Human waste contaminating urban water leads to 'superbug' spread -- study
2021-07-15
(Press-News.org) Contamination of urban lakes, rivers and surface water by human waste is creating pools of 'superbugs' in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMIC) - but improving access to clean water, sanitation and sewerage infrastructure could help to protect people's health, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied bodies of water in urban and rural sites in three areas of Bangladesh - Mymensingh, Shariatpur and Dhaka. They found more antibiotic resistant faecal coliforms in urban surface water compared to rural settings, consistent with reports of such bacteria in rivers across Asia.
Publishing their findings in mSystems today, researchers from the University of Birmingham and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh call for further research to quantify the drivers of antibiotic resistance in surface waters in Bangladesh.
Lead author Willem van Schaik, Professor of Microbiology and Infection at the University of Birmingham, commented: "The rivers and lakes of Dhaka are surrounded by highly-populated slums in which human waste is directly released into the water. The presence of human gut bacteria links to high levels of antibiotic resistance genes, suggesting that such contamination is driving the presence of these 'superbugs' in surface water.
"Interventions aimed at improving access to clean water, sanitation and sewerage infrastructure may thus be important to reduce the risk of antimicrobial resistance spreading in Bangladesh and other LMICs. While levels of antibiotic resistance genes are considerably lower in rural than in urban settings, we found that antibiotics are commonly used in fish farming and further policies need to be developed to reduce their use."
The prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria causing infections is increasing globally, but the clinical issues, including significant morbidity and mortality, posed by these bacteria are particularly alarming in LMICs. The prevalence multidrug-resistant E. coli among healthy humans is relatively high in Bangladesh, as it is in other LMICs.
Dhaka, has a population of around 16 million people, with a population density that ranks among the highest of any megacity, but less than 20% of households are directly connected to sewerage infrastructure.
The research team found that urban surface waters in Bangladesh are particularly rich in antibiotic resistance genes, with a higher number of them associated with plasmids indicating that they are more likely to spread through the population.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria that colonize the human gut can be passed into rivers, lakes and coastal areas through the release of untreated wastewater, the overflow of pit latrines during monsoon season or by practices such as open defecation.
These contaminated environments are often used for bathing, for the washing of clothes and food preparation equipment, thus increasing the risk of human gut colonisation by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
INFORMATION:
For more information, please contact Tony Moran, International Communications Manager, on +44 (0)782 783 2312. For out-of-hours enquiries, please call +44 (0) 7789 921 165.
Notes for editors
* The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world's top 100 institutions, its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers and teachers and more than 6,500 international students from over 150 countries
* 'Metagenome-wide analysis of rural and urban surface waters and sediments in Bangladesh identifies human waste as driver of antibiotic resistance' - Ross Stuart McInnes, Md. Hassan uz-Zaman, Imam Taskin Alam, Siu Fung Stanley Ho, Robert A. Moran, John D. Clemens, Md. Sirajul Islam, Willem van Schaik is published in mSystems.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-15
COVID-19 NEWS: CAN DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS HELP THE IMMUNE SYSTEM FIGHT CORONAVIRUS INFECTION?
Media Contact: Patrick Smith, pjsmith88@jhmi.edu
Johns Hopkins Medicine gastroenterologist Gerard Mullin, M.D., and a team of co-authors published an article May 11, 2021, in Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology that details the scientific rationale and possible benefits -- as well as possible drawbacks -- of several dietary supplements currently in clinical trials related to COVID-19 treatment.
According to business analysts, the U.S. nutritional supplement industry grew as much as 14.5% in 2020, due in large part to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mullin, associate professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University ...
2021-07-15
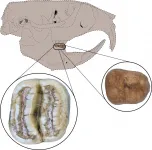
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Two fossil teeth from a distant relative of North American gophers have scientists rethinking how some mammals reached the Caribbean Islands.
The teeth, excavated in northwest Puerto Rico, belong to a previously unknown rodent genus and species, now named Caribeomys merzeraudi. About the size of a mouse, C. merzeraudi is the Caribbean's smallest known rodent and one of the region's oldest, dating back about 29 million years.
It also represents the first discovery of a Caribbean rodent from a North American lineage, a finding that complicates an idea ...
2021-07-15
A new study by the University of Malta and Staffordshire University highlights an urgent need for change in the curriculum and demonstrates how introducing longer, more frequent and more physically intense PE lessons can significantly improve children's weight and overall health.
Malta currently has one of the highest rates of obesity worldwide with 40% of primary and 42.6% of secondary school children being overweight or obese.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that children engage in at least 60 minutes of age-appropriate moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) daily, however ...
2021-07-15
New Rochelle, NY, July 14, 2021-Firsthand reports from nurses in correctional facilities detail the challenges they faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. These firsthand accounts are reported in a special issue on correctional nursing in the Journal of Correctional Health Care. Click here (https://www.liebertpub.com/toc/jchc/27/2) to read the issue now.
Karen Monsen, PhD, RN, School of Nursing, University of Minnesota, and colleagues present the Omaha System COVID-19 Response Guidelines, which provide evidence-based pandemic response interventions used in correctional ...
2021-07-15
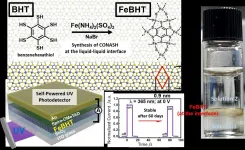
Converting light to electricity effectively has been one of the persistent goals of scientists in the field of optoelectronics. While improving the conversion efficiency is a challenge, several other requirements also need to be met. For instance, the material must conduct electricity well, have a short response time to changes in input (light intensity), and, most importantly, be stable under long-term exposure.
Lately, scientists have been fascinated with "coordination nanosheets" (CONASHs), that are organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials in which organic molecules are bonded to metal atoms in a 2D network. The interest in CONASHs stems mainly from their ability to absorb light at multiple wavelength ranges and convert ...
2021-07-15
Indiana Jones hates snakes. And he's certainly not alone. The fear of snakes is so common it even has its own name: ophidiophobia.
Kibret Mequanint doesn't particularly like the slithery reptiles either (he actually hates them too) but the Western University bioengineer and his international collaborators have found a novel use for snake venom: a body tissue 'super glue' that can stop life-threatening bleeding in seconds.
Over the past 20 years, Mequanint has developed a number of biomaterials-based medical devices and therapeutic technologies - some of which are either licensed to medical companies or are in the advanced stage of preclinical testing.
His latest collaborative research discovery ...
2021-07-15
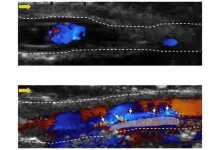
Penn State College of Engineering researchers set out to develop technology capable of localizing and imaging blood clots in deep veins. Turns out their work may not only identify blood clots, but it may also be able to treat them.
The team, led by Scott Medina, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, published its results in Advance Healthcare Materials.
"Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in deep veins, typically in a person's legs," said Medina. "It's a life-threatening blood clotting condition that, if left unaddressed, can cause deadly pulmonary embolisms -- when the clot travels to the lungs and blocks an artery. To manage DVT, and prevent these life-threating complications, it's critical to be able to rapidly detect, monitor and treat it."
The ...
2021-07-15
The research seeks to understand what drives decisions in data analyses and the process through which academics test a hypothesis by comparing the analyses of different researchers who tested the same hypotheses on the same dataset. Analysts reported radically different analyses and dispersed empirical outcomes, including, in some cases, significant effects in opposite directions from each other. Decisions about variable operationalizations explained the lack of consistency in results beyond statistical choices (i.e., which analysis or covariates to use).
"Our findings illustrate the importance of analytical choices and how different statistical methods can lead to different conclusions," says Martin Schweinsberg. ...
2021-07-15
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) typically suffer from impaired bone quality and quantity, with a non-vertebral fracture risk which is 4-to 6-fold higher than the fracture risk of matched controls. However, despite their high risk of fragility fractures, the vast majority of patients with chronic CKD stages 4 to 5D, are not receiving osteoporosis therapy.
A newly published review by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) CKD-MBD working group now provides concise recommendations, with a clear management algorithm, to support clinicians' knowledge and confidence in managing ...
2021-07-15
BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Massachusetts Eye and Ear indicates that the blood pressure drug losartan may benefit patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a hereditary condition associated with vestibular schwannomas, or noncancerous tumors along the nerves in the brain that are involved with hearing and balance. The findings, which are published in Science Translational Medicine, are especially important because vestibular schwannomas are currently treated with surgery and radiation therapy (which carry risks of nerve damage), and no drug is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat these tumors or their associated hearing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Human waste contaminating urban water leads to 'superbug' spread -- study