Study links cognitive decline with both bone loss and fracture risk
2021-07-21
(Press-News.org) New research published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research has found that cognitive decline is linked with accelerated bone loss and an increased fracture risk in women.
In the study of 1,741 women and 620 men aged ?65 years without dementia who were followed from 1997 through 2013, both genders experienced similar declines in cognitive function and bone mass.
After adjustments, cognitive decline was associated with bone loss in women but not men. Also, significant and clinical important cognitive decline in women was associated with a 1.7-fold higher risk of bone fractures over the subsequent 10 years.
Notably, the relationship between bone loss and cognitive decline was bidirectional with no evidence of one preceding the other. The relationship between cognitive decline, bone loss, and fracture risk in women may be driven by shared risk factors.
"These findings may help refine clinical practices guidelines regarding how bone loss and cognitive decline can be monitored in older age, to ensure appropriate and effective treatment," said lead author Dana Bliuc, PhD, MD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, in Australia. "This is particularly important because both bone loss and cognitive decline are 'silent conditions' that can go undetected for long periods of time, often until the conditions have severely progressed."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-21
When researchers evaluated consumers' understanding of allergy information on food labels, less than half of individuals found the information to be clear.
The study, which is published in Clinical & Experimental Allergy, involved two separate experiments with a total of 96 consumers with food allergies and 105 without. Investigators first randomly presented 18 different food products with labels suggesting peanut was, may be, or was not an ingredient, and then they presented three different formats of information: 'Produced in a Factory' and 'May contain' or 'Traces of'. Precautionary allergen labels (PALs) were especially problematic, ...
2021-07-21
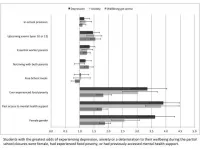
A new study published in JCPP Advances has compared the wellbeing of UK students who remained at home for schooling during the first lockdown period of the COVID-19 pandemic with those who accessed school in person.
In the study, which included 11,765 students in grades 8-13 (aged 12-21 years), females, students who had experienced food poverty, and those who had previously accessed mental health support were at greatest risk of depression, anxiety, and a deterioration in wellbeing. Students who accessed in-person schooling had poorer mental health, but this was accounted for by their different characteristics and background circumstances.
"Identifying ...
2021-07-21
Although in-school transmission of COVID-19 among K-12 students is low when safeguards are in place, the risk of acquiring COVID-19 during school bus transportation is unclear. A study published in the Journal of School Health reports on the bus transport experience of an independent school in Virginia.
For the study, the school monitored 1,154 students with asymptomatic PCR testing every 2 weeks initially and later every week from August 28, 2020-March 19, 2021, during highest community transmission. Fifteen buses served 462 students while operating at near capacity of 2 students in every seat, using a physical distancing minimum of 2.5 feet, universal masking, and simple ventilation techniques. ...
2021-07-21
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in Campbell Systematic Reviews identified and examined more than 100 risk and protective factors for radical attitudes, intentions, and behaviors (including terrorism) in democratic countries.
The factors can be grouped into five domains:
socio-demographic and background factors,
psychological and personality trait factors,
attitudinal and subjective belief related factors,
experiential factors, and
traditional criminogenic factors
While there is great variation, the most significant factors ...
2021-07-21
It's important to communicate about hard-to-see and complex environmental topics and issues with young people. In an article published in People and Nature, an international team reflects on the group's creation of the Shout Trout Workout, a lyric poem, comic, and music video for children aged 8-14 years old designed to entertain, engage, and enrich learning about migratory fishes and aquatic environments.
The authors hope that sharing their experiences and reflections will be useful and inspiring for those who aim to create learning enrichment and engagement materials about ecological ...
2021-07-21
Results from a study published in Ibis show that how close Golden Eagles will fly to wind turbines depends on habitat suitability inside and outside of a wind farm. Also, the largest impact of wind farms was a loss of Golden Eagle habitat, which could be mitigated by including the study's findings in wind farm planning.
The study included data from 59 GPS-tagged Golden Eagles before and after turbine operation at 80 wind farms across Scotland.
"Previous research on Golden Eagles, notably in the United States, has tended towards collision with turbine blades as the main consequence of their interaction with wind farms. Our study shows that across numerous wind farms in Scotland, this was not the case, but that deleterious habitat loss through avoidance of turbines was ...
2021-07-21
Researchers led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have discovered a link between cognitive decline and a faster rate of bone loss, and found that cognitive decline over five years increased future fracture risk in women. The association between cognitive decline and bone loss was weaker in men.
The study of individuals aged 65 and older was carried out over 16 years and has revealed a potential new approach to help identify older people who may be at risk of fracture.
"Bone loss and cognitive decline are major public health issues, but both are 'silent diseases' that can go undetected and untreated for long periods, often ...
2021-07-21
WASHINGTON (July 21, 2021) - Twenty-nine percent of Americans are taking more supplements today than they were before the COVID-19 pandemic, bringing the percentage of U.S. supplement-takers to 76%, according to a new survey conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of Samueli Foundation. Nearly two-thirds of those who increased supplement use (65%) cited a desire to enhance their overall immunity (57%) or protection from COVID-19 (36%) as reasons for the increase. Other common reasons for increasing supplement use were to take their health into their own hands (42%), improve their sleep (41%), and improve their mental health (34%).
"The COVID-19 pandemic is a catalyst for increased supplement use," said Wayne Jonas, MD, executive director ...
2021-07-21
Oncotarget published "Genomic clustering analysis identifies molecular subtypes of thymic epithelial tumors independent of World Health Organization histologic type" which reported that genomic information from 102 evaluable TETs from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset and from the IU-TAB-1 cell line underwent clustering analysis to identify molecular subtypes of TETs.
Six novel molecular subtypes of TETs from the TCGA were identified, and there was no association with WHO histologic subtype.
The IU-TAB-1 cell line clustered into the TH4 molecular subtype and in vitro testing of candidate therapeutics was performed.
Sensitivity to nelfinavir ...
2021-07-21
New research from Bocconi University in Milan highlights that, contrary to received wisdom, connections to organized crime harm a company's financial performance and increase by 25.5% its likelihood to go bust.
Using a novel dataset from AISI, the Italian Internal Intelligence and Security agency, Bocconi professors Antonio Marra, Donato Masciandaro, and Nicola Pecchiari in a paper co-authored with Pietro Bianchi (Florida International University) published online in The Accounting Review, identify 1,840 criminally connected firms headquartered in Italy's Lombardy region.
Lombardy, the Northern Italian region around Milan, is not ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study links cognitive decline with both bone loss and fracture risk