DNA assay aids in identifying and protecting North American wolves, coyotes
2021-07-20
(Press-News.org) Forensics specialists can use a commercial assay targeting mitochondrial DNA to accurately discriminate between wolf, coyote and dog species, according to a new study from North Carolina State University. The genetic information can be obtained from smaller or more degraded samples, and could aid authorities in prosecuting hunting jurisdiction violations and preserving protected species.
In the U.S., certain wolf subspecies or species are endangered and restricted in terms of hunting status. It is also illegal to deliberately breed wolves or coyotes with domesticated dogs.
"If it's a case where you have a whole specimen, authorities can typically identify it based on physical characteristics, though similarity between some species makes that method less than ideal," says Kelly Meiklejohn, assistant professor of forensic science at NC State and corresponding author of the research. "If you're working with cross-bred animals, or incomplete specimens, you need DNA-based methods to accurately determine what species you have."
Although some U.S. federal laboratories perform DNA-based identification of wolves and coyotes, their methods and genetic reference databases aren't publicly available. Meiklejohn partnered with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to see if it was possible to use a commercially available assay designed for dogs as a way to recover the mitochondrial genome from diverse North American canid species.
The mitochondrial genome is one of two genomes inherited from an animal's parents. Specifically, the mitochondrial genome is inherited from the mother. It is useful for species identification both because its circular shape makes it less prone to degradation, and because there are more copies of this genome per cell, increasing the chance of retrieving useful material from small or damaged samples.
The team used a method, called a 'hybridization capture,' in which about 80 base-pair long RNA fragments are used to isolate DNA for sequencing. Samples are incubated with the RNA fragments, and if there's a match, the fragment will bind with the sample's DNA. The bound DNA can be isolated and sequenced. In this case, the team used a hybridization capture panel designed for the dog mitochondrial genome.
"The fragments will bind if there is about 80% similarity, which is why we felt the dog kit would be useful for sequencing wolves and coyotes," Meiklejohn says. "Dogs only diverged from wolves around 20,000 years ago, so the mitochondrial genomes aren't that different."
They sequenced 51 samples, and were able to recover full mitochondrial genomes and successfully differentiate between four species of interest: dog, wolf, Mexican wolf, and coyote.
"Essentially, this finding means we can do more with less," Meiklejohn says. "In forensics we rarely have high quality DNA samples; they've usually been exposed to the environment and are degraded. The flexibility of this kit allows us to determine the species we're looking at, which in turn may aid in prosecuting hunting or breeding violations and protecting endangered canid species."
INFORMATION:
The research appears in Forensic Science International: Animals and Environments, and is supported by seed funding from NC State. Dyan Straughan and Mary Burnham-Curtis, from the U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, are coauthors.
Note to editors: An abstract follows.
"Using hybridization capture to obtain mitochondrial genomes from forensically relevant North American canids: assessing sequence variation for species identification"
DOI: 10.1016/j.fsiae.2021.100018
Authors: Melissa Scheible, Kelly Meiklejohn, North Carolina State University; Dyan Straughan, Mary Burnham-Curtis, U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service
Published: June 25, 2021 in Forensic Science International: Animals and Environments
Abstract:
The majority of DNA casework processed by forensic laboratories focuses on human samples, but material from canids (dogs, wolves, coyotes) can also be encountered. Undomesticated canids can be the center of forensic investigations in the U.S. since some species are endangered. As many wolf species are similar morphologically, identification in the field by wildlife officers is not always straight-forward, making molecular based-approaches ideal. While some published methods using mitochondrial DNA targets can discriminate among Canis species, they are either not compatible with highly degraded samples or cannot differentiate closely related sub-species. Although some U.S. laboratories regularly perform veterinary/wildlife casework including canid identifications, their validated methods and reference genetic databases are not publicly available. We aimed to assess the utility of alternative regions in the mitochondrial genome for discriminating among canid species, including the complete genome. To achieve this, we utilized a commercial hybridization capture panel composed of biotinylated RNA "baits" designed for the domestic dog to enrich canid mitochondrial genomes for next-generation sequencing. We used this panel to successfully sequence complete mitochondrial genomes for 51 samples, representing four U.S. forensically relevant canids (coyote, wolf, Mexican wolf, dog). While the complete mitochondrial genome permitted discrimination, we also assessed previously published mitochondrial DNA targets (n, 5) for resolution and identified four alternate ~200 bp fragments from ND1, ND5, COI and CYTB genes that could help resolve canids. The utility of these alternate regions should be assessed in future studies using forensic-type samples representing canids from diverse geographic areas, prior to casework implementation.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-20
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Diagnosing a rare medical condition is difficult. Identifying a treatment for it can take years of trial and error. In a serendipitous intersection of research expertise, an ill patient in this case a child and innovative technology, Bachmann-Bupp Syndrome has gone from a list of symptoms to a successful treatment in just 16 months.
The paper chronicling this lightning-fast scientific response to the Bachmann-Bupp Syndrome was published in the open-access journal, eLife.
For more than 25 years, André Bachmann, professor of pediatrics in Michigan State University College ...
2021-07-20
New research adds to a body of evidence indicating decisions about withdrawing life-sustaining treatment for patients with moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) should not be made in the early days following injury.
In a July 6, 2021, study published in JAMA Neurology, researchers led by UC San Francisco, Medical College of Wisconsin and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital followed 484 patients with moderate-to-severe TBI. They found that among the patients in a vegetative state, 1 in 4 "regained orientation" - meaning they knew who they were, their ...
2021-07-20
By Luciana Constantino | Agência FAPESP – A pregnant woman infected by zika virus does not face a greater risk of giving birth to a baby with microcephaly if she has previously been exposed to dengue virus, according to a Brazilian study that compared data for pregnant women in Rio de Janeiro and Manaus.
A zika epidemic broke out in Brazil in 2015-16 in areas where dengue is endemic. Both viruses are transmitted by the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Some of the states affected by the zika epidemic reported a rise in cases of microcephaly, a rare neurological disorder in which the baby’s brain fails to develop completely. Others saw no such rise.
According to this new study by Brazilian researchers, two factors explain the rise in microcephaly in only some areas: the ...
2021-07-20
When it comes to improving access to mental health services for children and families in low-income communities, a University of Houston researcher found having a warm handoff, which is a transfer of care between a primary care physician and mental health provider, will help build trust with the patient and lead to successful outcomes.
"Underserved populations face certain obstacles such as shortage of providers, family beliefs that cause stigma around mental health care, language barriers, lack of transportation and lack of insurance. A warm handoff, someone who serves as a go-between for experts and patients, can ensure connections are made," said Quenette L. Walton, assistant professor at the ...
2021-07-20
Irvine, CA - July 20, 2021 - In a new University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers found that a certain protein prevented regulatory T cells (Tregs) from effectively doing their job in controlling the damaging effects of inflammation in a model of multiple sclerosis (MS), a devastating autoimmune disease of the nervous system.
Published this month in Science Advances, the new study illuminates the important role of Piezo1, a specialized protein called an ion channel, in immunity and T cell function related to autoimmune neuroinflammatory disorders.
"We found that Piezo1 selectively restrains Treg cells, limiting their potential to mitigate ...
2021-07-20
Newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because they were given antibiotics may have their gut microorganisms restored with a maternal fecal transplant, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, which involved genetic analysis of mice, appears in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
The findings suggest that newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because their microbiome - the trillions of beneficial microorganisms in and on our bodies - were disturbed can have the condition reversed by transplanting fecal microbiota from their mother into their gastrointestinal tract after the antibiotic course has been completed.
Type 1 diabetes is the most ...
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON, July 20, 2021 -- In the wind power industry, optimization of yaw, the alignment of a wind turbine's angle relative to the horizonal plane, has long shown promise for mitigating wake effects that cause a downstream turbine to produce less power than its upstream partner. However, a critical missing puzzle piece in the application of this knowledge has recently been added -- how to automate the identification of which turbines are experiencing wake effects amid changing wind conditions.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, ...
2021-07-20
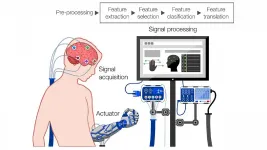
WASHINGTON, July 20, 2021 -- Surpassing the biological limitations of the brain and using one's mind to interact with and control external electronic devices may sound like the distant cyborg future, but it could come sooner than we think.
Researchers from Imperial College London conducted a review of modern commercial brain-computer interface (BCI) devices, and they discuss the primary technological limitations and humanitarian concerns of these devices in APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
The most promising method to achieve real-world BCI applications is through electroencephalography (EEG), a method ...
2021-07-20
Millions of people in countries around the world could face an increased risk of malnutrition as climate change threatens their local fisheries.
New projections examining more than 800 fish species in more than 157 countries have revealed how two major, and growing, pressures - climate change and over-fishing - could impact the availability of vital micronutrients from our oceans.
As well as omega-3 fatty acids, fish are an important source of iron, zinc, calcium, and vitamin A. A lack of these vital micronutrients is linked to conditions such as maternal mortality, stunted growth, and pre-eclampsia.
Analyses by an international team from the UK and Canada and led by scientists from Lancaster ...
2021-07-20
PHILADELPHIA -- (July 20, 2021) -- Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is an RNA processing mechanism that regulates gene expression by generating different ends on RNA transcripts of the same gene. Though it affects more than half of human genes, the significance of APA was poorly understood. Now a new study by The Wistar Institute describes an important function of APA in allowing certain mRNAs to reach specific sites of protein synthesis and reveals that length, sequence and structural properties can determine the destination (and fate) of mRNAs within the cell. These findings, published online in the journal Cell Reports, shed light on the consequences of APA that may represent a paradigm shift in the mRNA metabolism field.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] DNA assay aids in identifying and protecting North American wolves, coyotes