(Press-News.org) The COVID-19 pandemic knocked many women off schedule for important health appointments, a new study finds, and many didn't get back on schedule even after clinics reopened. The effect may have been greatest in areas where such care is already likely falling behind experts' recommendations.
The study, by health care researchers in the University of Michigan END
From birth control to mammograms, many women missed out on preventive care for all of 2020
Study shows even after in-person care restarted, women were 20% to 30% less likely to get such services than in 2019, especially those from lower-income and higher-minority areas
2021-07-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study examines the role of deep-sea microbial predators at hydrothermal vents
2021-07-16
The hydrothermal vent fluids from the Gorda Ridge spreading center in the northeast Pacific Ocean create a biological hub of activity in the deep sea. There, in the dark ocean, a unique food web thrives not on photosynthesis but rather on chemical energy from the venting fluids. Among the creatures having a field day feasting at the Gorda Ridge vents is a diverse assortment of microbial eukaryotes, or protists, that graze on chemosynthetic bacteria and archaea.
This protistan grazing, which is a key mechanism for carbon transport and recycling in microbial food webs, exerts a higher predation pressure at hydrothermal vent sites than in the surrounding deep-sea environment, a new paper finds.
"Our ...
COVID-19 vaccination: Examining negative dominance on social media
2021-07-16
Vaccine negativity and reluctance didn't just emerge during the COVID-19 pandemic. In a recent study published in the Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness journal, authors from Loyola University Maryland and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health explored the appearance of negative dominance - a concept in which negative messages outweigh positive, solution-oriented messages in audiences' perceptions - in the context of COVID-19 vaccine-related information and activity online.
Prior research has looked at media coverage to identify vaccine concerns among the public and its impact on vaccine-related beliefs and behaviors, the spread of misinformation and fake news on the Internet, and the role ...
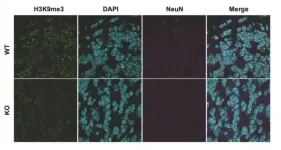
SUV39H2: A direct genetic link to autism spectrum disorders
2021-07-16
New research from the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan shows that a deficit in histone methylation could lead to the development of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). A human variant of the SUV39H2 gene led researchers to examine its absence in mice. Published in Molecular Psychiatry, the study found that when absent, adult mice exhibited cognitive inflexibility similar to what occurs in autism, and embryonic mice showed misregulated expression of genes related to brain development. These findings represent the first direct link between the SUV39H2 gene and ASD.
Genes are turned ...
Primary care payment model, telemedicine use for Medicare Advantage during pandemic
2021-07-16
What The Study Did: The association between primary care payment models and the use of telemedicine for Medicare Advantage enrollees during the COVID-19 pandemic was examined in this study.
Authors: Brian W. Powers, M.D., M.B.A., of Humana Inc. in Louisville, Kentucky, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1597)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
Outcomes of patients treated by female vs male physicians
2021-07-16
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether death, other hospital outcomes and processes of care differed between patients cared for by female and male physicians at hospitals in Canada.
Authors: Fahad Razak, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Toronto in Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1615)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news ...
Exploring gap between excess mortality, COVID-19 deaths in 67 countries
2021-07-16
What The Study Did: National health care systems have different capacities to correctly identify people who died of COVID-19. Researchers in this study analyzed the gap between excess mortality and COVID-19 confirmed mortality in 67 countries to determine the extent to which official data on COVID-19 deaths might be considered reliable.
Authors: Davide Golinelli, M.D., Alma Mater Studiorum-University of Bologna in Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17359)
Editor's ...
No sign of COVID-19 vaccine in breast milk
2021-07-16
Messenger RNA vaccines against COVID-19 were not detected in human milk, according to a small study by UC San Francisco, providing early evidence that the vaccine mRNA is not transferred to the infant.
The study, which analyzed the breast milk of seven women after they received the mRNA vaccines and found no trace of the vaccine, offers the first direct data of vaccine safety during breastfeeding and could allay concerns among those who have declined vaccination or discontinued breastfeeding due to concern that vaccination might alter human milk. The paper appears in JAMA Pediatrics.
Research has demonstrated that vaccines with mRNA inhibit transmission ...
New UK study reveals extent of brain complications in children hospitalized with COVID-19
2021-07-16
Although the risk of a child being admitted to hospital due to COVID-19 is small, a new UK study has found that around 1 in 20 of children hospitalised with COVID-19 develop brain or nerve complications linked to the viral infection.
The research, published in The Lancet Child and Adolescent Health and led by the University of Liverpool, identifies a wide spectrum of neurological complications in children and suggests they may be more common than in adults admitted with COVID-19.
While neurological problems have been reported in children with the newly described post-COVID condition paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally ...
New theory suggests blood immune and clotting components could contribute to psychosis
2021-07-16
A scientific review has found evidence that a disruption in blood clotting and the first line immune system could be contributing factors in the development of psychosis.
The article, a joint collaborative effort by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, Cardiff University and the UCD Conway Institute, is published in Molecular Psychiatry.
Recent studies have identified blood proteins involved in the innate immune system and blood clotting networks as key players implicated in psychosis.
The researchers analysed these studies and developed a new theory that proposes the imbalance of both of these systems leads to inflammation, which in turn contributes to the development of psychosis.
The work proposes that alterations ...
When mad AIOLOS drags IKAROS down: A novel pathogenic mechanism
2021-07-16
Tokyo, Japan - Primary immunodeficiencies, such as severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID), occur when the immune system does not work properly, leading to increased susceptibility to various infections, autoimmunity, and cancers. Most of these are inherited and have an underlying genetic causes. A team at TMDU has identified a novel disorder resulting from a mutation in a protein called AIOLOS, which functions through a previously unknown pathogenic mechanism called heterodimeric interference.
The gene family known as IKAROS zinc finger proteins (IKZFs) is associated with the development of lymphocyte, a type of white blood cell involved ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] From birth control to mammograms, many women missed out on preventive care for all of 2020Study shows even after in-person care restarted, women were 20% to 30% less likely to get such services than in 2019, especially those from lower-income and higher-minority areas