(Press-News.org) Oncotarget published "Ex vivo analysis of DNA repair targeting in extreme rare cutaneous apocrine sweat gland carcinoma" which reported a rare metastatic case with a PALB2 aberration identified previously as a familial susceptibility gene for breast cancer in the Finnish population.
As PALB2 exhibits functions in the BRCA1/2-RAD51-dependent homologous DNA recombination repair pathway, we sought to use ex vivo functional screening to explore sensitivity of the tumor cells to therapeutic targeting of DNA repair.
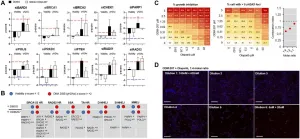
Drug screening suggested sensitivity of the PALB2 deficient cells to BET-bromodomain inhibition, and modest sensitivity to DNA-PKi, ATRi, WEE1i and PARPi.
A phenotypic RNAi screen of 300 DNA repair genes was undertaken to assess DNA repair targeting in more detail.
RNAi inhibition of RAD52-dependent HR on the other hand potentiated the efficacy of a novel BETi ODM-207.
Together these Oncotarget results describe the first ever CAC case with a BRCAness genetic background, evaluate combinatorial DNA repair targeting, and provide a data resource for further analyses of DNA repair targeting in PALB2 deficient cancers.
Together these Oncotarget results describe the first ever CAC case with a BRCAness genetic background
Dr. Juha K. Rantala from The University of Sheffield as well as The Misvik Biology Oy said, "Metastatic cutaneous apocrine gland carcinoma (CAC) is an extreme rare malignancy arising from a sweat gland with < 30 reported cases in the literature."
The tumorigenesis of these rare cancers is largely unclear, but histologically cutaneous apocrine gland carcinomas mimic metastatic apocrine breast cancer or apocrine carcinomas arising in ectopic breast tissue.
Given the rarity of metastatic CAC tumors and the heterogeneity of the treatments used, the survival benefits of cytotoxic agents in treatment of metastatic CAC remains unclear, as does the use of targeted therapies, which have been reported for a few individual patients.
The authors used multiomics methods for ex vivo analysis of the patient derived tumor cells with the aim to inform the treatment of the patient after relapse following 9 previous treatment regimens.
Of these, two different BET-bromodomain inhibitors; JQ1 and ODM-207 were the most potent drugs with known DNA repair targeting mechanisms. To assess DNA repair pathways essential for the tumor cells and contributing to sensitivity/resistance of the tumor cells to BETi, we use ex vivo functional RNAi screening to discover biological insights on the different DNA repair pathways with the PALB2 deficient cells.
To extend the analysis beyond the patient derived cells, the authors go on to assess with publicly available drug screening data the correlation between efficacy of PARP inhibitors Olaparib, Talazoparib and BETi on 800 model cell lines divided to unaltered or PALB2 altered cell lines.
The Rantala Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Outlet that although the efforts here ultimately did not result in successful treatment of the patient, the significance of this study is its demonstration that this type of functional ex vivo analyses if performed in the early stages of disease could provide valuable insights into treatment of rare cancers where there is limited data available to base treatment decisions on.
Their analyses of sensitivity of PALB2 deficient cancer cells to inhibition of the different DNA repair pathways also offer a valuable data resource for testing and building new hypothesis on.
In summary, by interrogating the patient-derived cells, they identify a potential therapeutic opportunity for targeting PALB2 deficient cells through inhibition of DNA repair with BETi or PARPi.
Moreover, they identify the PALB2 c.1592delT mutation as a potential susceptibility factor for non-melanoma skin cancer in the high cancer risk families carrying this founder mutation.
INFORMATION:
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27961
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27961/text/
Correspondence to - Juha K. Rantala - rantala@misvik.com
Keywords -
cutaneous apocrine sweat gland carcinoma,
ex vivo drug screening,
DNA repair,
PALB2,
rare cancer
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a bi-weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
Copyright © 2021 Impact Journals, LLC
Impact Journals is a registered trademark of Impact Journals, LLC
Oncotarget published "Caspase-11 and AIM2 inflammasome are involved in smoking-induced COPD and lung adenocarcinoma" which reported that cigarette smoking is the leading risk factor for COPD and lung cancer establishment.
Epidemiologically, COPD patients are 6.35 times more likely to develop lung cancer.
To mimic COPD, the authors exposed mice to nose-only cigarette smoke and used human samples of lung adenocarcinoma patients according to the smoking and COPD status.
Interestingly, higher expression of AIM2 in non-cancerous tissue of smoking COPD adenocarcinoma patients was correlated to a higher hazard ratio of poor survival ...
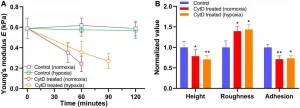
Oncotarget published "Dynamic cellular biomechanics in responses to chemotherapeutic drug in hypoxia probed by atomic force spectroscopy" which reported that by exploiting single-cell, force spectroscopy methods, the authors probed biophysical and biomechanical kinetics of brain, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancer cells with standard chemotherapeutic drugs in normoxia and hypoxia over 12-24 hours.
After exposure to the drugs, they found that brain, breast, and pancreatic cancer cells became approximately 55-75% less stiff, while prostate cancer cells became more stiff, due to either drug-induced ...
Butterflies and moths (order Lepidoptera) are one of the most diverse animal groups. To date, scientists have found as many as 5,000 species from the Alps alone. Having been a place of intensive research interest for 250 years, it is considered quite a sensation if a previously unknown species is discovered from the mountain range these days. This was the case when a Swiss-Austrian team of researchers described a new species of alpine moth in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Alpine Entomology, solving a 180-year-old mystery.
Decades of research work
Initially, the team - Jürg Schmid, a full-time dentist, author and passionate butterfly and moth researcher from Switzerland, and Peter Huemer, head of the natural science collections ...
Researchers are using computer models to simulate COVID-19 infections on a cellular level - the basic structural level of the human body.
The models allow for virtual trials of drugs and vaccines, opening the possibility of pre-assessment for drug and vaccine efficacy against the virus.
The research team at the University of Waterloo includes Anita Layton, professor of applied mathematics and Canada 150 Research Chair in mathematical biology and medicine, and Mehrshad Sadria, an applied mathematics PhD student.
The team uses "in silico" experiments to replicate how the human immune system deals with the COVID-19 virus. In silico refers to trials situated in the silicon of computer chips, as opposed to "in ...
PULLMAN, Wash. --Students who identify as LGBTQ+ in Washington state school districts with conservative voting records reported experiencing more bullying than their peers in more politically liberal areas, according to a new study.
For the study in the journal Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy, researchers explored the relationships among school district voting records in the 2016 presidential election, bullying experiences in schools and mental health outcomes of LGBTQ+ youth in the state.
The study shows LGBTQ+ students are at a higher risk for psychological distress and suicidality as a result of bullying, particularly in school districts that voted for former ...
WHAT:
In a perspective published in Neuropsychopharmacology, leaders from the National Institutes of Health address how using appropriate language to describe mental illness and addiction can help to reduce stigma and improve how people with these conditions are treated in health care settings and throughout society. The authors define stigma as negative attitudes toward people that are based on certain distinguishing characteristics. More than a decade of research has shown that stigma contributes significantly to negative health outcomes and can pose a barrier to seeking treatment for mental ...
New models of neutron stars show that their tallest mountains may be only fractions of millimetres high, due to the huge gravity on the ultra-dense objects. The research is presented today at the National Astronomy Meeting 2021.
Neutron stars are some of the densest objects in the Universe: they weigh about as much as the Sun, yet measure only around 10km across, similar in size to a large city.
Because of their compactness, neutron stars have an enormous gravitational pull around a billion times stronger than the Earth. This squashes every feature on the ...
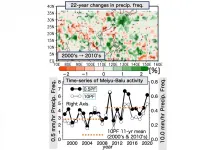
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have analyzed long-term precipitation radar data from satellites and found significantly enhanced rainfall over the most recent decade during the annual Meiyu-Baiu rainy season in East Asia. The data spans 23 years and gives unprecedented insight into how rainfall patterns have changed. They showed that the increased rainfall was driven by the decadal increased transport of moisture from the tropics and frequent occurrence of the upper tropospheric trough over the front.
From the second ...
Highlights
The results of a new study support the validity of a score that considers various patient-reported outcome measures and preferences for assessing health-related quality of life in individuals with kidney failure.
The score is calculated from assessments of cognitive function, depression, fatigue, pain interference, physical functioning, sleep disturbance, and ability to participate in social roles.
Washington, DC (July 16, 2021) -- Results from a new study support the validity of a score that considers various patient-reported measures and preferences for assessing health-related quality of life and promoting patient-centered care in individuals with kidney failure. The study appears in an upcoming issue of CJASN.
The ...
Highlights
The sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin reduced kidney, cardiovascular, and mortality risks in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease, similar to benefits seen in individuals with normal or moderately impaired kidney function.
Rates of serious side effects were similar in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease who received dapagliflozin or placebo.
Washington, DC (July 16, 2021) -- Studies have shown that diabetes drugs called sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors can provide kidney- and cardiovascular-related ...