(Press-News.org) GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Two fossil teeth from a distant relative of North American gophers have scientists rethinking how some mammals reached the Caribbean Islands.
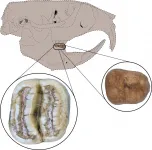
The teeth, excavated in northwest Puerto Rico, belong to a previously unknown rodent genus and species, now named Caribeomys merzeraudi. About the size of a mouse, C. merzeraudi is the Caribbean's smallest known rodent and one of the region's oldest, dating back about 29 million years.
It also represents the first discovery of a Caribbean rodent from a North American lineage, a finding that complicates an idea that has persisted since Darwin - that land-dwelling mammals colonized the islands from South America. The presence of C. merzeraudi in Puerto Rico suggests a second possibility: Some species may have rafted from North America.
The tiny rodent joins two other types of animals, an extinct rhinoceros-like species and bizarre, venomous shrews known as Solenodons, as the only known examples of Caribbean land-dwelling mammals with North American roots.
"This discovery demonstrates that overwater dispersal from North America was also a potential pathway to the Caribbean," said study co-author Jorge Velez-Juarbe, associate curator of mammalogy at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. "This challenges what we thought we knew about the origins of Antillean terrestrial mammals."
While Caribbean ecotourism brochures generally don't feature splashy images of rats, the islands were once home to a rich representation of rodents, including spiny rats, chinchillas, rice rats and hutias - all descendants of South and Central American forebears.
Fossil and molecular evidence suggest these rodents arrived in the islands in multiple waves over time, though how they got there - whether by scurrying over an ancient land bridge, island-hopping or rafting - has been hotly contested. The paucity of fossils from the early years of the Caribbean Islands further obscures the picture of the region's past biodiversity.
Caribeomys merzeraudi's teeth were so unusual that researchers initially struggled to discern what kind of animal they had come from, said study co-author Lazaro Vinola Lopez, a doctoral student in vertebrate paleontology at the Florida Museum of Natural History.
"We didn't know what it was for several months," he said. "We wondered whether this could be some other rodent from the Caribbean or even some kind of strange fish. It was so puzzling because they're not similar to anything else we had found in that region."
The team eventually pinpointed several tooth characteristics that are hallmarks of rodents known as geomorphs, a group that includes kangaroo rats, pocket mice and gophers. Caribeomys merzeraudi is the first geomorph found outside North America.
An exceptionally thick layer of tooth enamel, among other features, sets C. merzeraudi apart from its relatives and could indicate these rodents belonged to a distinct West Indian branch that evolved in isolation over several million years, Vinola Lopez said.
Scientists found the teeth while screen-washing sediment collected from a river outcrop in San Sebastian, a site that has yielded fossil sharks and rays, fish, turtles, a gharial, sea cows and the oldest known frog in the Caribbean, a coqui. In 2019, the team excavated fossil evidence of two large chinchillas, which likely grew up to 30 pounds. These South American rodents once shared Puerto Rico with the humble C. merzeraudi, which weighed less than a quarter pound.
Today, hutias, bats and Solenodons are the "last survivors of what was once a much more diverse group of Caribbean mammals" that included sloths and primates, Velez-Juarbe said.
Discovering C. merzeraudi opens up the tantalizing possibility that Caribbean mammals with North American origins may not be as exceptional as previously thought, Vinola Lopez said. But there's only one way to find out: "Go back to the locality and see what else we can find."
INFORMATION:
Laurent Marivaux of the University of Montpellier was the study's lead author. Other co-authors are Pierre-Henri Fabre of the University of Montpellier and the Natural History Museum; Francois Pujos of the Argentine Institute of Nivology, Glaciology and Environmental Sciences (IANIGLA); Hernan Santos-Merca, Eduardo Cruz, Alexandra Grajales Perez and James Padilla of the University of Puerto Rico; Kevin Velez-Rosado of the University of Michigan; and Jean-Jacques Cornee, Melody Philippon, Philippe Munch and Pierre-Olivier Antoine of the University of Montpellier.
A new study by the University of Malta and Staffordshire University highlights an urgent need for change in the curriculum and demonstrates how introducing longer, more frequent and more physically intense PE lessons can significantly improve children's weight and overall health.
Malta currently has one of the highest rates of obesity worldwide with 40% of primary and 42.6% of secondary school children being overweight or obese.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that children engage in at least 60 minutes of age-appropriate moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) daily, however ...
New Rochelle, NY, July 14, 2021-Firsthand reports from nurses in correctional facilities detail the challenges they faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. These firsthand accounts are reported in a special issue on correctional nursing in the Journal of Correctional Health Care. Click here (https://www.liebertpub.com/toc/jchc/27/2) to read the issue now.
Karen Monsen, PhD, RN, School of Nursing, University of Minnesota, and colleagues present the Omaha System COVID-19 Response Guidelines, which provide evidence-based pandemic response interventions used in correctional ...
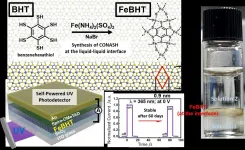
Converting light to electricity effectively has been one of the persistent goals of scientists in the field of optoelectronics. While improving the conversion efficiency is a challenge, several other requirements also need to be met. For instance, the material must conduct electricity well, have a short response time to changes in input (light intensity), and, most importantly, be stable under long-term exposure.
Lately, scientists have been fascinated with "coordination nanosheets" (CONASHs), that are organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials in which organic molecules are bonded to metal atoms in a 2D network. The interest in CONASHs stems mainly from their ability to absorb light at multiple wavelength ranges and convert ...
Indiana Jones hates snakes. And he's certainly not alone. The fear of snakes is so common it even has its own name: ophidiophobia.
Kibret Mequanint doesn't particularly like the slithery reptiles either (he actually hates them too) but the Western University bioengineer and his international collaborators have found a novel use for snake venom: a body tissue 'super glue' that can stop life-threatening bleeding in seconds.
Over the past 20 years, Mequanint has developed a number of biomaterials-based medical devices and therapeutic technologies - some of which are either licensed to medical companies or are in the advanced stage of preclinical testing.
His latest collaborative research discovery ...
Penn State College of Engineering researchers set out to develop technology capable of localizing and imaging blood clots in deep veins. Turns out their work may not only identify blood clots, but it may also be able to treat them.
The team, led by Scott Medina, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, published its results in Advance Healthcare Materials.
"Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in deep veins, typically in a person's legs," said Medina. "It's a life-threatening blood clotting condition that, if left unaddressed, can cause deadly pulmonary embolisms -- when the clot travels to the lungs and blocks an artery. To manage DVT, and prevent these life-threating complications, it's critical to be able to rapidly detect, monitor and treat it."
The ...
The research seeks to understand what drives decisions in data analyses and the process through which academics test a hypothesis by comparing the analyses of different researchers who tested the same hypotheses on the same dataset. Analysts reported radically different analyses and dispersed empirical outcomes, including, in some cases, significant effects in opposite directions from each other. Decisions about variable operationalizations explained the lack of consistency in results beyond statistical choices (i.e., which analysis or covariates to use).
"Our findings illustrate the importance of analytical choices and how different statistical methods can lead to different conclusions," says Martin Schweinsberg. ...
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) typically suffer from impaired bone quality and quantity, with a non-vertebral fracture risk which is 4-to 6-fold higher than the fracture risk of matched controls. However, despite their high risk of fragility fractures, the vast majority of patients with chronic CKD stages 4 to 5D, are not receiving osteoporosis therapy.
A newly published review by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) CKD-MBD working group now provides concise recommendations, with a clear management algorithm, to support clinicians' knowledge and confidence in managing ...
BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Massachusetts Eye and Ear indicates that the blood pressure drug losartan may benefit patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a hereditary condition associated with vestibular schwannomas, or noncancerous tumors along the nerves in the brain that are involved with hearing and balance. The findings, which are published in Science Translational Medicine, are especially important because vestibular schwannomas are currently treated with surgery and radiation therapy (which carry risks of nerve damage), and no drug is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat these tumors or their associated hearing ...
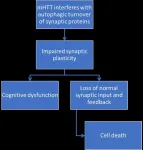
Amsterdam, July 15, 2021 - Huntington's Disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition characterized by motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms, and motor symptoms are often preceded by cognitive changes. Recent evidence indicates that autophagy plays a central role in synaptic maintenance, and the disruption in autophagy may be at the root of these early cognitive changes. Understanding this mechanism better may help researchers develop treatments for patients with HD early in their disease progression, report scientists in a review article published in the Journal of Huntington's Disease.
In this review, experts describe how autophagy, the cellular process responsible ...
We sleep on average one third of our time. But what does the brain do during these long hours? Using an artificial intelligence approach capable of decoding brain activity during sleep, scientists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, were able to glimpse what we think about when we are asleep. By combining functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), the Geneva team provides unprecedented evidence that the work of sorting out the thousands of pieces of information processed during the day takes place during ...