(Press-News.org) The climate crisis will lead to changes in distribution and habitat loss of stony corals in the tropical Atlantic, shows a new study published by the open access publisher Frontiers. The loss of such coral species could have devastating consequences for the marine ecosystems they inhabit. The results of the study highlight an urgent need for coral reef management in the Atlantic.
Researchers at the University of São Paulo projected current and future distributions of three key reef building corals of the tropical Atlantic (Mussismilia hispida, Montastraea cavernosa and the Siderastrea complex). They conclude that all three species will experience changes in range due to the climate crisis, which will elicit negative cascading effects on the biodiversity of reef ecosystems. The results are published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science.
Nature's engineers are threatened
Mussismilia hispida, Montastraea cavernosa and the Siderastrea complex are stony corals of the eastern and western Atlantic. They are ecosystem engineers: much like beavers who contribute to the structure of their terrestrial habitats by building dams, stony corals help build reefs by depositing calcium carbonate. They are vital for the health and function of these reefs, which are among the most diverse ecosystems on Earth.
"Coral reefs provide essential ecosystem services such as food provision, coastal protection and nutrient cycling, that benefit millions of people - including those who live far from any coral reef," says lead author and PhD candidate Silas Principe of the University of São Paulo.
"If species that are important in structuring the coral reefs are lost, the provision of all those services is consequently also threatened."
Human activity has long harmed corals worldwide, and coral reefs are already some of the most threatened ecosystems on the planet. Intense and long-lasting mass bleaching events, ocean acidification, pollution, urbanization, fisheries, and tourism are all leading to reduction and loss of coral cover. Now, the climate crisis is adding to those threats.
Climate change leads to changes in coral distribution, with key coral species moving within the tropics or to temperate waters at higher latitudes. Changes in distributions of these key species may have unprecedented cascading effects on entire marine wildlife communities, such as drastic changes in the structural complexity of reef ecosystems.
Concerning findings
Researching possible changes in stony coral distribution is important for planning and management of coral reef conservation. The researchers collected data on M. hispida, M. cavernosa and the Siderastrea complex from different databases and used species distribution models to model their suitability on their current habitat. They also modeled future changes in range under three different climate change scenarios (most pessimistic, most optimistic, and moderate).
They found that, even in the most optimistic scenario, all three species could experience changes in their distributions. Especially in the western Atlantic, decreases in the abundance of stony corals are expected under all three scenarios. Several areas along the Brazilian coast and the Caribbean will lose habitat suitability. These projections are especially critical for the Brazilian coast, where there are fewer habitat-building coral species.
The researchers urge conservation and management efforts to be focused on regions such as the Abrolhos region, northeast coast of Brazil, western Caribbean, and the Gulf of Mexico. "We show that important reef builder species of the Atlantic will face shifts in its distribution due to climate change," Principe said.
"Certain areas, such as the Abrolhos region in the coast of Brazil, will completely lose at least one of its species in any of the future scenarios. Major areas in the Caribbean will also lose species in the future, although in the coast of Africa some species may expand their current range."
But the results also indicate that there is hope for Atlantic stony corals. "Although our results predict major negative impacts on Atlantic shallow reefs, we also identified several areas where none or less changes are predicted. Managers and policy makers can use this to support the planning process of conservation areas." Principe concludes: "Researchers and conservationists can use these results to focus research efforts on the so-called 'refuge areas' that may constitute safe areas for coral species in the future."
INFORMATION:
To prepare for the next pandemic and provide a coordinated approach to vaccination across the country, Canada should create Canadian Immunization Services based on the Canadian Blood Services model, authors propose in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
The authors, including a leading health policy and immunization expert, a blood system expert and a former federal minister of health, are Dr. Kumanan Wilson, professor, Department of Medicine and member of the Centre for Health Law, Policy and Ethics, University of Ottawa; Dr. Graham Sher, CEO, Canadian Blood Services; and Dr. Jane Philpott, Dean, Faculty of Health Sciences, Queen's University.
"If we want to be better prepared for the ...
Philadelphia, July 19, 2021 - University of Minnesota School of Public Health researchers recently completed a study to determine how food-insecure young (emerging) adults (18-29 years of age) adapted their eating and child feeding behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. The researchers also sought to identify barriers to food access and opportunities to improve local access to resources for emerging adults. Their END ...
Oncotarget published "Ex vivo analysis of DNA repair targeting in extreme rare cutaneous apocrine sweat gland carcinoma" which reported a rare metastatic case with a PALB2 aberration identified previously as a familial susceptibility gene for breast cancer in the Finnish population.
As PALB2 exhibits functions in the BRCA1/2-RAD51-dependent homologous DNA recombination repair pathway, we sought to use ex vivo functional screening to explore sensitivity of the tumor cells to therapeutic targeting of DNA repair.
Drug screening suggested sensitivity of the PALB2 deficient cells to BET-bromodomain inhibition, and modest ...
Oncotarget published "Caspase-11 and AIM2 inflammasome are involved in smoking-induced COPD and lung adenocarcinoma" which reported that cigarette smoking is the leading risk factor for COPD and lung cancer establishment.
Epidemiologically, COPD patients are 6.35 times more likely to develop lung cancer.
To mimic COPD, the authors exposed mice to nose-only cigarette smoke and used human samples of lung adenocarcinoma patients according to the smoking and COPD status.
Interestingly, higher expression of AIM2 in non-cancerous tissue of smoking COPD adenocarcinoma patients was correlated to a higher hazard ratio of poor survival ...
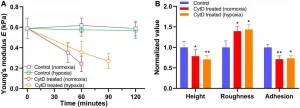
Oncotarget published "Dynamic cellular biomechanics in responses to chemotherapeutic drug in hypoxia probed by atomic force spectroscopy" which reported that by exploiting single-cell, force spectroscopy methods, the authors probed biophysical and biomechanical kinetics of brain, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancer cells with standard chemotherapeutic drugs in normoxia and hypoxia over 12-24 hours.
After exposure to the drugs, they found that brain, breast, and pancreatic cancer cells became approximately 55-75% less stiff, while prostate cancer cells became more stiff, due to either drug-induced ...
Butterflies and moths (order Lepidoptera) are one of the most diverse animal groups. To date, scientists have found as many as 5,000 species from the Alps alone. Having been a place of intensive research interest for 250 years, it is considered quite a sensation if a previously unknown species is discovered from the mountain range these days. This was the case when a Swiss-Austrian team of researchers described a new species of alpine moth in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Alpine Entomology, solving a 180-year-old mystery.
Decades of research work
Initially, the team - Jürg Schmid, a full-time dentist, author and passionate butterfly and moth researcher from Switzerland, and Peter Huemer, head of the natural science collections ...
Researchers are using computer models to simulate COVID-19 infections on a cellular level - the basic structural level of the human body.
The models allow for virtual trials of drugs and vaccines, opening the possibility of pre-assessment for drug and vaccine efficacy against the virus.
The research team at the University of Waterloo includes Anita Layton, professor of applied mathematics and Canada 150 Research Chair in mathematical biology and medicine, and Mehrshad Sadria, an applied mathematics PhD student.
The team uses "in silico" experiments to replicate how the human immune system deals with the COVID-19 virus. In silico refers to trials situated in the silicon of computer chips, as opposed to "in ...
PULLMAN, Wash. --Students who identify as LGBTQ+ in Washington state school districts with conservative voting records reported experiencing more bullying than their peers in more politically liberal areas, according to a new study.
For the study in the journal Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy, researchers explored the relationships among school district voting records in the 2016 presidential election, bullying experiences in schools and mental health outcomes of LGBTQ+ youth in the state.
The study shows LGBTQ+ students are at a higher risk for psychological distress and suicidality as a result of bullying, particularly in school districts that voted for former ...
WHAT:
In a perspective published in Neuropsychopharmacology, leaders from the National Institutes of Health address how using appropriate language to describe mental illness and addiction can help to reduce stigma and improve how people with these conditions are treated in health care settings and throughout society. The authors define stigma as negative attitudes toward people that are based on certain distinguishing characteristics. More than a decade of research has shown that stigma contributes significantly to negative health outcomes and can pose a barrier to seeking treatment for mental ...
New models of neutron stars show that their tallest mountains may be only fractions of millimetres high, due to the huge gravity on the ultra-dense objects. The research is presented today at the National Astronomy Meeting 2021.
Neutron stars are some of the densest objects in the Universe: they weigh about as much as the Sun, yet measure only around 10km across, similar in size to a large city.
Because of their compactness, neutron stars have an enormous gravitational pull around a billion times stronger than the Earth. This squashes every feature on the ...