(Press-News.org) As the Covid-19 pandemic raged, news reports show that sales of electronic air cleaners have surged due to concerns about airborne disease transmission. But a research team at the Georgia Institute of Technology has found that the benefits to indoor air quality of one type of purifying system can be offset by the generation of other pollutants that are harmful to health.
Led by Associate Professor Nga Lee "Sally" Ng in Georgia Tech's School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, the team evaluated the effect of a hydroxyl radical generator in an office setting. Hydroxyl radicals react with odors and pollutants, decomposing them, and hydroxyl radical generators have been marketed to inactivate pathogens such as coronaviruses.
However, Ng's study found that in the process of cleaning the air, the hydroxyl radicals generated by the device reacted with volatile organic compounds present in the indoor space. This led to chemical reactions that quickly formed organic acids and secondary organic aerosols that can cause health problems. Secondary organic aerosols is a major component of PM2.5 (particulate matter with a diameter smaller than 2.5 ?m), and exposure to PM2.5 has been associated with cardiopulmonary diseases and millions of deaths per year.
The paper, "Formation of oxidized gases and secondary organic aerosol from a commercial oxidant-generating electronic air cleaner," is published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
While the pandemic has made various types of electronic cleaners increasingly popular, Ng explained that consumers are probably not aware of the secondary chemistry taking place in the air, with the pollutants generated not being directly emitted by the cleaning device itself.
"There are increasing concerns regarding the use of electronic air cleaners as these devices can potentially generate unintended byproducts via oxidation chemistry similar to that in the atmosphere," Ng said.
Two types of air cleaning technologies are commonly used to remove indoor pollutants such as particles or volatile organic compounds and to inactivate pathogens: mechanical filtration and electronic air cleaners that generate ions, reactive species, or other chemical products such as photocatalytic oxidation, plasma, and oxidant-generating equipment (e.g., ozone, hydroxyl radical), among others.
Ng's team selected a hydroxyl generator for the study. They measured the oxygenated volatile organic compounds and the chemical composition of particles generated by the device in an office on the Georgia Tech campus.
While previous research reported pollutant formation from various electronic air cleaners (ionizers, plasma systems, photocatalytic systems with ultraviolet lamps, etc.), Ng believes that her team's study is the first to monitor the chemical composition of secondary pollutants in both gas and particle phases during the operation of an electronic device that dissipates oxidants in a real-world setting.
Advanced instrumentation made Ng's study possible. Gas-phase organic compounds were measured using a high-resolution time-of-flight chemical ionization mass spectrometer, purchased through a National Science Foundation major instrumentation grant. The study received support from Georgia Tech's Covid-19 Rapid Response fund.
Ng noted that future studies on air cleaning technology should not be limited to inactivation of viruses or reduction of volatile organic compounds, but should also evaluate potential oxidation chemistry and the formation of unintended harmful gaseous and particulate chemicals.
"More studies need to be conducted on the effects of these devices in a variety of environments," Ng said.
"Electronic air cleaners greatly rose in prominence because of the pandemic, and now there are a lot of these devices out there. Millions of dollars are being spent on these devices by businesses and schools. The market is huge.
"Our results show that care must be taken when choosing an adequate and appropriate air cleaning technology for a particular environment and task," she said.
Ng stressed the importance of future studies concerning the unintended effects of electronic purifiers, as these devices are not currently well regulated and do not have testing standards.
"There needs to be more peer-reviewed scientific data on electronic air cleaners," Ng said. "We hope that additional studies will lead to more government guidelines and regulation."
INFORMATION:
CITATION: Joo et al., "Formation of oxidized gases and secondary organic aerosol from a commercial oxidant-generating electronic air cleaner." (Environmental Science & Technology Letters)
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.estlett.1c00416
About the Georgia Institute of Technology
The Georgia Institute of Technology, or Georgia Tech, is a top 10 public research university developing leaders who advance technology and improve the human condition.
The Institute offers business, computing, design, engineering, liberal arts, and sciences degrees. Its nearly 40,000 students representing 50 states and 149 countries, study at the main campus in Atlanta, at campuses in France and China, and through distance and online learning.
As a leading technological university, Georgia Tech is an engine of economic development for Georgia, the Southeast, and the nation, conducting more than $1 billion in research annually for government, industry, and society.
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland has 3D printed a soft robotic hand that is agile enough to play Nintendo's Super Mario Bros. - and win!
The feat, highlighted on the front cover of the latest issue of Science Advances, demonstrates a promising innovation in the field of soft robotics, which centers on creating new types of flexible, inflatable robots that are powered using water or air rather than electricity. The inherent safety and adaptability of soft robots has sparked interest in their use for applications like prosthetics and biomedical devices. Unfortunately, controlling the fluids that make these soft ...
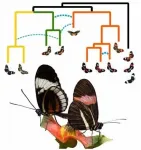
Evolution is often portrayed as a tree, with new species branching off from existing lineages, never again to meet. The truth however is often much messier. In the case of adaptive radiation, in which species diversify rapidly to fill different ecological niches, it can be difficult to resolve relationships, and the phylogeny (i.e. evolutionary tree) may look more like a bush than a tree. This is because lineages may continue to interbreed as new species are established, and/or they may diverge and then re-hybridize, resulting in genetically mixed populations (known as admixture). Even after species diverge, the introduction of genes from one species to another (known as introgression) can occur. All of ...
A UC San Francisco study has found that the antibiotic azithromycin was no more effective than a placebo in preventing symptoms of COVID-19 among non-hospitalized patients, and may increase their chance of hospitalization, despite widespread prescription of the antibiotic for the disease.
"These findings do not support the routine use of azithromycin for outpatient SARS-CoV-2 infection," said lead author Catherine E. Oldenburg, ScD, MPH, an assistant professor with the UCSF Proctor Foundation. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19.
Azithromycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, is widely prescribed as a treatment for COVID-19 in the United States and the rest of the world. "The hypothesis is that it has anti-inflammatory properties that ...
ATLANTA--An oral prodrug developed by a team of scientists led by Binghe Wang, Regents' Professor of Chemistry at Georgia State University, delivers carbon monoxide to protect against acute kidney injury, according to a new paper published in Chemical Science.
Although carbon monoxide (CO) gas is toxic in large doses, scientists have discovered it can have beneficial effects by reducing inflammation and protecting cells against injury. Previous studies have demonstrated the protective effects of CO against injury in the kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and liver, among other organs. For the past five years, Wang and his collaborators have worked to design a safe way to deliver CO to human patients via prodrugs -- inactive compounds that ...
The COVID-19 pandemic knocked many women off schedule for important health appointments, a new study finds, and many didn't get back on schedule even after clinics reopened. The effect may have been greatest in areas where such care is already likely falling behind experts' recommendations.
The study, by health care researchers in the University of Michigan END ...
The hydrothermal vent fluids from the Gorda Ridge spreading center in the northeast Pacific Ocean create a biological hub of activity in the deep sea. There, in the dark ocean, a unique food web thrives not on photosynthesis but rather on chemical energy from the venting fluids. Among the creatures having a field day feasting at the Gorda Ridge vents is a diverse assortment of microbial eukaryotes, or protists, that graze on chemosynthetic bacteria and archaea.
This protistan grazing, which is a key mechanism for carbon transport and recycling in microbial food webs, exerts a higher predation pressure at hydrothermal vent sites than in the surrounding deep-sea environment, a new paper finds.
"Our ...
Vaccine negativity and reluctance didn't just emerge during the COVID-19 pandemic. In a recent study published in the Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness journal, authors from Loyola University Maryland and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health explored the appearance of negative dominance - a concept in which negative messages outweigh positive, solution-oriented messages in audiences' perceptions - in the context of COVID-19 vaccine-related information and activity online.
Prior research has looked at media coverage to identify vaccine concerns among the public and its impact on vaccine-related beliefs and behaviors, the spread of misinformation and fake news on the Internet, and the role ...
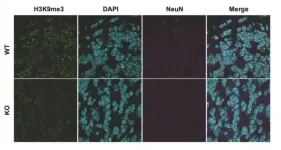
New research from the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan shows that a deficit in histone methylation could lead to the development of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). A human variant of the SUV39H2 gene led researchers to examine its absence in mice. Published in Molecular Psychiatry, the study found that when absent, adult mice exhibited cognitive inflexibility similar to what occurs in autism, and embryonic mice showed misregulated expression of genes related to brain development. These findings represent the first direct link between the SUV39H2 gene and ASD.
Genes are turned ...
What The Study Did: The association between primary care payment models and the use of telemedicine for Medicare Advantage enrollees during the COVID-19 pandemic was examined in this study.
Authors: Brian W. Powers, M.D., M.B.A., of Humana Inc. in Louisville, Kentucky, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1597)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether death, other hospital outcomes and processes of care differed between patients cared for by female and male physicians at hospitals in Canada.
Authors: Fahad Razak, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Toronto in Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1615)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news ...