INFORMATION:
Note
Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases are diseases of the brain, in which gradual degeneration of neurons leads to loss of speech, memory, and thinking. Most often they affect people over 65 years old. The global number of people suffering from Alzheimer's disease alone in 2010 was estimated at 35.6 million. By 2050, growth is projected to 115.4 million. Effective drugs for the prevention and treatment of ailments of this type have not yet been created. Existing remedies are aimed only at suppressing symptoms, but cannot stop the process of neurodegeneration itself.
Chemists found an effective remedy for "aged" brain diseases
Scientists obtained substances that provide a breakthrough in the treatment of neurodegenerative pathologies
2021-07-19
(Press-News.org) Russian scientists have synthesized chemical compounds that can stop the degeneration of neurons in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and other severe brain pathologies. These substances can provide a breakthrough in the treatment of neurodegenerative pathologies. New molecules of pyrrolyl- and indolylazine classes activate intracellular mechanisms to combat one of the main causes of "aged" brain diseases - an excess of so-called amyloid structures that accumulate in the human brain with age. The essence of the study was published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Experts from the Institute of Cytology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Organic Synthesis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the Ural Federal University (UrFU) took part in the study.
"Our compounds activate the synthesis of specific heat shock proteins and cause their accumulation in the cell," said research co-author, professor of the Department of Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry at UrFU Irina Utepova. "Proteins of this type make it possible to protect neuronal tissue from an excess of toxic amyloids and to protect cells from various types of stress, including proteotoxic stress characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases."
Important advantages of compounds from the series of pyrrolyl- and indolylazine classes are a profitable synthesis technology and low toxicity.
The obtained compounds were tested in cellular models of Alzheimer's disease and secondary injuries after traumatic brain injury. In both cases, the new substances demonstrated a significant therapeutic effect, increasing the survival of neuronal cells. The most effective compound has been tested in living tissues of rats with secondary injuries after traumatic brain injury.
According to scientists, the use of pyrrolylazine in rehabilitation therapy allowed the animals to avoid the appearance of movement disorders and degeneration of hippocampal neurons. The research team has been continued to study the mechanism of action of new compounds and is preparing for their preclinical testing.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
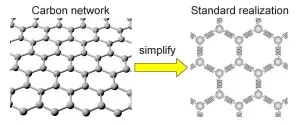
The mathematics of repulsion for new graphene catalysts
2021-07-19
A new mathematical model helps predict the tiny changes in carbon-based materials that could yield interesting properties.
Scientists at Tohoku University and colleagues in Japan have developed a mathematical model that abstracts the key effects of changes to the geometries of carbon material and predicts its unique properties.
The details were published in the journal Carbon.
Scientists generally use mathematical models to predict the properties that might emerge when a material is changed in certain ways. Changing the geometry of three-dimensional (3D) graphene, which is made of networks of carbon atoms, by adding chemicals or introducing topological defects, can improve its catalytic properties, for example. But it has been difficult for scientists to understand why this happens exactly.
The ...
Understanding the physics in new metals
2021-07-19
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and the Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), working in an international team, have developed a new method for complex X-ray studies that will aid in better understanding so-called correlated metals. These materials could prove useful for practical applications in areas such as superconductivity, data processing, and quantum computers. Today the researchers present their work in the journal Physical Review X.
In substances such as silicon or aluminium, the mutual repulsion of electrons hardly affects the material properties. Not so with so-called correlated materials, in which the electrons interact strongly with one another. The movement of one electron in a correlated material leads ...
The era of single-spin color centers in silicon carbide is approaching
2021-07-19
Prof. LI Chuanfeng, Prof. XU Jinshi and their colleagues from Prof. GUO Guangcan's group, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), realized the high-contrast readout and coherent manipulation of a single silicon carbide divacancy color center electron spin at room temperature for the first time in the world, in cooperation with Prof. Adam Gali, from the Wigner Research Centre for Physics in Hungary. This work was published in National Science Review on July 5, 2021.
Solid-state spin color centers are of utmost importance in many applications of quantum technologies, the outstanding one among which is the nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center in diamond. Since the detection ...
African swine fever: No risk to consumers
2021-07-19
African swine fever (ASF), first detected in Germany in domestic pigs on 15 July 2021, does not pose a health hazard to humans. "The ASF pathogen cannot be transferred to humans", explains Professor Dr. Dr. Andreas Hensel, President of the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR). "No risk to health is posed by direct contact with diseased animals or from eating food made from infected domestic pigs or wild boar".
The ASF pathogen is a virus which infects domestic pigs and wild boar and which leads to a severe, often lethal, disease in these animals. It is transferred via direct contact or with excretions from infected animals, or through ticks. The ASF virus is endemic to infected wild animals ...
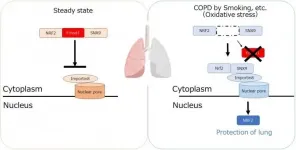
A breath of fresh air for emphysema research
2021-07-19
Tokyo, Japan - Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) causes illness and death worldwide. It is characterized by destruction of the walls of tiny air sacs in the lungs, known as emphysema, and a decline in lung function. Little has been known about the mechanisms by which it begins to develop. But now, researchers from Japan have found a protein that promotes the development of the early stages of emphysema, with the potential to be a therapeutic target.
COPD can be triggered by environmental factors such as cigarette smoking that result in lung inflammation. The development of inflammation involves the movement ...
Personalized immunotherapy response studied in body-on-a-chip cancer models
2021-07-19
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, JULY 19, 2021 -- Wake Forest researchers and clinicians are using patient-specific tumor 'organoid' models as a preclinical companion platform to better evaluate immunotherapy treatment for appendiceal cancer, one of the rarest cancers affecting only 1 in 100,000 people. Immunotherapies, also known as biologic therapies, activate the body's own immune system to control, and eliminate cancer.
Appendiceal cancer is historically resistant to systemic chemotherapy, and the effect of immunotherapy is essentially unknown because clinical trials are difficult to perform due to lack of ...
COVID-19 made unequal access to food worse, study suggests
2021-07-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - When COVID-19 hit, affluent Columbus residents responded by taking significantly fewer trips to large grocery and big-box stores, apparently ordering more online and stocking up when they did go out to shop.
With fewer options available to them, low-income people had to double down on what they had always done: regular trips to the local dollar stores and small groceries to get their family's food.
That's the conclusion of a new study that analyzed traffic to Columbus grocery sellers before, during and after the COVID-19 lockdown.
Dollar stores and small local grocers in neighborhoods housing mostly low-income people of color didn't see as much of a decline in customers during the lockdown as did large grocery and big-box stores, ...
Bonding's next top model -- Projecting bond properties with machine learning
2021-07-19
Tokyo, Japan - Designing materials that have the necessary properties to fulfill specific functions is a challenge faced by researchers working in areas from catalysis to solar cells. To speed up development processes, modeling approaches can be used to predict information to guide refinements. Researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science have developed a machine learning model to determine characteristics of bonded and adsorbed materials based on parameters of the individual components. Their findings are published in Applied Physics Express.
Factors such as the length and strength of bonds in materials play ...
COVID-19 antibodies persist at least nine months after infection
2021-07-19
Testing of an entire Italian town shows antibody levels remain high nine months after SARS-CoV-2 infection, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic.
Researchers from the University of Padua and Imperial College London tested more than 85 percent of the 3,000 residents of Vo', Italy, in February/March 2020 for infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and tested them again in May and November 2020 for antibodies against the virus.
The team found that 98.8 percent of people infected in February/March showed detectable levels of antibodies in November, and there was no difference between people who had suffered symptoms of COVID-19 and those that had been symptom-free. The results are ...
Why identical mutations cause different types of cancer
2021-07-19
Why do alterations of certain genes cause cancer only in specific organs of the human body? Scientists at the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), the Technical University of Munich (TUM), and the University Medical Center Göttingen have now demonstrated that cells originating from different organs are differentially susceptible to activating mutations in cancer drivers: The same mutation in precursor cells of the pancreas or the bile duct leads to fundamental different outcomes. The team discovered for the first time that tissue specific genetic interactions are responsible for the differential susceptibility of the biliary and the pancreatic epithelium towards ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Chemists found an effective remedy for "aged" brain diseasesScientists obtained substances that provide a breakthrough in the treatment of neurodegenerative pathologies