus life in nine Indiana cities, including rural and urban
Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, M.S.
In addition to being a research scientist at Regenstrief Institute, Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, is an associate professor at Indiana University School of Medicine and a practicing geriatrician.
Jennifer Carnahan, M.D., MPH, M.A.
In addition to her role as a research scientist at Regenstrief, Jennifer Carnahan, M.D., MPH, M.A., is an assistant professor of medicine at Indiana University School of Medicine.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-15
Bone density, skin and hair health, and the mobility of joints depend to a great extent on the microelement of silicon. We mostly get it with food, but silicon is also consumed with some biologically active additives that promise beauty, longevity, and youth. The element can also be found in drinking water of a natural origin: usually, it is included in the compound of sodium salt and metasiliconic acid. However, in the case of microelements, one should be extremely careful: a deficiency could lead to diseases, but an overdose could bring negative effects too.
Together with colleagues from the Chuvash State University and the Hamburg Medical University, scientists of Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University studied the effect of prolonged silicon consumption in relatively ...
2021-07-15
To date, there are no effective antidotes against most virus infections. An interdisciplinary research team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now developed a new approach: they engulf and neutralize viruses with nano-capsules tailored from genetic material using the DNA origami method. The strategy has already been tested against hepatitis and adeno-associated viruses in cell cultures. It may also prove successful against corona viruses.
There are antibiotics against dangerous bacteria, but few antidotes to treat acute viral infections. Some infections can be prevented by vaccination but developing new vaccines is a long and laborious process.
Now an interdisciplinary research team from the Technical University of Munich, the Helmholtz Zentrum München and ...
2021-07-15
A new study finds that resilience is a dynamic process, rather than a fixed trait - and suggests this may have significant ramifications for the business world.
"Organizations are interested in cultivating a resilient workforce, because they want people who are able to remain committed to an organization and its goals over time," says Patrick Flynn, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of human resources management at North Carolina State University's Poole College of Management.
"Our work here does a couple things," Flynn says. "First it finds that resilience is more of a process than a characteristic. Second, it identifies some of the ...
2021-07-15
RUDN University chemists obtained a metal-containing complex with an unusual planar architecture. The unexpected structure was formed due to the spontaneous fixation of carbon dioxide from the air during the reaction. This compound exhibits unusual magnetic properties (spin glass behaviour). This can be useful for creating memory storage devices. The results are published in the Journal of Organometallic Chemistry
Coordination polymers are hybrid crystalline coordination compounds contained of infinitely repeating fragments (structural elements). These structural ...
2021-07-15
The mitochondrion has garnered quite the reputation for its role as the "powerhouse of the cell." These tiny, but mighty organelles play various life-sustaining roles, from powering our own cells and organs to fueling chemical and biological processes. But when they aren't working properly, a number of rare diseases can occur.
Mitochondrial diseases are a group of debilitating genetic disorders that affect one in 5,000 people throughout the world, most of them being children. Along with these diseases come a variety of health concerns including, but not limited to, heart ...
2021-07-15
The pandemic has taught us that almost all companies have to sell on the internet. Bots are a technology that facilitates e-commerce. They are digital assistants that can answer customer queries about products that are sold or help to locate them, as well as supporting customers in the purchasing process. "In whatever language; and moreover, chatbots never get tired: They're available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year", said Jordi Cabot, the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) researcher who created Xatkit, a company specialized in their development. This technology has existed for some time in big companies and is now also helping improve the digital competitiveness ...
2021-07-15
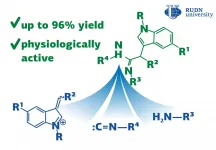
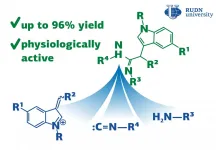
The RUDN University chemists have discovered a reaction for the synthesis of acetimidamides, heterocyclic compounds with biological activity that can be used for the synthesis of hormones, anti-inflammatory and other medical drugs. The reaction goes in one step with an efficiency of up to 96%. The results are published in the journal Molecules.
Traditional chemical synthesis goes in several stages and requires the isolation and purification of intermediates at each stage. It is not efficient and not environmentally friendly as it increases the loss of substances and the consumption of solvents, and there is a problem of waste disposal. ...
2021-07-15
Scientists have uncovered a way to control many genes in engineered yeast cells, opening the door to more efficient and sustainable production of bio-based products.
The study, published in Nucleic Acids Research by researchers from DSM's Rosalind Franklin Biotechnology Center in Delft, the Netherlands, and the University of Bristol, has shown how to unlock CRISPR's potential for regulating many genes simultaneously.
Baker's yeast, or Saccharomyces cerevisiae to give it it's full name, is considered as a workhorse for biotechnology. Not only has it been used for producing bread and beer for thousands of years, but today it can also be engineered to produce an array of other useful compounds that form the basis of pharmaceuticals, fuels, and food additives. However, achieving ...
2021-07-15
According to the World Health Organization, a third wave of COVID infections is now all but inevitable in Europe. A COVID tracker developed by IIASA researcher Asjad Naqvi, aims to identify, collect, and collate various official regional datasets for European countries, while also combining and homogenizing the data to help researchers and policymakers explore how the virus spreads.
While many comparisons have been made between the COVID-19 pandemic and similar events in history, one thing sets this pandemic apart from others: the unprecedented amount of knowledge and data that is constantly being generated to understand how the pandemic is unfolding. For a high-income region like Europe, the quality of information made available on a daily basis is exceptionally ...
2021-07-15
The Institut Pasteur, in partnership with the French National Health Insurance Fund (CNAM), Santé publique France and the Ipsos Social Research Institute, recently presented the results of the ComCor epidemiological study on circumstances and places of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The aim of the study was to identify the socio-demographic factors, places visited and behaviors associated with a higher risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2. The study contains two parts:
the first part describes the circumstances of infection of index cases diagnosed positive for SARS-CoV-2 during the curfew period, especially when the person considered as the source of infection is known;
the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Looking beyond the numbers to see pandemic's effect on nursing home residents