Unsustainable Arctic shipping risks accelerating damage to the Arctic environment
The economic and environmental pros and cons of melting Arctic ice creating shorter shipping routes through the polar region are weighed up in ground-breaking research from UCL experts in energy and transport.
2021-07-19
(Press-News.org) The economic and environmental pros and cons of melting Arctic ice creating shorter shipping routes through the polar region are weighed up in ground-breaking research from UCL experts in energy and transport.
They conclude that policy makers must properly assess the environmental trade-offs and costs in addition to the commercial benefits and opportunities in Arctic shipping. The authors also want to see more incentives to drive technological developments that will accelerate the uptake of green fuels and technologies.
The Arctic is the fastest-warming region on the planet.
Shorter Arctic shipping routes, which mean less fuel used are already used by a handful of ships, when areas of the Arctic ice melt during the summer. But the period when these routes are navigable is predicted to extend with increases in global warming and, if warming fails to remain within the 1.5?C/2?C limit set out in the Paris agreement, permanent Arctic ice may be a thing of the past.
The research, published in Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, looked at the financial competitiveness of Arctic shipping, considering the impact of emissions from these vessels on the environment.
They looked at two policy scenarios, one being business-as-usual, where there is no policy on emissions, and the other operating under an Arctic specific zero-emissions policy, where ships which could run using energy from renewable sources were considered.
When environmental costs are ignored, fossil fuel based residual fuel oil is cheaper than alternative fuels. However, when the environmental impacts of accelerating climate change and the adverse effects of ship emissions on human health are considered, residual fuel ships are no longer feasible because of their contribution to greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions.
The experts conclude that, in the second scenario, green ammonia fuel cell ships are the most commercially viable and that policies which facilitate the introduction of such zero carbon fuels and zero emission technologies should be encouraged. Green ammonia is an example of a fuel that can be emissions free in both its production and use, given a green electric infrastructure.
Lead author Joseph Lambert (UCL Energy Institute) said: "Significant change is under way in the Arctic region due to global warming and from a shipping perspective we should prepare for what this means through assessing all the opportunities, risks and trade-offs that aren't exclusively financial. These routes may become more financially competitive as global warming increases and Arctic ice retreats, but more factors must be considered. It is critical that the Arctic ice maintains its permanency - in order to stay within global warming targets and to protect the region's ecology."
Co-author Dr Tristan Smith (UCL Energy Institute), who supervised the research, said: "This is a novel work that shows the economic costs alongside the environmental costs for the Arctic route, as well as showing how certain technology choices, that could be incentivised through policy, could significantly reduce the environmental costs that would otherwise arise from Arctic shipping. The paper shows a clear justification for governments to intervene now to prevent a melting Arctic's enabling of a reduction in shipping costs because of further acceleration of the degradation of this crucial ecosystem."
The researchers say impacts that need to be explored include the effects of ecological damage, and how policy can be structured to address the environmental concerns.
INFORMATION:
Notes to Editors
For more information, embargoed copies of the paper, or to speak to the researchers involved, please contact:
Jane Bolger, UCL Media Relations. T: +44 (0)20 3108 9040, E: j.bolger@ucl.ac.uk
A techno-economic environmental cost model for Arctic shipping is published in Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice
The DOI for this paper is: 10.1016/j.tra.2021.06.022
About UCL - London's Global University
UCL is a diverse community with the freedom to challenge and think differently.
Our community of more than 41,500 students from 150 countries and over 12,500 staff pursues academic excellence, breaks boundaries and makes a positive impact on real world problems.
We are consistently ranked among the top 10 universities in the world and are one of only a handful of institutions rated as having the strongest academic reputation and the broadest research impact.
We have a progressive and integrated approach to our teaching and research - championing innovation, creativity and cross-disciplinary working. We teach our students how to think, not what to think, and see them as partners, collaborators and contributors.
For almost 200 years, we are proud to have opened higher education to students from a wide range of backgrounds and to change the way we create and share knowledge.
We were the first in England to welcome women to university education and that courageous attitude and disruptive spirit is still alive today. We are UCL.
http://www.ucl.ac.uk| Follow @uclnews on Twitter | Watch our YouTube channel | Listen to UCL podcasts on SoundCloud | Find out what's on at UCL Minds | #MadeAtUCL
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-19
Ishikawa, Japan - Powering everything from smartphones to electric cars, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have evolved markedly with advances in technology and revolutionized our world. The next step in the progress of technology is developing even better batteries to power electronic devices for longer durations. One promising technique for increasing battery performance involves the atomic substitution of positively charged ions or "cations" in the cathode material. However, doing so systematically for different substituent cations to determine the ideal ones experimentally is complex and expensive, leaving us with simulations as the only viable option for narrowing down the choices.
Several studies have reported an improved battery life and ...
2021-07-19
This summer, if you see a butterfly with wings that are blue on top with orange spots underneath, you may have crossed paths with a male European Common Blue (or Polyommatus icarus), a newly introduced species in Canada.
Could it be a fluke? Probably not, according to a group of researchers from the University of Ottawa who have taken a close look at this captivating blue creature. They are in fact the first to study its ecology.
"The results of our study suggest that the Polyommatus icarus (P. icarus) could become widespread in the future since it prefers urban areas," said uOttawa PhD student Stephanie Rivest, who is the first ...
2021-07-19
The final stage of cataclysmic explosions of dying massive stars, called supernovae, could pack an up to six times bigger punch on the surrounding interstellar gas with the help of cosmic rays, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Oxford. The work will be presented by PhD student Francisco Rodríguez Montero today (19 July) at the virtual National Astronomy Meeting (NAM 2021).
When supernovae explode, they emit light and billions of particles into space. While the light can freely reach us, particles become trapped in spiral loops by magnetic shockwaves generated during the explosions. Crossing back and forth through shock fronts, these particles are accelerated almost to the speed of light and, on escaping the supernovae, are thought ...
2021-07-19
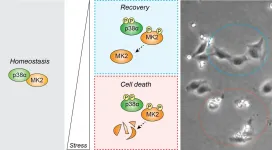
Living organisms are often exposed to stress stimuli generated either by external or internal factors, and they need to respond accordingly. At a cellular level, stress usually triggers the activation of survival pathways that contribute to the recovery of cell homeostasis. However, when stress is too high, a process of cell death is initiated that eliminates the damaged cell.
Scientists led by ICREA researcher Dr. Angel Nebreda, head of the Signalling and Cell Cycle laboratory at IRB Barcelona, have identified an important role of the p38-MK2 pathway in determining cell fate in response to stress.
"Our ...
2021-07-19
Computer vision technology is increasingly used in areas such as automatic surveillance systems, self-driving cars, facial recognition, healthcare and social distancing tools. Users require accurate and reliable visual information to fully harness the benefits of video analytics applications but the quality of the video data is often affected by environmental factors such as rain, night-time conditions or crowds (where there are multiple images of people overlapping with each other in a scene). Using computer vision and deep learning, a team of researchers led by Yale-NUS College Associate Professor of Science (Computer Science) Robby Tan, who is also from the National University of Singapore's (NUS) Faculty of Engineering, ...
2021-07-19
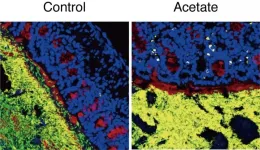
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS) have discovered that acetate, a major metabolite produced by some intestinal bacteria, is involved in regulating other intestinal bacteria. Specifically, experiments showed that acetate could trigger an immune response against potentially harmful bacteria. The findings, published in the scientific journal Nature, will lead to the development of new ways to regulate the balance of intestinal bacteria.
You may be surprised to know that 40 trillion important bacteria live in our intestines. They help keep us healthy by producing essential nutrients and eliminating foreign pathogens. On the other ...
2021-07-19
Some COVID-19 patients who experience acute respiratory failure respond by significantly increasing their respiratory effort - breathing faster and more deeply
There is concern among some doctors that this level of respiratory effort can lead to further damage to these patients' lungs.
Working with an international team of leading intensive care clinicians, engineering researchers at the University of Warwick have used computational modelling to provide new evidence that high respiratory efforts in COVID-19 patients can produce pressures and strains inside the lung that can result in injury.
The impact of high breathing efforts on the lungs of patients suffering with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 ...
2021-07-19
The carbon-hydrogen bonds in alkanes--particularly those at the ends of the molecules, where each carbon has three hydrogen atoms bound to it--are very hard to "crack" if you want to replace the hydrogen atoms with other atoms. Methane (CH(4)) and ethane (CH(3)CH(3)) are made up, exclusively, of such tightly bound hydrogen atoms. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team of researchers has now described how they break these bonds while forming new carbon-nitrogen bonds (amidation).
If it were possible to easily break the C-H bonds in hydrocarbons, it would be possible to synthesize complex organic ...
2021-07-19
The struggle to get your child to go to sleep and stay asleep is something most parents can relate to. Once the bedtime battle is over and the kids have finally nodded off, many parents tune out as well.
But University of South Australia researcher Professor Kurt Lushington is calling for parents to check on their small snoozers before switching off.
He says knowing the quality of a child's sleep is important, as it could be an indicator of sleep-disordered breathing - an under-reported medical condition that can affect a child's health and wellbeing.
"During sleep, the muscles keeping the upper airway stiff relax, and as a consequence, the airway narrows, which ...
2021-07-19
Computer vision has progressed much over the past decade and made its way into all sorts of relevant applications, both in academia and in our daily lives. There are, however, some tasks in this field that are still extremely difficult for computers to perform with acceptable accuracy and speed. One example is object tracking, which involves recognizing persistent objects in video footage and tracking their movements. While computers can simultaneously track more objects than humans, they usually fail to discriminate the appearance of different objects. This, in turn, can lead to the algorithm to mix up objects in a scene and ultimately produce incorrect tracking results.
At the Gwangju Institute of Science ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Unsustainable Arctic shipping risks accelerating damage to the Arctic environment
The economic and environmental pros and cons of melting Arctic ice creating shorter shipping routes through the polar region are weighed up in ground-breaking research from UCL experts in energy and transport.