African swine fever: No risk to consumers
Pathogen cannot be transferred to humans
2021-07-19
(Press-News.org) African swine fever (ASF), first detected in Germany in domestic pigs on 15 July 2021, does not pose a health hazard to humans. "The ASF pathogen cannot be transferred to humans", explains Professor Dr. Dr. Andreas Hensel, President of the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR). "No risk to health is posed by direct contact with diseased animals or from eating food made from infected domestic pigs or wild boar".
The ASF pathogen is a virus which infects domestic pigs and wild boar and which leads to a severe, often lethal, disease in these animals. It is transferred via direct contact or with excretions from infected animals, or through ticks. The ASF virus is endemic to infected wild animals in Africa, but there have also repeatedly been outbreaks in southern Europe. The pathogen has been spreading north-westwards since 2007 from Georgia through Armenia, Azerbaijan and Russia. Cases of ASF have been registered in wild boar along with outbreaks in domestic pigs in the Baltic states since 2014. The virus has also been detected in Romania, Hungary, Poland and the Czech Republic. In September 2018, the pathogen was also found in wild boars in Belgium and thus for the first time in Western Europe. On 10 September 2020, the ASF virus has been detected for the first time in Germany in a wild boar in Brandenburg. The first cases of ASF in domestic pigs in Germany were detected in two pig farms in Brandenburg on 15 July 2021.
The pathogen is very stable and can remain infectious in food over several months. If unheated food or food scraps from infected animals are fed to non-infected animals, the virus can therefore spread to previously ASF-free regions, thus infecting domestic pig herds too.
Although the ASF virus does not pose a hazard or a risk to humans, the meat of domestic pigs and wild boar should always be prepared under hygienic conditions, just like all other raw meats, as it can also contain other pathogens, advises the BfR. It should be kept refrigerated and prepared separately from other foods before cooking. When heating, a temperature of 70 degrees Celsius or higher should be reached at all parts of the food for at least two minutes, the BfR recommends.
The BfR has compiled some frequently asked questions about ASF for further information. They can be downloaded on the BfR website.
https://www.bfr.bund.de/en/frequently_asked_questions_about_african_swine_fever__asf_-205379.html
INFORMATION:
About the BfR
The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) is a scientifically independent institution within the portfolio of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) in Germany. It advises the Federal Government and Federal Laender on questions of food, chemical and product safety. The BfR conducts its own research on topics that are closely linked to its assessment tasks.
This text version is a translation of the original German text which is the only legally binding version.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-19
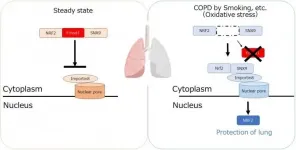
Tokyo, Japan - Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) causes illness and death worldwide. It is characterized by destruction of the walls of tiny air sacs in the lungs, known as emphysema, and a decline in lung function. Little has been known about the mechanisms by which it begins to develop. But now, researchers from Japan have found a protein that promotes the development of the early stages of emphysema, with the potential to be a therapeutic target.
COPD can be triggered by environmental factors such as cigarette smoking that result in lung inflammation. The development of inflammation involves the movement ...
2021-07-19
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, JULY 19, 2021 -- Wake Forest researchers and clinicians are using patient-specific tumor 'organoid' models as a preclinical companion platform to better evaluate immunotherapy treatment for appendiceal cancer, one of the rarest cancers affecting only 1 in 100,000 people. Immunotherapies, also known as biologic therapies, activate the body's own immune system to control, and eliminate cancer.
Appendiceal cancer is historically resistant to systemic chemotherapy, and the effect of immunotherapy is essentially unknown because clinical trials are difficult to perform due to lack of ...
2021-07-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - When COVID-19 hit, affluent Columbus residents responded by taking significantly fewer trips to large grocery and big-box stores, apparently ordering more online and stocking up when they did go out to shop.
With fewer options available to them, low-income people had to double down on what they had always done: regular trips to the local dollar stores and small groceries to get their family's food.
That's the conclusion of a new study that analyzed traffic to Columbus grocery sellers before, during and after the COVID-19 lockdown.
Dollar stores and small local grocers in neighborhoods housing mostly low-income people of color didn't see as much of a decline in customers during the lockdown as did large grocery and big-box stores, ...
2021-07-19
Tokyo, Japan - Designing materials that have the necessary properties to fulfill specific functions is a challenge faced by researchers working in areas from catalysis to solar cells. To speed up development processes, modeling approaches can be used to predict information to guide refinements. Researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science have developed a machine learning model to determine characteristics of bonded and adsorbed materials based on parameters of the individual components. Their findings are published in Applied Physics Express.
Factors such as the length and strength of bonds in materials play ...
2021-07-19
Testing of an entire Italian town shows antibody levels remain high nine months after SARS-CoV-2 infection, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic.
Researchers from the University of Padua and Imperial College London tested more than 85 percent of the 3,000 residents of Vo', Italy, in February/March 2020 for infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and tested them again in May and November 2020 for antibodies against the virus.
The team found that 98.8 percent of people infected in February/March showed detectable levels of antibodies in November, and there was no difference between people who had suffered symptoms of COVID-19 and those that had been symptom-free. The results are ...
2021-07-19
Why do alterations of certain genes cause cancer only in specific organs of the human body? Scientists at the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), the Technical University of Munich (TUM), and the University Medical Center Göttingen have now demonstrated that cells originating from different organs are differentially susceptible to activating mutations in cancer drivers: The same mutation in precursor cells of the pancreas or the bile duct leads to fundamental different outcomes. The team discovered for the first time that tissue specific genetic interactions are responsible for the differential susceptibility of the biliary and the pancreatic epithelium towards ...
2021-07-19
The climate crisis will lead to changes in distribution and habitat loss of stony corals in the tropical Atlantic, shows a new study published by the open access publisher Frontiers. The loss of such coral species could have devastating consequences for the marine ecosystems they inhabit. The results of the study highlight an urgent need for coral reef management in the Atlantic.
Researchers at the University of São Paulo projected current and future distributions of three key reef building corals of the tropical Atlantic (Mussismilia hispida, Montastraea cavernosa and the Siderastrea complex). They ...
2021-07-19
To prepare for the next pandemic and provide a coordinated approach to vaccination across the country, Canada should create Canadian Immunization Services based on the Canadian Blood Services model, authors propose in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
The authors, including a leading health policy and immunization expert, a blood system expert and a former federal minister of health, are Dr. Kumanan Wilson, professor, Department of Medicine and member of the Centre for Health Law, Policy and Ethics, University of Ottawa; Dr. Graham Sher, CEO, Canadian Blood Services; and Dr. Jane Philpott, Dean, Faculty of Health Sciences, Queen's University.
"If we want to be better prepared for the ...
2021-07-19
Philadelphia, July 19, 2021 - University of Minnesota School of Public Health researchers recently completed a study to determine how food-insecure young (emerging) adults (18-29 years of age) adapted their eating and child feeding behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. The researchers also sought to identify barriers to food access and opportunities to improve local access to resources for emerging adults. Their END ...
2021-07-19
Oncotarget published "Ex vivo analysis of DNA repair targeting in extreme rare cutaneous apocrine sweat gland carcinoma" which reported a rare metastatic case with a PALB2 aberration identified previously as a familial susceptibility gene for breast cancer in the Finnish population.
As PALB2 exhibits functions in the BRCA1/2-RAD51-dependent homologous DNA recombination repair pathway, we sought to use ex vivo functional screening to explore sensitivity of the tumor cells to therapeutic targeting of DNA repair.
Drug screening suggested sensitivity of the PALB2 deficient cells to BET-bromodomain inhibition, and modest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] African swine fever: No risk to consumers
Pathogen cannot be transferred to humans